This page contains the AQA GCSE Biology B2 Cell Divion Kerboodle Answers for revision and understanding of AQA GCSE Biology B2. This page also contains the link to the notes and video for the revision of this topic.
B 2.1 Cell Division AQA GCSE Biology B2 Cell Division Kerboodle Answers:Page No. 27
Banner 1
- a. Chromosome: A thread like structure made of nucleic acid and proteins and found in nucleus, are known as chromosome. They contain genetic information in form of genes.
- Gene: Gene is a unit of heredity which is transferred from one generation to next generation. Genes are responsible for specific characteristics.
- DNA: DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid and it is self replicating molecule which contains encrypted genetic information. It is present in all the living organisms as a constituent of chromosomes.
- Three stages of the cell cycle life and their process is explained below. The length of these stages depends upon the organism and growth stage of the organisms. The three stages are as follows:
Stage 1: Longest stage in the cell cycle. This stage is also known as Interphase. During this stage:
: Cell increases in size, mass and number of sub-cellular structure such as mitochondria, ribosomes and chloroplasts.
: Replication of DNA takes place during this stage.
Stage 2: Mitosis: Chromosomes arranged and pulled toward at each end of the dividing cell and division of nucleus take place.
Stage 3: Division of cytoplasm and cell membrane occurs in this stage and the final result is two identical daughter cells.

- a. In organisms growth and repair of cells are required continuously during the life span. For these division of cells plays important role. Cell Division is important for growth, repair, and development of multi cellular organisms. Therefore cell division by mitosis is so importany in thr body.
- It is necessary for the number of chromosomes to stay same when the cells divide to make other normal body cells. If the number of chromosomes didn’t stay the same after cell division then it will not result in stable cells, tissues, or organs in human body. Life depends on stable cellular reproduction and metabolism over long periods of time. So to maintain stability of characteristics of cells, tissues and organs the number of chromosomes should remain same after every cell division.
B 2.2 Growth and Differentiation AQA GCSE Biology B2 Cell Division Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 29
1.a. The process by which a cell becomes specialized in order to perform a specific function. From a single embryo a whole human body forms because of the cells are getting differentiation. This process is defined as differentiation.
- Cell differentiation is when stem cells turn into specialised cells. Stem cells are cells that have not yet been assigned a role within the body, and can be found mainly in bone marrow. When they specialise, they have a certain role to fill, and will adapt to that role, such as nerve cells having long thin strands to communicate to other cells. Cell differentiation is important in living organisms because it changes stem cells into useful cells within the body.
- Differentiation in plants and animals differ as follows- In case of plants there are so many cells which have capability of differentiation but in case of animals most of the cells lose the ability to differentiate at an early stage. In case of plants cells can redifferentiate become stem cells but in case of animal fate of cells are predefined.
- Fertilised ovum is single cell where as an adult human body has 37.2 trillion cells. So order of magnitude is 13 by which the human body is bigger than the original fertilised ovum. (1*100-1013= 13)
- The difference in differentiation patterns affects our ability to clone plants and animals. It is easier to clone a plant rather an animal because in case of plants almost all have tendency to revert to stem cells. In case of animals all the cells differentiate at early stage and only few remain as stem cells. On the other hand in case of plants from a parent plant identical plant population can be cloned easily from a part of meristem tissue.
B 2.3 Steam Cells AQA GCSE Biology B2 Cell Division Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 31
1.a. The difference between a stem cell and a normal body cell can be explained as-stem cells are undifferentiated cells and they can divide further, get differentiate into different cell types. Whereas a normal body cell in differentiated cell it cannot give rise to other type of cell.
- In case of human three sources of stem cells are:
Umbilical cord blood of new born babies
Connecting tubes of liver and pancreas to small intestine
Bone marrow
In case of plants three sources of stem cells are:
- Root apical meristem
- Shoot apical meristem
- Leaf apical meristem
- In human body some parts stop working because the damaged cells cannot be replaced in them.
For example spinal injuries and type I diabetes will result in permanent damaged cells which cannot be replaced and repair. Stem cells help to solve these issues and provide the new cells that can be used to treat the disease. The damaged cells can be replaced using the stem cells. New organs can be generated from embryonic stem cells. The above explained are the advantages of using stem cell to treat diseases.
3.a. Some plants are rare and at a verge of extinction. Some plants needs to be cultivated at large scale for sale purpose. For research purpose genetically identical plants are required to study the specific trait or to study the effect of certain variable on that identical plant population. Solution of these problems can be achieved by cloning the plant and generating a large number of identical plants. Therefore the ability to clone large numbers of individual plants is such an advantage in plant research.
- Rare plants species can be saved from extinction by cloning them using some meristem tissue part of the parent plant. This way of plant cloning is safe and reliable and enables us to save rare species of plants from extinction.
B 2.4 Steam Cells AQA GCSE Biology B2 Cell Division Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 33
- Three examples where the use of stem cells could provide new treatment are
Spinal cord after injuries
Diabetes
Heart after damage in a heart attack
- Summary of main arguments for and against the use of embryonic stem cells in medical research are as follows:
Pros:
- Stem cell research can potentially help treat a range of medical problems. It could lead humanity closer to better treatment and possibly cure a number of diseases:
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Heart Diseases, Stroke and Diabetes (Type 1)
- Birth Defects
- Spinal Cord Injuries
- Replace or Repair Damaged Organs
- Reduced Risk of Transplantation (You could possibly get a copy of your own heart in a heart-transplantation in the future
- Stem cells may play a major role in cancer.
- Better treatment of these diseases could also give significant social benefits for individuals and economic gains for society.
Cons:
- “We should not mess with human life.”
- “Humans should not be trying to play God”
- Some argue that stem cell research in the far future can lead to knowledge on how to clone humans. It is hard to say whether this is true, but we have seen devastating consequences of other research-programs, even with good intentions, such as nuclear research.
- Scientists are hoping to overcome the ethical objections to using embryonic stem cells in their research. It is reported that umbilical cord blood of new born babies and amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus have stem cells. These stem cells can be used to overcome the issues and etnical concerns. Research is going on developing ways in which adult embryonic stem cells can grow.
Adult stem cells have been successfully used to treat some heart diseases and for growing new organs such as tracheas. Stem cell research area is known as therapeutic cloning. If the stem cells are generated from the same body then the chances of their rejection are become less or negative. Scientists have been reported stem cells in the connecting tubes of liver and pancreas to small intestine. They have turned these cells into special insulin producing cells in the pancreas so they play special role in controlling blood sugar level. This has been tested in mice and trial in human needs to be done for the same.
Summary questions AQA GCSE Biology B2 Cell Division Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 34
- a. Series of stages through which cell divides is known as cell cycle.
- i. In case of early embryo the cell cycle length is short as compare to a 5 year old child because at the time of embryo development into a complete human body division of cell should be fast and to achieve the speed and requirement the cell cycle should be competed in a short period of time. On the other hand in case of 5 year old child cell cycle rate is slow. This is how we expect the length of the cell cycle to vary between an early embryo in the first days after fertilisation and a 5 year old child
- In case of 13 year old student and a 70 year old adult, the length of cell cycle is shorter as compared to an adult of 70 years.
- a. Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth. Mitosis will result in the formation of two identical daughter cells. Mitosis is important for repair and replacement of damaged cells.
- In cell cycle three stages are there. The length of these stages depends upon the organism and growth stage of the organisms. The three stages of cell cycle are as follows:
Stage 1: Longest stage in the cell cycle. This stage is also known as Inter phase. During this stage:
: Cell increases in size, mass and number of sub-cellular structure such as mitochondria, ribosomes and chloroplasts.
: Replication of DNA takes place during this stage.
Stage 2: Mitosis: Chromosomes arranged and pulled toward at each end of the dividing cell and division of nucleus take place.
Stage 3: Division of cytoplasm and cell membrane occurs in this stage and the final result is two identical daughter cells.
The cell cycle and Mitosis. Three different stages are there in cell cycle. Length of these stages varies. Mitosis will result in two identical daughter cells.

c.During the whole life span several cells get injured, old and need to be replaced by new cells to maintain the integrity of the body. So to achieve the integrity cell division plays important role thus the cell cycle. Therefore the cell cycle is very important during the development of the baby from a fertilised egg and is also important all through life.
d.
- Stage 1 of cell cycle variable among all the stages.
- Cell cycle is likely to be very rapid in a human being during early stages of development and it will become relatively slow with increasing age.
- a. Stem cells are nothing but an undifferentiated cell of a multi cellular organism which is capable of giving rise to indefinitely more cells of the same type, and from which certain other kinds of cell arise by differentiation.
- In human body some parts stop working because the damaged cells cannot be replaced in them. For example spinal injuries and type I diabetes will result in permanent damaged cells which cannot be replaced and repair. Stem cells help to solve these issues and provide the new cells that can be used to treat the disease. The damaged cells can be replaced using the stem cells. New organs can be generated from embryonic stem cells. Therefore it is hoped that many different medical problems may be cured using stem cells.
- Summary of main arguments for and against the use of embryonic stem cells in medical research are as follows:
Pros:
- Stem cell research can potentially help treat a range of medical problems. It could lead humanity closer to better treatment and possibly cure a number of diseases:
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Heart Diseases, Stroke and Diabetes (Type 1)
- Birth Defects
- Spinal Cord Injuries
- Replace or Repair Damaged Organs
- Reduced Risk of Transplantation (You could possibly get a copy of your own heart in a heart-transplantation in the future
- Stem cells may play a major role in cancer.
- Better treatment of these diseases could also give significant social benefits for individuals and economic gains for society
Cons:
- “We should not mess with human life.”
- “Humans should not be trying to play God”
- Some argue that stem cell research in the far future can lead to knowledge on how to clone humans. It is hard to say whether this is true, but we have seen devastating consequences of other research-programs, even with good intentions, such as nuclear research.
- a.
In case of plants stem cells are found mostly in the apical regions. Therefore we can expect to find stem cells in plant there. These regions are regions where growth is continuous.
- The stem cells differ in animals and plants in the following ways- In case of plants stem cells are always there in the form of materialistic zones but in animals stems cells are limited. In case of plants there are so many stem cells which have capability of differentiation into different cell types but in case of animals most of the cells lose the ability to differentiate at an early stage. In case of plants cells can re differentiate become stem cells but in case of animal fate of cells are predefined
- Two examples of use of plant stem cell to produce the plant clones are-
In horticulture of plant stem cells are used to create new identical plants, eg. orchids. In case of banana which we eat in our daily life plants are produce from cloning of plants.
In case of normal reproduction the same genetic background is not guaranteed but in case of cloning from stem cells plants with identical genetic information can be generated.
- Stem cells might also be involved in this type of therapy in the future because stem cells have the tendency to differentiate into different type of cells according to the provided conditions. If stem cells can be differentiated in nerve cells, skin cells, blood cells etc.
- a.
Stem cells are capable in division and repair the injuries by converting themselves into the surrounding cells type. Thus stem cells might help in overcoming such injuries.
- Human system is more complex and less understood than any other organism. Thus human treatments are so far behind those used by vets.
Practice questions AQA GCSE Biology B2 Cell Division Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 35.
Banner 2
01.1Gene is the smallest structure out of the following structures.
01.2 DNA is the molecule that makes up the chromosome.
02.1. Two daughter will form as a result of mitosis division.
02.2.18 pair plus one pair of sex chromosomes will be present in each new cat cell will contajn after mitosis.
02.3. Two reasons why cell division is important are as follows:
In organisms growth and repair of cells are required continuously during the life span. For these division of cells plays important role.
Cell Division is important for growth, repair, and development of multi cellular organisms.
3.1 In case of an embryonic cell the cell cycle will be shortest.
03.2. It is shortest in embryonic cell because at this stage the rate of growth and division is faster than rest of the stages of life.
03.3.The answer is 18. Because 17% of 18 is 3.06 or 3. The total number of cells the student can see is 18 and among 18, 17% cells or only 3 cells are in stage 3.
03.4. During the different stages of cell cycle changes occurs. These changes are as follows:
Stage 1: In this stage cell size and mass increases. DNA replication will take palce.
Stage 2: this is mitosis stage. During this stage chromosome arranged themselves at the end of each side of dividing cells.
Stage 3: in this stage cytoplasm of cells divide. And two identical cells will form.
04.1. A new leaf can grow even though when there is no trace left of original leaf because leaves are attached to stem at the nodes. Every node has meristem which will result in the growth of new leaf.
04.2. Unlike the plant, most animals cannot grow back parts of their body after they have been cut off because in case of animals stem cells are not present in every part of the body and also every cell has not the tendency to become a stem cell as plants do posses this property.
04.3. Scientist can obtain more specimens by making clones of the parent plants.
05.1. Bone marrow is an example where stem cells are relatively common.
05.2. The benefits and issue of using therapeutic cloning in medicine are-
Pros:
- Stem cell research can potentially help treat a range of medical problems. It could lead humanity closer to better treatment and possibly cure a number of diseases:
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Heart Diseases, Stroke and Diabetes (Type 1)
- Birth Defects
- Spinal Cord Injuries
- Replace or Repair Damaged Organs
- Reduced Risk of Transplantation (You could possibly get a copy of your own heart in a heart-transplantation in the future
- Stem cells may play a major role in cancer.
- Better treatment of these diseases could also give significant social benefits for individuals and economic gains for society
Cons:
- There are some cons which are related to religious belief and technical issues regarding stem cell usage.
- “We should not mess with human life.”
- “Humans should not be trying to play God”
- Some argue that stem cell research in the far future can lead to knowledge on how to clone humans. It is hard to say whether this is true, but we have seen devastating consequences of other research-programs, even with good intentions, such as nuclear research.
Banner 3
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: I have tried by level best to provide the answers and video explanations to the best of my knowledge. All the answers and notes are written by me and if there is any similarity in the content then it is purely coincidental. But this is not an alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it. References: BBC Bitesize AQA GCSE Science Kerboodle textbook Wikipedia Wikimedia Commons Join Our Free Facebook Group : Get A* in GCSE and A LEVEL Science and Maths by Mahima Laroyia: https://www.facebook.com/groups/expertguidance.co.uk/ For Free Tips, advice and Maths and Science Help
This page contains the detailed and easy notes for AQA GCSE Biology Cell Biology for revision and understanding Cell Biology.
Banner 1
AQA GCSE Paper 1: Complete Revision Summary
Cell Biology
4.1 Cell Biology
- Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cell
- Animal Cell and Plant Cell
- Specialized Plant Cells
- Specialized Animal Cells
- Microscopy
- Culturing Microorganisms
- Cell Division: Mitosis
- Stem Cells
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Active Transport
Eukaryotic Cells – Plants and Animals
Prokaryotic Cells – Bacteria
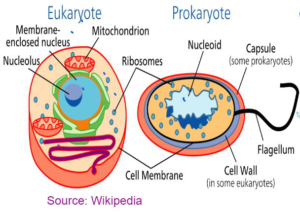
| EUKARYOTIC | PROKARYOTIC |
| Nucleus is present. | Nucleus is absent. |
| All membrane bound organelles are present | Membrane bound organelles are absent. |
| DNA is enclosed in the nucleus | DNA lies naked in the cytoplasm. |
| They are multicellular | They are mostly unicellular |
| DNA is linear | DNA Is circular |
| Ribosomes are big | Ribosomes are small |
| They are big cells | They are small cells. |
| Example: Plants and Animals | Example: Bacterial Cell |
Banner 2
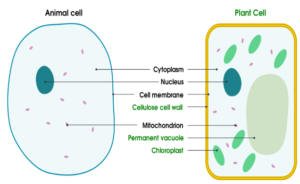
Animal Cells
NUCLEUS
- It is the brain of the cell
- It controls the activities of the cells
- It contains DNA which holds our genetic information.
RIBOSOMES
- It is the site for protein synthesis.
- They are involved in making of proteins and enzymes required by the cell
CYTOPLASM
- Jelly like fluid which fills the cell.
- It is the site where all the chemical reactions of the cells take place as it contains all the major enzymes
CELL MEMBRANE
- It the membrane that surrounds the cells
- It controls what goes in and out of the cell.
MITOCHONDRIA
- It is the powerhouse of the cell
- It produced energy for the cell as it is the site for aerobic respiration
Banner 3
Plant Cell
PERMANENT VACUOLE
- It is filled with cell sap.
- It gives rigidity to the cells and makes the cell turgid
CELL WALL
- Made up of cellulose.
- It is the layer outside of the cell membrane
- It supports the plant and maintain its shape.
CHLOROPLAST
- It is the site for photosynthesis
- It contains a green pigment, chlorophyll which absorbs light and prepared food.
Plant versus Animal Cell
| ORGANELLE | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Nucleus | Present | Present |
| Cell Membrane | Present | Present |
| Mitochondria | Present | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present | Present |
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Permanent Vacuole | Present | Absent |
| Chloroplast | Present | Absent |
Banner 4
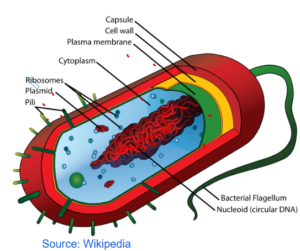
Bacterial Cell
Cell Wall
- No cellulosic
- made up of peptidoglycan
Circular DNA
- No nucleus
- Single DNA loop found naked in the cytoplasm
Plasmid
- Extra chromosomal materials
- They are in the form of small rings
- They give special properties to bacteria like antibiotic resistance
Pilli
- Hair like structures
- Found on the surface
- That helps bacteria to reproduce
Capsule
- Slime layer
- that protects the bacteria
Flagellum
- Tail like structure
- Helps the bacteria to move.
Banner 5
BACTERIAL VERSUS PLANT VERSUS ANIMAL CELLS
SPECIALISED ANIMAL CELLS
Special cells which have some extra features that allows them to perform specific functions
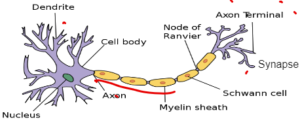
NERVE CELL
Function is to send electrical impusles round the body
- Dendrites – They are hair like structures that receives the impulses
- Axon – Long stalk the transmits the nerve impulses
- Synapse – They transmit impulses from one neurone to another
MUSCLE CELL
- Functions is to contract to bring about the movement of different parts of the body
- They are made up of special fibres which helps them to contract and relax
- Contain special proteins that allows them to contract and relax
- They have loads of mitochondria which provides them energy to contract
- They can store special storage carbohydrate called glycogen which acts as fuel for the muscles

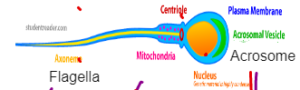
SPERM CELL
Functions is to swim to the egg and fertilize it
- Flagella – Helps it to swim to large distances
- Mitochondria – Provides Energy to swim
- Nucleus – Contains genetic information
- Acrosome – Contains Hydrolytic enzyme to break the egg wall and penetrate inside the egg to fuse with the egg nucleus
Specialized Plant Cells
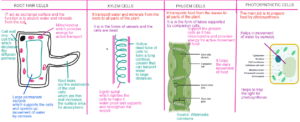
MICROSCOPES
Are the devices that use to see the cells which we cannot see by our naked eye.
MAGNIFICATION
The property of the microscope to enlarge the object.
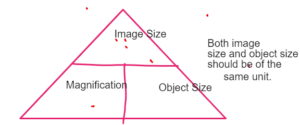
RESOLUTION
The property of the microscope to distinguish between two closed placed objects.

Baneer 6
Light and Electron Microscopes
| LI&HT MICROSCOPES | ELECTRON MICROSCOPES |
| Uses beam of light to focus on the object. | Use beam of electron.to focus on the object. |
| It is easy to handle | It is not easy to handle |
| It is small and compact | It is big and non portable |
| It does not require much expertise to handle | It requires proper training to handle |
| It can view the live samples | Samples have to be dead |
| No special sample preparations are required | Special sample preparations ace required |
| Lower resolving power – 0.2μm | Greater resolving power 0.5nm |
| Small magnifying power – x1000 -1500 | Greater magnifying power – x100000 |
| Can form colour images | Form 2D or 3D black and white images |
Banner 7
MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCE IN AND OUT OF THE CELLS
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of particles from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration.
- Particles move against the concentration gradient.
- It requires energy.
- Cells involved in active transport should have lots of mitochondria
PASSIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of particles from the region of high concentration to a low concentration.
- Particles move along the concentration gradient.
- It does not require energy
- Having numerous mitochondria is not a requirement
DIFFUSTON
OSMOSIS
Banner 8
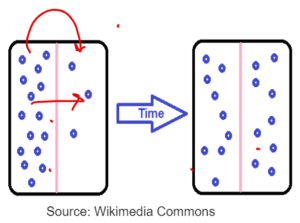
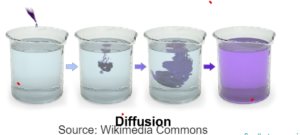
DIFFUSION
- It the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- It is passive process
- It happens along the concentration gradient
- No use of energy.
Banner 9
FACTORS AFFECTING DIFFUSION
SURFACE AREA
- Greater the surface area greater is the rate of diffusion as particle will get more room for movement.
- All the exchange surfaces have greater surface area like root cells has root hairs and intestine cells has villi.
CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
- Greater the difference in concentration in the two region greater is the rate of diffusion.
- All the exchange surfaces maintain steepest concentration gradient
- Like root cells are closed to xylem and Villi has rich blood supply.
DIFFUSION DISTANCE
- Smaller the diffusion distance greater is the rate of diffusion as the particles have to travel a smaller distance.
- All the exchange surfaces maintain a smaller diffusion distance by being one cell thick.
TEMPERATURE
- Greater the temperature greater is the rate of diffusion as particles will get more kinetic energy for movement
- Rate of Diffusion = Surface area x Concentration gradient/Diffusion Distance


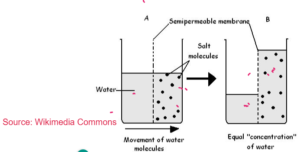
OSMOSIS – Special Case of Diffusion
Osmosis is the net movement of water particles from the region of high concentration of water particles to low concentration of water particles across a semi permeable membrane.
Movement of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a semi permeable membrane.
Special Case:
- It is the diffusion of only water molecules
- It required a semi permeable or partially membrane
- Membrane that allows only specific molecules to pass through like water.
OSMOSIS IN PLANTS
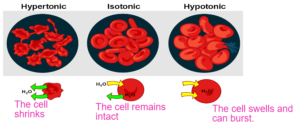
- Hypertonic – The outer solution has a less concentration of water than inside the cell.
- Isotonic – The outer solution has same concentration of water than inside the cell.
- Hypotonic – The outer solution has a greater concentration of water than inside the cell.
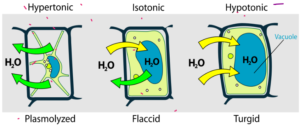
Plasmolyzed – The water moves out of the cells due to osmosis due to higher concentration of water inside the cell than outside. The cell membrane recetes from the cell wall
Flaccid – There will no net water movement so no pressure on the cell. It will be flaccid
Turgid – The water moves into the cell due to osmosis due to higher concentration of water outside the cell. The water will create pressure called turgor pressure on the cell wall making cell rigid and turgid.
Osmosis in Animals
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of substances from the region of low concentration to a region of higher concentration with the use of energy.
- Dependent on respiration as it requires energy. So the cells involved in active transport has lots of mitochondria.
- In Plants water and minerals are absorbed by active transport to absorb maximum of water and minerals.
- In animals, the digested food gets absorbed into the blood by active transport to ensure maximum absorption
- Salt glands are present in some marine organisms which removes the salt by active transport.
Banner 10
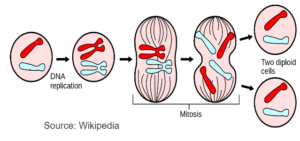
CELL CYCLE
Interphase –
- It is the longest phase of the cell cycle
- The cell grows in size and prepares all the proteins and enzymes needed for division.
- Replication of DNA where DNA duplicates its content.
Mitosis
- It is the division of the nucleus in which parent cell splits into two daughter nuclei containing same number of chromsomes as the parent cell.
Cytokinesis
- It is the division of the cytoplasm which .takes place after the division of the nucleus.
Mitosis
- It is the type of cell division in which a parent nucleus divides to form two daughter nuclei with exactly the same number of chromomes as that of the parent nucleus.
- The daughter cells produced are genetically identical to the parent and are clones.
- This division is important for growth, regneration and repair.
- Mitosis is also important in asexual reproduction.
CELL DIFFERENTIATION
- It is the process by which cell becomes specialised to perform a specific function.
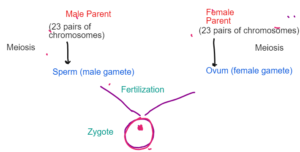
- Male Parent (23 pairs of chromosomes) Meiosis
Sperm (male gamete)
- Female Parent (23 pairs of chromosomes) Meiosis
Ovum (Female gamete)
Animal Differentiation
- In animals majority of the cells are differentiated at an early stage and different cells have specific functions like nerve cell, muscle cells.
- Adult stem cells replaced the old and worn out cells in human but adult stem cells have limited specialization power
- Majority of the differentiation is permanent
Plant Differentiation
- Plants are the storehouse of stem cells
- Root meristems and shoot meristems are the parts of actively growing part of the cells which contains stem cells.
- The plants can be cloned easily as it has many undifferentiate cells and differentiation is not permanent.
STEM CELLS
- Undifferentiate mass of cells that can differentiate into any cell type are known as stem cells.
- Sources of Stem Cells : Embryo, left over remains of the embryo and the umbilical chord are the sources of embryonic stem cells.
- Bone marrow is the source of adult stem cells.
- Can solve the rejection problem if the transplanted organ is made from the person’s own stem cells.
- Can be possible cure of neuro-degenerative diseases
- Can be the potential cure of diabetes.
- Therapeutic cloning.
- Organ damage problem
ISSUES AGAINST STEM CELLS
- It can lead to cancer as the stem cells are rapidly dividing.
- The stem cells can be contaminated and can cause unwanted diseases to the patient.
- Research is still slow and expensive
- Research happens on aborted embryos which is considered as a potential source of life and many religions have ethical concerns against it.
- The knowledge of the genes switched on and off using differentiation is still incomplete.
Banner 11
KEY TERMS!!!
- Cells – Basic structural and functional unit of the living organism.
- Mitochondria —The cell organelle which is the site of aerobic respiratiom
- Nucleus — The cell organelle which controls the activities of the cell
- Cytoplasm –The jelly like fluid which fills the cell and contains enzymes for chemical reactions.
- Ribosomes — The cell organelle which is the site for protein synthesis
- Prokaryotic – Cell The primitive cell without nucleus or membrane bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cell —The advanced cell type with nucleus and membrane bound organelle
- Cell Wall— The outer layer of the plant cell which provide shape and support
- Cell Membrane – The layer that controls what goes in and out of the cell.
- Vacuole – Organelle present in plant cell which has cell sap and make the cell turgid.
- Microscopes – Devices that is used to see the object which are not visible by a naked
- Resolution – Ability to distinguish between closely placed objects.
- Magnification — Ability to enlarge an object
- Xylem – Transport tissue in plants that transports water and minerals.
- Phloem – Transport tissue in plants that transports food
- Diffusion – Movement of substance from a higher concentration to a lower concentration.
- Osmosis — Movement of water from high concentration of water to low concentration of water across semi permeable membrane
- Plasmolysis— Shrinking of plant cell when placed in hypertonic solution.
- Turgid — Fully swollen cell which has gained water by osmosis.
- Flaccid— soft cell due to no net movement of water.
- Mitosis — Cell division that produces identical daughter cells.
- Differentiation – Cell specialization
- Stem Cells – Undifferentiated mass of cells that can specialize to any cell type
- Therapeutic cloning — Using adult stem cells to produce embryonic stem cells and differentiating them to produce a required cell type
Banner 12
Disclaimer:
I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
