This page contains the AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Questions and kerboodle answers for revision and understanding Rates and Equilibrium.This page also contains the link to the notes and video for the revision of this topic.
Banner 1
C8.1 Rate of Reaction AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page no-129
1 a Answer In the practical, marble chips was in excess but not the hydrochloric acid. Since all the hydrochloric has been used up there was no acid left to react with those marble chips. Therefore, marble chips remained and no gas was given off.
b Answer When the graph levels off, there was no change in the concentration of the reactant mixture. At that point, the reaction had finished.
2 a i Graph showing amount of product increasing with time
ii.The graph showing the amount of reactants with time
b Answer The gradient of the line on the graph of concentration versus time give the information of the rate of a reaction.
Banner 2
C8.2 Collision theory and Surface Area AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 131
1 The factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction are Temperature, Surface Area of solids, Concentration of Solutions, Pressure of Gases and the presence of a catalyst.
2 Iron nail cut into small pieces have a greater surface area to volume ratio. Greater surface area to volume ratio results in more frequent collision between the iron nail and the molecules of air and water. There will be more chances of successful collisions with increase in collision. Therefore, it will react more quickly with air and water and will rust easily as compared to whole iron nail.
3 Chewing the food increases the surface area of the food. The surface area to volume ratio of food particles increases with chewing. Greater the surface area more the collision between the acid and the food particles. As a result, acid gets greater area of the food to react with making the digestion more effective.
4 Answer Activation energy is the minimum energy required before a reaction can occur. Activation energy is important in a reaction as it is just not the frequency of collisions that is important. The reactants should collide with enough energy for the reaction to take place.
- a
I zinc granules [1 mark]
I Mean Rate of reaction with Zinc Granules = 25/225 = 0.11 cm3/s
ii Mean Rate of reaction with Zinc Pellets = 25/114 = 0.219 cm3/s
b
b Answer Zinc Pellets will have a greater surface area to volume ratio as compared to zinc granules. There will be more collisions between the zinc pellets and dilute sulfuric acid as compared to zinc granules and hydrochloric acid. More collisions will increase the chances of successful collision increasing the rate of reaction. Hence the reaction will take less time to complete. Therefore, the reaction took only 114 s to collect the same volume of gas with the zinc pellets.
C. Moles of hydrogen gas: 0.001 moles
Moles of Zinc reacted = 0.001 moles
Mass of Zinc = 0.001* 65
=0.065 g
Banner 3
C8.3 The effect of Temperature AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page no – 133
1.a Answer Increasing the temperature increases reaction rates because of the increase in the number of high energy collisions. Increasing the temperature makes the particles to collide more often. More the collisions increases the chances of collisions greater than the activation energy (successful collisions) It is only these collisions (possessing at least the activation energy for the reaction) which result in a reaction.
b Answer 10 degrees rise will double the rate of a reaction.
2.a The tablets fizz in water as it releases carbon dioxide gas by the reaction of sodium hydrogen carbonate and citric acid contained in the tablets with the water.
- Answer The reaction will take less time to finish as the temperature increases as the reaction rate will increase.
- Answer Increasing the temperature will increase the kinetic energy of the molecules. Therefore molecules will collide more and increases collision will also increase the chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of reaction. Increase in temperature also increases the energy of the molecules so the number of particles having energy greater or equal to the activation energy increases which will increase the chances of successful collision increases the rate of reaction.
3.The pressure cooker has a greater pressure inside it. The increased pressure makes the particles to collide faster. Furthermore, higher temperature in the pressure cooker increases the collisions which further increases the chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of the reaction making food to cook faster.
Banner 4
C8.4 The Effect of concentration and pressure AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 135
1.a Answer The graph with the steepest slope shows the fastest reaction. So Green line shows the faster reaction.
b High resolution of a balance means that it should measure the small changes in the mass.
2.a Answer Graph showing the volume of gas against time at high, medium and low concentration.
B Answer The amount of product formed in a reaction is directly proportional to the amount of limiting reactant used. This means that a graph showing the amount of product formed against amount of limiting reactant will give a positive correlation.
3 Answer When the acid cleaners are diluted, the number of particles of calcium carbonate decreases resulting in fewer collisions. Fewer collision decreases the chances of successful collisions thereby decreasing the reaction rate.
Banner 5
C8.5 The effect of catalysts AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 137
1.a Answer A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the reaction. This pathway has lower activation energy than the one followed by the uncatalysed reaction. As a result, a greater proportion of reacting particles have enough energy to react.
b Volume = 50 cm3
Time = 3 minutes and 12 seconds = 192 seconds
Answer Rate of Reaction = 50/192 = 0.2604cm3/s
2.Answer Solid catalysts are shaped as tiny beads or cylinders with holes in them as they increase the surface area to volume ratio. Greater the surface area to volume ratio, more are the chances for collisions, increasing the rate of the reaction.
3.Answer The number of moles of catalyst needed to speed up a chemical reaction is small as compared to the number of catalyst As the catalyst are not being used up in the reaction, they are required in a very small quantity only.
4.Answer a. Haber’s Process
Nitrogen + Hydrogen = Ammonia
Catalyst used = Iron
- Making Margarine
Vegetable Oil + H2 = Margarine
Catalyst used = Nickel
- Oswald Process
Ammonia + Oxygen = Nitric Acid
Catalyst used = Platinum
- Contact Process
sulfur+dioxygen(O2)=sulfur dioxide
Catalyst Used : Vanadium Oxide
5 Catalyst are very useful in the chemical industry. Catalysts speed up the rate of reaction, which saves money because the plant doesn’t have to operate for as long to produce the same amount of product.
Catalysts allow the reaction to work at a much lower temperature. This reduces the energy used up in a reaction which is good for sustainable development.
They save industries money.
They never get used up in a reaction so once you’ve got them you can use them over and over again.
Baneer 6
C8.6 Reversible Reactions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 139
1 Answer A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction where the reactants form products that, in turn, react together to give the reactants back. Reversible reactions will reach an equilibrium point where the concentrations of the reactants and products will no longer change.
2 In the demonstration, the phenolphthalein indicator will change the colour. When it will in acid it will be colourless. When it will be in alkali it will turn pink purple.
- Reversible change of phenolphthalein in acid and alkali
HPhe = H+ + Phe-
(colourless) (pink-purple)
4.Thermochromic materials will change colour with temperature. So they will be ideal for thermometer.
5 Answer.
A reversible reaction involving white anhydrous copper(II) sulfate and blue hydrated copper(II) sulfate. In the presence of water the copper sulfate crystals will turn blue.
A similar reversible reaction takes place between anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride (which is blue) and water to produce hydrated cobalt(II) chloride (which is pink). Heating pink hydrated cobalt(II) chloride makes it turn blue.
| Word Equation: | Anhydrous Cobalt (II) chloride + Water ⇌ Hydrated Cobalt (II) chloride |
| Formula Equation: | CoCl2(s) + 6H2O (l) ⇌ CoCl2.6H2O (s) |
Banner 7
C8.7 Energy and Reversible Reactions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 141
1.a Answer In a reversible reaction, if the reaction in one direction is exothermic than the opposite direction is endothermic and vice versa.
b Answer Anhydrous copper(ll) sulfate is used as a test for water. Add copper sulfate (CuSO4) to a sample.
If water is present the anhydrous copper sulfate will change from white to blue.
c Answer As humidity increases, cobalt chloride will shift from blue to pink, with a purplish color serving as the mid-phase hue between these two colors. According to the American Chemistry Council, cobalt chloride has a crystalline structure that changes as the molecules shift to make room for water molecules, leading to the color change that makes this substance ideal for detecting the presence of humidity.
d. Answer When water is added to blue cobalt (II) chloride, The reaction is exothermic so the energy is transferred to the surroundings.
2 a Answer W + X = Y + Z
B Answer The reverse reaction is endothermic so the energy is transferred from the surroundings.
3.a Answer The 2 in front of H2O means that every molecule of CaCl2 is combined with 2 moles of H2O molecules
b Answer Weak acids and bases may undergo reversible reactions. For example, carbonic acid and water react this way:
H2CO3 (l)+ H2O(l)⇌ HCO−3 (aq)+ H3O+(aq)
c Answer When heated, wet cobalt chloride paper can turn back from pink to blue as the water molecules are burned off and the original crystalline structure of the chemical is restored.
d Answer 2 moles of water will be lost when 0.50 moles of pink cobalt (ll) chloride is turned completely into blue cobalt (ll) chloride. So mass of 2 moles of water will be 36 g.
Banner 8
C8.8 Dynamic Equilibrium AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Page 143 Kerboodle Answers
1.Answer In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the forward reaction rate and the reverse reaction rate are equal. The result of this equilibrium is that the concentrations of the reactants and the products do not change.
2.Answer In a chemical equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products do not change. But the forward and reverse reactions have not stopped – they are still going on at the same rate as each other. This is what happens in a dynamic equilibrium.
3.Answer chemists describe chemical equilibrium as dynamic as the reaction does not stop at equilibrium. The reaction is still taking place but at the same rate in both the directions so overall we see no change in the concentration but the reaction is still taking place at the same rate in both directions.
4.4. Answer ICl + Cl2 = ICl3
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, whenever a system in equilibrium is subject to change, the reaction will move to the side to counteract our change. In the above reaction, Increasing ICL or Cl2 will shift the reaction to the side where ICL and Cl2 can me used up making ICl3 which is the forward side. So pumping more Cl2 rather than removing will shift the reaction to the right making ICl3.
Banner 9
C8.9 Altering Conditions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page 145
1.Answer- Increasing pressure will shift the reaction to the side with less number of gas molecules. So the reaction will shift towards producing less volume of gas molecules so the amount of product formed will decrease by increasing the pressure.
2 Answer Increasing the temperature will shift the reaction to the endothermic side so the reaction will shift toward right making more hydrogen gas.
3 a Answer Increasing the pressure will shift the reaction to the side with the least number of gaseous molecules. So in this reaction, increasing pressure will shift the reaction towards right where there less number of gaseous molecules. So the colors will be pale yellow of the reaction mixture as the reaction will shift towards the right.
b Answer Increasing the temperature will shift the reaction to the endothermic side. Increasing temperature will shift the reaction to the left, forming more NO2 which will give a brown color to the mixture.
4.Answer
Increasing pressure will shift the reaction to the side where there are less number of gaseous moles. In this reaction there are an equal number of moles on both sides. So there will be no effect of the change of pressure on this reaction as it has equal number of gaseous moles on both sides.
Banner 10
C8 Summary Questions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 146
c
a In the reaction between marble chips and acids carbon dioxide is formed as a gas. The positive test for this gas is the limewater test in which gas is passed through lime water and carbon dioxide will turn limewater cloudy.
b i Answer calcium carbonate + nitric acid → calcium nitrate + water +carbon dioxide
II Answer CaCO3(s) + 2HNO3(aq) → Ca(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
C Answer
To investigate the effect of the rate of the reaction, the marble chips are reacted with nitric acid. This reaction produces a gas so the reactants will decrease in mass with the evolution of the gas. Greater the change in mass more will be the rate of reaction. In this investigation, the student has taken two different concentration of acids. The marble chips are added in the conical flask with the different concentration of acid and the conical flask was weighed every 30 seconds for 2.5 minutes. The loss in mass of the flask is equivalent to mass of gas produced and is recorded every 30 seconds and the graph is plotted.
D Graph of the reaction between marble chips and acids at two different concentrations
d Answer
both lines drawn as smooth curves and labelled
E (i) To calculate the rate of both the reaction, we will draw a tangent on the graph and measure the gradient of the tangent.
For A Rates = 0.59 g/min , for B Rate = 0.29 g/min
II Answer
rate of reaction in B ≈ half that in A
f Answer As the rate of reaction in B is half than that of A so the volume of the gas produced is also half in B than A
g initial concentration of acid in A = twice the concentration of acid in B
h Answer Since the concentration of A is double than B there are more H+ ions in A than in B. Greater the number of H+ ions more will be the collision and more collisions result in more chances of successful collisions.
2
a To make the investigation a fair test the students needs to control the variables like temperature, mass of the reactants, surface area, volume and the concentration of the reactant.
b In the reaction between Zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas is given off. Hydrogen gas can be tested by bringing a lighted splint near the mouth of the gas and it burns with a squeaky pop.
c Zinc reacts with hydrochloric Acid forming Zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
d Steeper the graph, more is the rate of reaction. Line 1 is steeper which shows the faster reaction rate which is due to the largest surface area to volume ratio of zinc.
e Pieces with large surface area to volume ratio will react slowly.
f The powdered zinc will react more vigorously due to greater surface area to volume ratio. If the student react the same mass of powdered zinc with the acid the result will be steepest of all the curves and the graph will level quickly.
g Greater the surface area of the reactant, more will be the rate of collisions. Greater the collision more will be the chances of successful collision resulting in increased rate of reaction.
h According to balanced chemical equation, 1 moles of Zinc will give 1 moles of hydrogen. 0.13 g of Zinc = 0.002 moles of Zinc and it will given 0.002 moles of hydrogen. 1 mole of hydrogen occupies 24 dm3 of gas so 0.002 moles of hydrogen will occupy 0.002*24 = 0.048 dm3.
3.a Catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being used up in the reaction.
b Hydrogen peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen.
2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
C To work out the best catalyst for decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, we can take the same amount different metal oxides in separate test tubes and add the same volume of acid in all of them. Will plot the graph of volume of oxygen released at different time interval and the graph with the steepest curve will have a faster rate so it will be the most effective catalyst.
- d) Rate = volume/time
= 40/16 = 2.5 cm3/s
40 cm3 to moles = 40/24000 moles =1.6 X 10-3 moles
Rates = 1.6 X 10-3 moles/16 s = 1X 10-4 moles
- e) After the reaction, the mixture will be of metal oxides and unreacted reactants. The mixture can be filtered off and the filter paper is dried to get the samples.
Banner 11
Practice questions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 147
01.1
01.2
01.3
01.4
01.1 Answer The mixture turned cloudy due to the solid product which is sulfur / S.
01.2 The student should make sure the rate of mixing of the reactants is same in both reactions.
01.3 As the concentration increases there are more collisions in a given volume. Greater the collisions more are the chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of the reactions.
1.4 As the temperature increases, particles get more kinetic energy. Greater the kinetic energy more are the collisions. Temperature increases the energy of the particles so there are more number of molecules with energy greater than the activation energy increases the rate of reaction.
02.1 In the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide is produced which is a gas which can escape causing the mass to decrease.
02.2 Student used a cotton wool plug to prevent the materials from falling out.
02.3 Answer- As calcium carbonate chips are in excess, hydrochloric acid is a limiting factor. The concentration of hydrochloric acid decreased so there is no hydrochloric acid for the calcium carbonate to react decreasing the rate of the reaction.
02.4 Answer Powdered calcium carbonate has a greater surface area to volume ratio. Greater the surface area to volume ratio, the greater are the collisions and greater collisions means more chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of the reaction.
03.1: increasing pressure increases the yield increasing the temperature decreases the yield
Reaction 2: increasing pressure decreases the yield increasing the temperature increases the yield
3.2 Increase in pressure decreases the volume so particles collide more frequently in the small volume. Greater the collisions more are the chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of the reaction.
3.3 Increasing the pressure shifts the reaction to the less gas molecules side. So with the increase in pressure the equilibrium shifts to the right, increasing the yield of the reaction.
Banner 11
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: I have tried by level best to provide the answers and video explanations to the best of my knowledge. All the answers and notes are written by me and if there is any similarity in the content then it is purely coincidental. But this is not an alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
AQA GCSE Science Kerboodle textbook
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Join Our Free Facebook Group : Get A* in GCSE and A LEVEL Science and Maths by Mahima Laroyia: https://www.facebook.com/groups/expertguidance.co.uk/
For Free Tips, advice and Maths and Science Help
This page contains the detailed and easy notes for AQA GCSE Chemistry The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change for revision and understanding The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change.
Banner 1
New (9-1) AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2: Complete Revision Summary
THE RATE AND EXTENT OF CHEMICAL CHANGE
Banner 2
4.6 The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change
- The Rate of reaction
- Factors Affecting Rates of Reaction
- Collision Theory
- Catalysts
- Reversible Reaction
- Dynamic Equilibrium
- Altering Conditions
RATE OF REACTION
- In a reaction, the concentration of reactants decreases with time
- In a reaction, the concentration of products increases with time.

- a) Weigh the mass of the reactants at different time interval and plot the graph.
- b) If the products are gas, we can measure the volume of gas evolved at different time intervals
- c) If the precipitation reaction, we can measure absorbance value.
Banner 3
COLLISSION THEORY
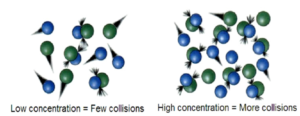
For a reaction to take place, the three important things are required.
COLLISIONS
- For the reactions to take place the particles should collide or bump into each other.
ACTIVATION ENERGY (SUCCESSFULL COLLISIONS)
- The particles should collide with the minimum energy required to start the reaction- Activation Energy.
- The collision with the energy equal to or greater than activation energy is successful collision.
CORRECT ORIENTATION
- The particles should have correct orientation for the reaction to take place.
Banner 4
FACTORS AFFECTING RATE OF REACTION
| FACTOR | EFFECT | EXPLANATIONS |
| SURFACE AREA | With increase in surface area the rate of reaction increases Powdered reactants react faster. | Greater the surface area or surface area to volume ratio more particles will be exposed and reactants have greater chance of colliding increasing the rate of reaction. |
| TEMPERATURE | With increase in temperature the reaction rate increases. | With increase in temperature; the particles gain kinetic energy They collide more frequency Greater the collision greater are the chances of successful collisions Also as the energy increases more particles have energy equal or greater than activation energy increasing the rate of a reaction |
| CONCENTRATION OF REACTANTS | With increase in concentration of reactant the reaction rate Increases. | Increasing the concentration increases more particles in the given volume More the particles more the chance of collisions Greater the collision greater the chance of successful collision increasing the rate of the reaction. |
| PRESSURE | With increase in pressure the rate of reaction of the gaseous reactants increases. | Increasing the pressure increases the rate of the reaction as there will be more particles in a lesser volume. So they bump into each other more increasing the rate of the reaction |
| CATALYST | With the use of catalyst the rate of reaction increases. | Catalyst increases the rate of the reaction by providing the alternative route that works by lowering the activation energy. So there are more number of particles with energy equal to activation energy increasing the rate of the reaction. |
Banner 5
CATALYSTS
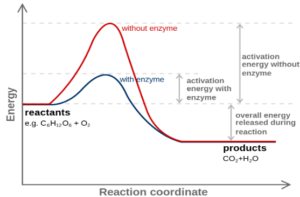
- Catalysts increases the rate of the reaction by providing an alternative route
- The alternative route lowers the activation energy
- As the activation energy is lowered there are more number of particles having energy equal to or greater than the activation energy increasing the rate of the reaction.
- Required in small quantity and is regenerated after the reaction.
Example
The catalysts help those reactions to carry out at a lower temperature which require very high temperature so saves us on energy and electricity costs.
Baneer 6
REVERSIBLE REACTION
Reactions that proceed both in forward and reverse direction.
Eg – N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
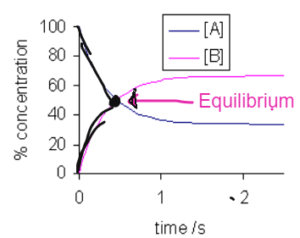
At the start the concentration of the reactants decreases. The reactants decreases and the concentration of products start to increase.
A ⇌ B
There comes a point where concentration of reactants and the products are same as the rate of appearance of products and rate of disappearance of reactants is the same. That point is the equilibrium point.
Banner 7
DYNAMIC EQUIBRIUM
- When rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of reverse reaction.
- The reactions does not stop at equilibrium. The reactions takes place with the same rate in both the direction so overall we see no change.
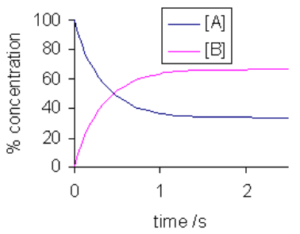
CONDITIONS FOR DYNAMIC EQUILBRIUM
- a) It has to be closed system. Nothing should leave or enter the system.
- b) The rate of forward reaction should be equal to the rate of reverse reaction.
Le Chattelier’s Principle
When the system in equilibrium is subject to a change, the equilibrium is moved to a direction to counteract the chance.
Concentration ⇌
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
Forward direction ammonia is made in the reverse direction nitrogen and hydrogen are used up.
Add nitrogen Right
Add hydrogen Right
Add ammonia Left
Remove Ammonia Right
So in habers process nitrogen and hydrogen are continously added and unreacted are recycled and ammonia is removed as soon as it is formed.
Pressure
- More the gas molecules more the pressure.
- Less the pressure less the gas molecules.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
- Increasing pressure = Less gas side = Right
- Decreasing pressure: = more gas side = Left
- So high pressure is required for manufacture of ammonia.
Temperature and Equilbrium
- If ΔH is negative the forward reaction is exothermic and produces heat.
- If the forward is exothermic the reverse is endothermic and vice versa.
EXOTHERMIC REACTION (Produces heat)
ENDOTHERMIC REACTION (Takes in heat)
Eg N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
ΔH = -93KJ/mol
- Forward reaction is exothermic produces heat. Reverse reaction is endothermic and takes in heat.
- Increase in temperature will shift the equilibrium side which is left and decrease in temperature will shift to more heat side which is right.
Banner 8
KEY TERMS
- a) Rate of a reaction – It is the decrease in the concentration of reactants per unit time, or the increase in the concentration of products per unit time,
- b) Collision Theory – For the reactions to take place the particles should collide or bump into each other. Low concentration = few collisions. High Concentration = more collisions.
- c) Activation Energy – the minimum energy required to start the reaction.
- d) Catalysts – A catalyst is a substance that changes the speed of a chemical reaction without chemically altering it at the end of the reaction.
- e) Reversible Reaction – Reactions that proceed both in forward and reverse direction.
- f) Dynamic Equilibrium – When rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of reverse reaction.
- g) Le Chatellier’s Principle – When the system in equilibrium is subject to a change, the equilibrium is moved to a direction to counteract the chance.
- h) Exothermic – Produces Heat
- i) Endothermic – Takes in Heat
Banner 9
Disclaimer:
I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
C8- Rates And Equilibrium
- Rate of Reaction 1 MS
- Rate of Reaction 1 QP
- Rate of Reaction 2 MS
- Rate of Reaction 2 QP
- Rate of Reaction 3 MS
- Rate of Reaction 3 QP
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 1 MS
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 1 QP
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 2 MS
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 2 QP
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 3 MS
- Reversible Reactions & Dynamic Equilibrium 3 QP
This page contains the AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Questions and kerboodle answers for revision and understanding Rates and Equilibrium.This page also contains the link to the notes and video for the revision of this topic.
Banner 1
C8.1 Rate of Reaction AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page no-129
1 a Answer In the practical, marble chips was in excess but not the hydrochloric acid. Since all the hydrochloric has been used up there was no acid left to react with those marble chips. Therefore, marble chips remained and no gas was given off.
b Answer When the graph levels off, there was no change in the concentration of the reactant mixture. At that point, the reaction had finished.
2 a i Graph showing amount of product increasing with time
ii.The graph showing the amount of reactants with time
b Answer The gradient of the line on the graph of concentration versus time give the information of the rate of a reaction.
Banner 2
C8.2 Collision theory and Surface Area AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 131
1 The factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction are Temperature, Surface Area of solids, Concentration of Solutions, Pressure of Gases and the presence of a catalyst.
2 Iron nail cut into small pieces have a greater surface area to volume ratio. Greater surface area to volume ratio results in more frequent collision between the iron nail and the molecules of air and water. There will be more chances of successful collisions with increase in collision. Therefore, it will react more quickly with air and water and will rust easily as compared to whole iron nail.
3 Chewing the food increases the surface area of the food. The surface area to volume ratio of food particles increases with chewing. Greater the surface area more the collision between the acid and the food particles. As a result, acid gets greater area of the food to react with making the digestion more effective.
4 Answer Activation energy is the minimum energy required before a reaction can occur. Activation energy is important in a reaction as it is just not the frequency of collisions that is important. The reactants should collide with enough energy for the reaction to take place.
- a
I zinc granules [1 mark]
I Mean Rate of reaction with Zinc Granules = 25/225 = 0.11 cm3/s
ii Mean Rate of reaction with Zinc Pellets = 25/114 = 0.219 cm3/s
b
b Answer Zinc Pellets will have a greater surface area to volume ratio as compared to zinc granules. There will be more collisions between the zinc pellets and dilute sulfuric acid as compared to zinc granules and hydrochloric acid. More collisions will increase the chances of successful collision increasing the rate of reaction. Hence the reaction will take less time to complete. Therefore, the reaction took only 114 s to collect the same volume of gas with the zinc pellets.
C. Moles of hydrogen gas: 0.001 moles
Moles of Zinc reacted = 0.001 moles
Mass of Zinc = 0.001* 65
=0.065 g
Banner 3
C8.3 The effect of Temperature AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page no – 133
1.a Answer Increasing the temperature increases reaction rates because of the increase in the number of high energy collisions. Increasing the temperature makes the particles to collide more often. More the collisions increases the chances of collisions greater than the activation energy (successful collisions) It is only these collisions (possessing at least the activation energy for the reaction) which result in a reaction.
b Answer 10 degrees rise will double the rate of a reaction.
2.a The tablets fizz in water as it releases carbon dioxide gas by the reaction of sodium hydrogen carbonate and citric acid contained in the tablets with the water.
- Answer The reaction will take less time to finish as the temperature increases as the reaction rate will increase.
- Answer Increasing the temperature will increase the kinetic energy of the molecules. Therefore molecules will collide more and increases collision will also increase the chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of reaction. Increase in temperature also increases the energy of the molecules so the number of particles having energy greater or equal to the activation energy increases which will increase the chances of successful collision increases the rate of reaction.
3.The pressure cooker has a greater pressure inside it. The increased pressure makes the particles to collide faster. Furthermore, higher temperature in the pressure cooker increases the collisions which further increases the chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of the reaction making food to cook faster.
Banner 4
C8.4 The Effect of concentration and pressure AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 135
1.a Answer The graph with the steepest slope shows the fastest reaction. So Green line shows the faster reaction.
b High resolution of a balance means that it should measure the small changes in the mass.
2.a Answer Graph showing the volume of gas against time at high, medium and low concentration.
B Answer The amount of product formed in a reaction is directly proportional to the amount of limiting reactant used. This means that a graph showing the amount of product formed against amount of limiting reactant will give a positive correlation.
3 Answer When the acid cleaners are diluted, the number of particles of calcium carbonate decreases resulting in fewer collisions. Fewer collision decreases the chances of successful collisions thereby decreasing the reaction rate.
Banner 5
C8.5 The effect of catalysts AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 137
1.a Answer A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the reaction. This pathway has lower activation energy than the one followed by the uncatalysed reaction. As a result, a greater proportion of reacting particles have enough energy to react.
b Volume = 50 cm3
Time = 3 minutes and 12 seconds = 192 seconds
Answer Rate of Reaction = 50/192 = 0.2604cm3/s
2.Answer Solid catalysts are shaped as tiny beads or cylinders with holes in them as they increase the surface area to volume ratio. Greater the surface area to volume ratio, more are the chances for collisions, increasing the rate of the reaction.
3.Answer The number of moles of catalyst needed to speed up a chemical reaction is small as compared to the number of catalyst As the catalyst are not being used up in the reaction, they are required in a very small quantity only.
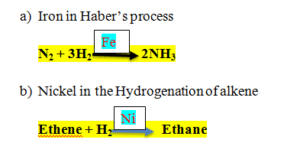
4.Answer a. Haber’s Process
Nitrogen + Hydrogen = Ammonia
Catalyst used = Iron
- Making Margarine
Vegetable Oil + H2 = Margarine
Catalyst used = Nickel
- Oswald Process
Ammonia + Oxygen = Nitric Acid
Catalyst used = Platinum
- Contact Process
sulfur+dioxygen(O2)=sulfur dioxide
Catalyst Used : Vanadium Oxide
5 Catalyst are very useful in the chemical industry. Catalysts speed up the rate of reaction, which saves money because the plant doesn’t have to operate for as long to produce the same amount of product.
Catalysts allow the reaction to work at a much lower temperature. This reduces the energy used up in a reaction which is good for sustainable development.
They save industries money.
They never get used up in a reaction so once you’ve got them you can use them over and over again.
Baneer 6
C8.6 Reversible Reactions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 139
1 Answer A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction where the reactants form products that, in turn, react together to give the reactants back. Reversible reactions will reach an equilibrium point where the concentrations of the reactants and products will no longer change.
2 In the demonstration, the phenolphthalein indicator will change the colour. When it will in acid it will be colourless. When it will be in alkali it will turn pink purple.
- Reversible change of phenolphthalein in acid and alkali
HPhe = H+ + Phe-
(colourless) (pink-purple)
4.Thermochromic materials will change colour with temperature. So they will be ideal for thermometer.
5 Answer.
A reversible reaction involving white anhydrous copper(II) sulfate and blue hydrated copper(II) sulfate. In the presence of water the copper sulfate crystals will turn blue.
A similar reversible reaction takes place between anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride (which is blue) and water to produce hydrated cobalt(II) chloride (which is pink). Heating pink hydrated cobalt(II) chloride makes it turn blue.
| Word Equation: | Anhydrous Cobalt (II) chloride + Water ⇌ Hydrated Cobalt (II) chloride |
| Formula Equation: | CoCl2(s) + 6H2O (l) ⇌ CoCl2.6H2O (s) |
Banner 7
C8.7 Energy and Reversible Reactions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 141
1.a Answer In a reversible reaction, if the reaction in one direction is exothermic than the opposite direction is endothermic and vice versa.
b Answer Anhydrous copper(ll) sulfate is used as a test for water. Add copper sulfate (CuSO4) to a sample.
If water is present the anhydrous copper sulfate will change from white to blue.
c Answer As humidity increases, cobalt chloride will shift from blue to pink, with a purplish color serving as the mid-phase hue between these two colors. According to the American Chemistry Council, cobalt chloride has a crystalline structure that changes as the molecules shift to make room for water molecules, leading to the color change that makes this substance ideal for detecting the presence of humidity.
d. Answer When water is added to blue cobalt (II) chloride, The reaction is exothermic so the energy is transferred to the surroundings.
2 a Answer W + X = Y + Z
B Answer The reverse reaction is endothermic so the energy is transferred from the surroundings.
3.a Answer The 2 in front of H2O means that every molecule of CaCl2 is combined with 2 moles of H2O molecules
b Answer Weak acids and bases may undergo reversible reactions. For example, carbonic acid and water react this way:
H2CO3 (l)+ H2O(l)⇌ HCO−3 (aq)+ H3O+(aq)
c Answer When heated, wet cobalt chloride paper can turn back from pink to blue as the water molecules are burned off and the original crystalline structure of the chemical is restored.
d Answer 2 moles of water will be lost when 0.50 moles of pink cobalt (ll) chloride is turned completely into blue cobalt (ll) chloride. So mass of 2 moles of water will be 36 g.
Banner 8
C8.8 Dynamic Equilibrium AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Page 143 Kerboodle Answers
1.Answer In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the forward reaction rate and the reverse reaction rate are equal. The result of this equilibrium is that the concentrations of the reactants and the products do not change.
2.Answer In a chemical equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products do not change. But the forward and reverse reactions have not stopped – they are still going on at the same rate as each other. This is what happens in a dynamic equilibrium.
3.Answer chemists describe chemical equilibrium as dynamic as the reaction does not stop at equilibrium. The reaction is still taking place but at the same rate in both the directions so overall we see no change in the concentration but the reaction is still taking place at the same rate in both directions.
4.4. Answer ICl + Cl2 = ICl3
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, whenever a system in equilibrium is subject to change, the reaction will move to the side to counteract our change. In the above reaction, Increasing ICL or Cl2 will shift the reaction to the side where ICL and Cl2 can me used up making ICl3 which is the forward side. So pumping more Cl2 rather than removing will shift the reaction to the right making ICl3.
Banner 9
C8.9 Altering Conditions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page 145
1.Answer- Increasing pressure will shift the reaction to the side with less number of gas molecules. So the reaction will shift towards producing less volume of gas molecules so the amount of product formed will decrease by increasing the pressure.
2 Answer Increasing the temperature will shift the reaction to the endothermic side so the reaction will shift toward right making more hydrogen gas.
3 a Answer Increasing the pressure will shift the reaction to the side with the least number of gaseous molecules. So in this reaction, increasing pressure will shift the reaction towards right where there less number of gaseous molecules. So the colors will be pale yellow of the reaction mixture as the reaction will shift towards the right.
b Answer Increasing the temperature will shift the reaction to the endothermic side. Increasing temperature will shift the reaction to the left, forming more NO2 which will give a brown color to the mixture.
4.Answer
Increasing pressure will shift the reaction to the side where there are less number of gaseous moles. In this reaction there are an equal number of moles on both sides. So there will be no effect of the change of pressure on this reaction as it has equal number of gaseous moles on both sides.
Banner 10
C8 Summary Questions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 146
c
a In the reaction between marble chips and acids carbon dioxide is formed as a gas. The positive test for this gas is the limewater test in which gas is passed through lime water and carbon dioxide will turn limewater cloudy.
b i Answer calcium carbonate + nitric acid → calcium nitrate + water +carbon dioxide
II Answer CaCO3(s) + 2HNO3(aq) → Ca(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
C Answer
To investigate the effect of the rate of the reaction, the marble chips are reacted with nitric acid. This reaction produces a gas so the reactants will decrease in mass with the evolution of the gas. Greater the change in mass more will be the rate of reaction. In this investigation, the student has taken two different concentration of acids. The marble chips are added in the conical flask with the different concentration of acid and the conical flask was weighed every 30 seconds for 2.5 minutes. The loss in mass of the flask is equivalent to mass of gas produced and is recorded every 30 seconds and the graph is plotted.
D Graph of the reaction between marble chips and acids at two different concentrations
d Answer
both lines drawn as smooth curves and labelled
E (i) To calculate the rate of both the reaction, we will draw a tangent on the graph and measure the gradient of the tangent.
For A Rates = 0.59 g/min , for B Rate = 0.29 g/min
II Answer
rate of reaction in B ≈ half that in A
f Answer As the rate of reaction in B is half than that of A so the volume of the gas produced is also half in B than A
g initial concentration of acid in A = twice the concentration of acid in B
h Answer Since the concentration of A is double than B there are more H+ ions in A than in B. Greater the number of H+ ions more will be the collision and more collisions result in more chances of successful collisions.
2
a To make the investigation a fair test the students needs to control the variables like temperature, mass of the reactants, surface area, volume and the concentration of the reactant.
b In the reaction between Zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas is given off. Hydrogen gas can be tested by bringing a lighted splint near the mouth of the gas and it burns with a squeaky pop.
c Zinc reacts with hydrochloric Acid forming Zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
d Steeper the graph, more is the rate of reaction. Line 1 is steeper which shows the faster reaction rate which is due to the largest surface area to volume ratio of zinc.
e Pieces with large surface area to volume ratio will react slowly.
f The powdered zinc will react more vigorously due to greater surface area to volume ratio. If the student react the same mass of powdered zinc with the acid the result will be steepest of all the curves and the graph will level quickly.
g Greater the surface area of the reactant, more will be the rate of collisions. Greater the collision more will be the chances of successful collision resulting in increased rate of reaction.
h According to balanced chemical equation, 1 moles of Zinc will give 1 moles of hydrogen. 0.13 g of Zinc = 0.002 moles of Zinc and it will given 0.002 moles of hydrogen. 1 mole of hydrogen occupies 24 dm3 of gas so 0.002 moles of hydrogen will occupy 0.002*24 = 0.048 dm3.
3.a Catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being used up in the reaction.
b Hydrogen peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen.
2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
C To work out the best catalyst for decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, we can take the same amount different metal oxides in separate test tubes and add the same volume of acid in all of them. Will plot the graph of volume of oxygen released at different time interval and the graph with the steepest curve will have a faster rate so it will be the most effective catalyst.
- d) Rate = volume/time
= 40/16 = 2.5 cm3/s
40 cm3 to moles = 40/24000 moles =1.6 X 10-3 moles
Rates = 1.6 X 10-3 moles/16 s = 1X 10-4 moles
- e) After the reaction, the mixture will be of metal oxides and unreacted reactants. The mixture can be filtered off and the filter paper is dried to get the samples.
Banner 11
Practice questions AQA GCSE Chemistry C8 Rates and Equilibrium Kerboodle Answers Page No 147
01.1
01.2
01.3
01.4
01.1 Answer The mixture turned cloudy due to the solid product which is sulfur / S.
01.2 The student should make sure the rate of mixing of the reactants is same in both reactions.
01.3 As the concentration increases there are more collisions in a given volume. Greater the collisions more are the chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of the reactions.
1.4 As the temperature increases, particles get more kinetic energy. Greater the kinetic energy more are the collisions. Temperature increases the energy of the particles so there are more number of molecules with energy greater than the activation energy increases the rate of reaction.
02.1 In the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide is produced which is a gas which can escape causing the mass to decrease.
02.2 Student used a cotton wool plug to prevent the materials from falling out.
02.3 Answer- As calcium carbonate chips are in excess, hydrochloric acid is a limiting factor. The concentration of hydrochloric acid decreased so there is no hydrochloric acid for the calcium carbonate to react decreasing the rate of the reaction.
02.4 Answer Powdered calcium carbonate has a greater surface area to volume ratio. Greater the surface area to volume ratio, the greater are the collisions and greater collisions means more chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of the reaction.
03.1: increasing pressure increases the yield increasing the temperature decreases the yield
Reaction 2: increasing pressure decreases the yield increasing the temperature increases the yield
3.2 Increase in pressure decreases the volume so particles collide more frequently in the small volume. Greater the collisions more are the chances of successful collisions increasing the rate of the reaction.
3.3 Increasing the pressure shifts the reaction to the less gas molecules side. So with the increase in pressure the equilibrium shifts to the right, increasing the yield of the reaction.
Banner 11
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: I have tried by level best to provide the answers and video explanations to the best of my knowledge. All the answers and notes are written by me and if there is any similarity in the content then it is purely coincidental. But this is not an alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
AQA GCSE Science Kerboodle textbook
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Join Our Free Facebook Group : Get A* in GCSE and A LEVEL Science and Maths by Mahima Laroyia: https://www.facebook.com/groups/expertguidance.co.uk/
For Free Tips, advice and Maths and Science Help
