This page contains the AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Bonding and Structure Questions and kerboodle answers for revision and understanding Bonding Structure.This page also contains the link to the notes and video for the revision of this topic.
Banner 1
C3.1 States of matter AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers : Page No. 37
| Solid | Liquid | Gas | |
| Arrangement of particles | In solids, the particles are Close together and They have a Regular pattern | In Liquids, the particles are less Closer than solids but more closer than gas but they have Random arrangement | In gas particles are Far apart and have Random arrangement |
| Movement of particles | In solids since there is less space in between the particles they cannot move but they Vibrate on the spot | In liquids particles have spaces between them so they Move around | In gases the particles have large intermolecular spaces between them so they Move quickly in all directions |
| Diagram |
Solids:
Solids have a fixed shape and cannot flow.
Solids cannot be compressed or squashed.
Liquids:
Liquids flow and take the shape of their container.
Liquids cannot be compressed or squashed.
Gases:
Gases flow and completely fill their container.
Gases can be compressed or squashed.
- When the gas is cooled down, its temperature first decreases and then as it reaches the condensation point. As it reaches the condensation points the temperature remains constant and all the gas particles converts into liquids. When all the gas particles converts to liquid the temperature of the particles decreases until it reaches the freezing point. At the freezing point the temperature remains constant until all liquids convert into solid.
- Density = Mass/Volume. According to this formula, if the volume increases density will decrease and if the volume decreases density will increase.
For the fixed mass of gas, the increase in temperature will increase the volume of the gas which in turn will decrease the density of the gas. On the other hand, increase in pressure will decrease the volume of the gas which will, in turn, increase the density of the gas
4. Melting point is the temperature at which the solid turns into a liquid. Different substances have different melting points because they are made up of different substances which have different intermolecular forces between them so they require different amounts of energy to overcome these forces and hence they have different melting points
5.We can investigate the effect of temperature on evaporation by taking paper towel and water at room temperature and hot water around 60 degrees. For this experiment we will first fill the plastic bag with room temperature water and hot water. We will next take two paper towel and put a drop of room temperature of water on both of them and weigh them. After weighing we will put on paper towel on the bag with room temperature water and other paper towel on the bag with hot water. After some time, we will remove the paper towel and weigh them again. We will observe the paper towel on hot water bag will have less mass and will show more evaporation.
Banner 2
C3.2 Atoms into ions AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers : Page No. 39
- a. Answer.
- A. Covalent bond forms when two atoms share a pair of electrons.
- Ionic bond are formed as a result of gaining and losing electrons.
- a. Aluminium form 3+ ions by loosing three electrons from its outermost shell.
- Fluorine forms -1 ions by gaining one electron
- Potassium, forms +1 ions by losing an electron.
- Oxygen, O forms 2- ions by gaining an electron.
- In ionic bonding, group 1 atoms donates their one electron from their outermost shell to group 7 atoms. Group 1 atoms after losing an electron becomes positively charged and group 7 atoms after gaining an electron becomes -1 charge. The strong electrostatic forces develops between oppositely charged ions resulting in ionic bonding.
- In the example above sodium atom with electronic configuration 2,8,1 loses one electron and become Na+ ions and chlorine atoms with electronic configuration 2,7 gain an electron and become Cl-ion. The electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions form ionic bonding.
Banner 3
C 3.3 Ionic bonding AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers
Page No. 41
- a.
| Atomic number | Atom | Electronic structure of atom | Ion | Electronic structure of ion |
| 9 | F | 2,7 | F- | 2,8 |
| 3 | Li | 2,1 | Li˖ | 2 |
| 16 | S | 2,8,6 | S2- | 2,8,8 |
| 20 | Ca | 2,8,8,2 | Ca2+ | 2,8 |
- a. Answer.
The charges of ions of Group 1, 2 and 3 are equal to their group number.
- Answer.
The charge of ions of these group 5,6, 7 and 8 are equal to group number -8.
3.A Potassium and oxygen Ionic Bonding
Ionic compounds.
k2O
potassium wants to get rid of 1 electron
Oxygen wants 2 electrons
Potassium gives up its 1 valence electron
Oxygen takes 1 electron from each potassium
Each potassium positive
(2 more electrons than it has protons!)
- Aluminium and fluorine ionic bonding
- a. Answer.
Potassium has the charge of +1 and bromine has the charge of -1 so when they form a compound the charges cancel out and they form KBr. In Potassium oxide, potassium has the charge of +1 but oxygen form -2 ions. So to balance the charge on oxygen two potassium are required therefore the formulae is K₂O.
- Magnesium has a charge of +2 as magnesium ions are formed by losing two electrons. Oxygen has a charge of -2 as oxygen ions are formed by gaining two electrons. These two equal and opposite charge of Mg2+ and O2- cancel each other and forms a compounds MgO. On the other hand chlorine forms -1 ions by gaining an electron and magnesium for 2+ ions by losing two electrons. So two balance 2+ charge of magnesium 2- charge of chlorine are needed so chlorine atoms are multiplied by 2 giving the formula MgCl2.
Answer.
Ions are electrically charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons. They have the same electronic structures as noble gases. Atom is neutral as it has an equal number of protons and electrons. But all atoms try to gain full outer shell noble gas electronic configuration. When an atom loses an electron it forms positively charged ions as they have more protons than electrons. When an atom gains electrons it forms negatively charged ions as they more electrons than protons. Metal generally have less electrons in their outermost shell so they loose an electron to gain full outer shell. Non metals generally have more electrons in their outermost shell therefore they gain an electron to gain full outer shell noble gas electronic configuration.
In ionic bonding, metal loses an electron and becomes positively charged. Nonmetal gains an electron and becomes negatively charged. The strong electrostatic force develop between the oppositely charged ions resulting in ionic bonding.
Banner 4
C3.4 Giant ionic structures AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers Page No. 43
1.See water is a good conductor of electricity due to the presence of sodium chloride ions. Sodium chloride ions being ionic dissociate into ions which act as charge carrier and conduct electricity.
2.Metal ions being positively charge move to the negative electrode and non metal ions being negatively charge move to the positive electrode.
Lithium ions – Being positive move to negative electrode.
Chloride ions – being negative move to positive electrode.
Bromide ions – being negative move to positive electrode.
Calcium ions – Being positive move to negative electrode.
Sodium ions -Being positive move to negative electrode.
Zinc ions-Being positive move to negative electrode.
Oxide ions -being negative move to positive electrode.
Iodide ions-being negative move to positive electrode.
Barium ions – Being positive move to negative electrode.
- Answer.
Ionic compounds have high melting points because the electrostatic interactions that hold the compounds together are very strong. In ionic compounds, the electrostatic force of attraction between cations and anions holds the compound together. As electrostatic force of attraction are strong, they require large amounts of energy to overcome these electrostatic force of attraction. Therefore, ionic compounds have high melting points.
4.. Ionic compounds are not good at conducting electricity in the solid state, but they do conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when they are in the molten state (liquid by melting).
In solid state, the ions are held by strong electrostatic force of attraction. But when they are in liquid or molten state the ions dissociate and hence they are free to move.
Therefore, ionic compounds conduct electricity when they are in liquid state as the ions are free to move around.
- Aluminum oxide has a higher melting point than sodium oxide. For alumina, the ionic lattice is composed of Al3+ and O2− ions. Because the electrostatic force of attraction should be greater we would predict that alumina should have the greater melting point. The aluminum cation is also smaller than the sodium cation and thus more polarizing.
Banner 5
C 3.5 Covalent bonding AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers : Page No. 45
- Answer.
A covalent bond is between a metal and a non-metal. Hence the following will show the covalent bonding.
hydrogen iodide
sulfur dioxide.
- Answer.
Answer 3.
- Answer.
Hydrogen atom attains the electronic structure of helium gas and chlorine atoms attains the electronic structure of Argon gas.
- Answer.
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of two electrons between the two non metals. The electrons are in the highest energy level which are being shared. There is a strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive charge nucleus and the shared pair of electrons between the two atoms which results in covalent bonding.
Baneer 6
C 3.6 Structures of simple molecules AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Page No. 47
- Intermolecular forcesare defined as the set of attractive and repulsive forces that occur between the molecules as a result of the polarity of the molecules.
- The chemical formula of sucrose is C12H22O11.
- 2. a. Answer.
Diamond has a giant molecular structure. Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms. A lot of energy is needed to separate the atoms in diamond. This is because covalent bonds are strong, and diamond contains very many covalent bonds. This makes diamond’s melting point and boiling point very high.
- Answer.
It is the intermolecular forces that determine the melting point of the compound. Nitrogen molecules has weak intermolecular forces between them which can be easily broken down. As a result, it has a lower boiling point.
3.
4.
3.SF6 molecules are simple molecular compounds. They are insulators and do not conduct electricity therefore they are used to stop sparks inside the electrical switches.
- Answer.
hydrogen chloride is a simple molecular structure whereas sodium is a giant ionic structure. There is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charged ions in sodium chloride giving it a high melting point of 801.
Banner 7
C 3.7 Giant covalent structures AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers Page No. 49
- a. Answer.
Graphite and fullerenes are the two allotropes of carbon.
- Answer.
Allotropes are the different forms of the same elements in the same state. .
- Substance with giant covalent structure have:
Very high melting points.
High boiling points
Variable conductivity.
Layered structure of Graphite
4.Graphite is soft due to its layered structure. When a little pressure is applied, the layers of graphite slide past each other which makes the graphite soft. Therefore, it can be used as a lubricant to reduce the friction between two surfaces that are rubbing together.
5.Diamond and graphite are both allotropes of carbon; they are both made entirely of the same element (carbon) but they differ in the way that the atoms bond with each other and arrange themselves in a structure. Each carbon atom has 4 electrons in its outer shell that it can share with other atoms in order to form 4 covalent bonds. Diamond is a giant covalent structure; each valence electron (outer shell electron) of every carbon atom forms a covalent bond, which means that there are no free electrons.
Since electrical conductivity relies on the flow of free electrons, diamond is not a good conductor. Graphite on the other hand, although also only made up of carbon atoms, is the only non-metal that can conduct electricity. This is because only 3 of the available valence electrons form covalent bonds leaving 1 spare electron, which then becomes delocalised. This delocalised electron is no longer associated with one particular carbon atom and it is able to move freely between the carbon layers of graphite and conduct electricity.
Banner 8
C 3.8 Fullerences and graphane AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 51
- a. Answer.
Fullerene is able to fit inside the hydrophobic cavity of HIV proteases, inhibiting the access of substrates to the catalytic site of enzyme. It can be used as radical scavenger and antioxidant.
- Answer.
The name is a reference to Buckminster Fuller, as C60 resembles his trademark geodesic domes. Buckminsterfullerene is the most common naturally occurring fullerene molecule, as it can be found in small quantities in soot.
- Answer.
Fullerene C60, C₆₀.
- Graphene is a sheet of single carbon atoms bonded together in a honeycomb shape. Because it is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, graphene is already used in computers and electronics. But it’s also incredibly strong for its slight weight, potentially making it an ideal material for body armour.
- a.Graphene is a single layer of graphite with delocalized electrons which makes it a good conductor of electricity. .
- Graphenehas unique properties that exceed those of graphite. Although graphite is often used to reinforce steel, it cannot be utilized as a structural material on its own because of its sheer planes. In contrast, grapheneis the strongest material ever found; it is more than 40 times stronger than diamond and more than 300 times stronger than A36 structural steel.
Since graphite has a planar structure, its electronic, acoustic, and thermal properties are highly anisotropic. This means phones pass much more easily along the planes than they do when trying to pass via the planes. However ,graphene has very high electron mobility and, like graphite, is a good electrical conductor, due to the occurrence of a free pi (p) electron for each carbon atom.
However, graphene has much higher electrical conductivity than graphite, due to the occurrence of quasi-particles, which are electrons that function as if they have no mass and can travel long distances without scattering. In order to fully realize this high level of electrical conductivity, doping needs to be carried out to overcome the zero density of states which can be visualized at the Dirac points of graphene.
Banner 9
C 3.9 Bonding in metals AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 53
- Answer.
Metals are crystals. It means that the particles are close together and in a regular arrangement. Metals have loose electrons in the outer shells which form a ‘sea’ of delocalized negative charge around the close-packed positive ions.
- a. Answer.
Ions are electrically charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons. They have the same electronic structures as noble gases.
Metal atoms form positive ions, while non-metal atoms form negative ions. The strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions are called ionic bonds.
- Answer.
Delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond. In organic chemistry, this refers to resonance in conjugated systems and aromatic compounds.
- Answer.
There is a lattice of Mg2+ cations with two valence electrons from each magnesium atom delocalized in an electron sea. That is, the two valence electrons from each magnesium atom do not belong to any particular atom, but are shared among all the Mg2+ centres. It is held together by electrostatic forces of attraction.
C 3.10 Giant metallic structures AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 55
- a. Answer.
Metals are malleable – they can be bent and shaped. This is because they consist of layers of atoms. These layers can slide over one another when the metal is bent, hammered or pressed.
- i. Answer.
Malleable means that metal can be hammered into shapes .
- Answer.
Ductile means that the metal can be drawn out into wires.
- Answer.
Alloy is a mixture of metals with other metals or a non metal. Metal has a regular arrangement in which layers can slide past each other. Alloys are atoms with different sizes which distort the regular arrangement of metals and prevent the layers to slide past each other making alloys stronger than metals.
3.Metals form giant lattice in which there is a regular arrangement of fixed positive ions in the sea of delocalised electrons. The delocalized electrons are free to move and therefore they conduct electricity. Due to the presence of free delocalised electrons, metals are good conductors of thermal energy and electricity.
4.Answer.
Aluminium has a charge of +3 and sodium has a charge of +1. Greater the charge, the greater the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charge ions and delocalized electrons increasing the strength of metallic bonding. Aluminium due to greater charge has a greater strength of metallic bonding therefore more energy is needed to overcome the electrostatic force of attraction in aluminium than sodium therefore aluminium has a higher melting point than sodium.
Banner 11
C 3.11 Nanoparticles AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 57
- Nanoscience is the study of particles ranging from 1 to 100 nm in size.
- a) 50 nm in metre will be 5 X 10-8 m.
- b) 50 nm in um will be 5 X 10-2 m
- Nanoparticles of a material show different properties compared to larger particles of the same material. Forces of attraction between surfaces can appear to be weak on a larger scale, but on a nanoscale they are strong.
One reason for this is the surface area to volume ratio. In nanoparticles this is very large. Atoms on the surface of a material are often more reactive than those in the centre, so a larger surface area means the material is more reactive.
Banner 12
C 3.12 Applications of nanoparticles AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers: Page No. 59
- Nanoparticles are used in self cleaning glass, deodorants, as catalyst and used in medicine for drug delivery.
.
- A. The advantage of using nanoparticles as a catalyst is that they have a large surface area and hence are effective as a catalyst and are required in small quantity.
b.People are concerned about the use of nanoparticles as catalysts as they have a large surface area so a small spark can cause violent explosion. Furthermore, it can enter the environment and cause a risk to the environment. They can also penetrate the skin and enter the blood causing health problems.
- a. Nanoparticles are effective in cosmetic industry as they penetrate and absorb deeper into the skin. Furthermore, they are very effective in blocking the sun radiation and are useful as a sun cream.
- Nanoparticles can fight against cancer as they can find their way and penetrate into the tumour cells due to their leaky blood vessels. Once they enter the tumour cells they can be heated by lasers to kill the tumour cells.
- If we get a nano machine that will reproduce itself then the nanoparticles will accumulate in the environment damaging and eating way the environment. They can also penetrate the skin and enter the bloodstream causing damage to the living being. Eventually, it will lead to destruction of the whole Earth halting the further research.
Banner 12
Summary Questions AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers :Page No. 60
- a. Liquid to solid change is freezing
- Gas to liquid change is condensation
- Solid to liquid change is melting
- Liquid to gas change is evaporation
- Solid to gas change is sublimation
- A. Group 1
- Group 2
- Group 7.
- Group 6
- Group 4
- a.
| Giant covalent | Giant ionic | Simple molecules |
| silicon dioxide | magnesium oxide | ammonia |
| graphite | lithium chloride | hydrogen bromide |
- Answer.
ammonia, hydrogen bromide are liquid at 25 degrees.
- Answer.
Graphite behaves in a surprising way as it is a conductor despite being a non metal and a covalent structure.
- a. Hydrogen Iodide, chloride (VII) oxide, phosphorus (V) fluoride will be covalently bonded.
- The bonding between two nonmetals is covalent bonding. As we have two non metals above so they are covalently bonded.
- The remaining substance in the list have the bonding between a metal and a non metal which will be ionic bonding.
- (i) The chemical formula of Hydrogen Iodide will be HI
(ii) The chemical formula of Calcium bromide will be
5.1
| Chloride Cl- | Oxide O2- | Sulphate SO42- | Phosphate (IV) PO43- | |
| Potassium K+ | KCl | K2O | K2SO4 | K3PO4 |
| Magnesium Mg2+ | MgCl2 | MgO | MgSO4 | Mg3(PO4)2 |
| Iron (IIi) Fe3+ | FeCl3 | Fe2O3 | Fe2(SO4)3 | FePO4 |
6.Covalent Bonding in Hydrogen and Carbon Dioxide
7.A. Manufactures of the socks use silver nanoparticles to kill bacteria.
1.People are worried to wear the socks made up of silver nanoparticles as it can get through the skin and enter the blood causing health problems
- Silver nanoparticles can leach into the ground while washing or from the manufacturing waste that comes while preparing these socks.
- 3.5 × 10¯⁸m we will times by 10^9 to get the answer in nm which will be 35 nm.
- To work out the formulae from the ball and stick structure, we can count the number of each ion and work out the simple ratio. In the figure,the simple ratio of both the ions is 1:1 therefore the formula of the compound is NaCl.
Banner 12
Practice Questions AQA GCSE Chemistry C3 Structure and Bonding Kerboodle Answers : Page No. 61
01.1. Sun Cream is one another use of nanoparticles.
01.2. Nanoparticles have a very high surface area to volume ratio hence they are required in very small quantities.
1.3 People are concerned about the use of nanoparticles in deodorants as it can penetrate the skin and accumulate in the blood causing a health problem. It can also cause damage to the environment.
1.4 Coarse particles of a carbon is 10000 times bigger than the nanoparticle. We will arrive at this answer by dividing the size of both the particles.
2.1 A or E is liquid at room temperature as they have low melting point.
02.2 D is giant covalent as it has the highest melting and boiling point.
02.3. C has giant ionic structure as it conducts electricity when molten and does not conduct electricity in solid.
02.4. Metal has a fixed positive ions located in the sea of delocalised electrons.
02.5. H2 will have a higher boiling point than G2 due to stronger intermolecular forces.
- The electronic structures of an atom of magnesium and an atom of fluorine are shown in figure 1.
02.5. Answer.
03.1. Answer.
Magnesium ions loses two electrons to form Mg2+ ions and chlorine gains one electron to form -1 ions. So to complete outer shell of magnesium we need magnesium to lose two electrons and give to two chlorine atoms to form magnesium chloride.
3.2 In molten state, the ions of Magnesium fluoride will be free to move therefore can conduct electricity. In the solid state, magnesium fluoride ions are held in giant lattice therefore are not able to move and conduct electricity.
03.3. The ball and stick model is not a true representation of the structure of an ionic compound because in a ball and stick model we assure the atoms to be perfect spheres with no gaps between them. In an actual structure, the ions do not touch each other and are no perfect spheres.
Banner 12
DISCLAIMER
Disclaimer: I have tried by level best to provide the answers and video explanations to the best of my knowledge. All the answers and notes are written by me and if there is any similarity in the content then it is purely coincidental. But this is not an alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
AQA GCSE Science Kerboodle textbook
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Join Our Free Facebook Group : Get A* in GCSE and A LEVEL Science and Maths by Mahima Laroyia: https://www.facebook.com/groups/expertguidance.co.uk/
For Free Tips, advice and Maths and Science Help
This page contains the detailed and easy notes for AQA GCSE Chemistry Bonding, Structure and Properties of Matter for revision and understanding Bonding, Structure and Properties of Matter.
Banner 1
AQA GCSE Paper 1: Complete Revision Summary
Bonding, Structure and Properties of Matter
4.2 Bonding, Structure and Properties of Matter
- Ionic Bonding
- Covalent Bonding
- Metallic Bonding
- State of Matter
- Ionic compounds
- Covalent Compounds
- Diamond and Graphite
- Nanoparticles
- Graphene and Fullerene
Banner 2
BONDING
Atoms bond to gain full outer shell or noble gas electronic configuration
Ionic Bonding
- transfer of electron between metals and non metals
- between metal and non metals
Covalent Bonding
- sharing of electron between non metals
- between non metals
Metallic Bonding
- Electrostatic force of attraction between fixed positive ions and delocalised electrons.
- between Metals
Carbon dioxide (CO2) – Covalent
Ammonia (NH3) – Covalent
Nitrogen (N2) – Covalent
Water (H2O) – Covalent
Sodium chloride -Ionic Bonding
Calcium fluoride— Ionic Bonding
Banner 3
IONIC BONDING: Metals and Non Metals
- It is between a metal and a non metal
- Metal loses an electron and become positively charged.
- Non- Metal gains an electron and becomes negatively charged.
- There is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charged ions resulting in ionic bonding.
Dot and Cross Diagram
- Write the symbols
- Write electronic configuration
- show outer electrons
- show transfer
- show charges
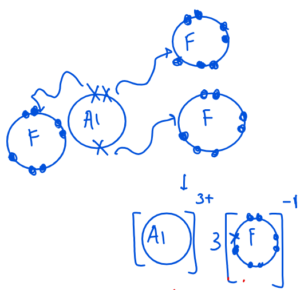
Example – Aluminium Fluoride
Al = 2,8,3
F = 2,7
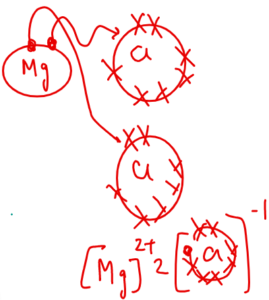
Example – Magnesium chloride
Mg = 2,8,2
Cl = 2,8,7
PROPERTIES OF IONIC COMPOUNDS
Ionic Compound Properties
- Brittle solids with definite crystal shapes
In Ionic compounds, there is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between the opposite charged ions. This results in the formation of giant ionic lattice.
- Good insulators in solid form, but become good conductors in liquid or dissolved form.
In the solid form, the ions are not free to move as they are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction. In molten or when they are dissolved in water the ions are free to move and conduct electricity.
- High melting and boiling point compared to molecular compounds
In Ionic compounds, there is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between the opposite charged ions. This results in the formation of giant ionic lattice. Large amount of energy is required to overcome the strong electrostatic force of attraction. Therefore, ionic compounds have high melting and boiling point.
Greater the charge of an ionic lattice, stronger is the electrostatic force of attraction. Greater the melting and bp.
For éx – Aluminium chloride > Magnesium chloride > sodium chloride
FORMULAE OF IONIC COMPOUNDS
- Write the Symbols
- Write the charges
- (Upto group the charge is same as the group number. After group 4 it is group number -8)
- Criss Cross
- a) Sodium Oxide = Na2O
- b) Magnesium Nitride = Mg3N2
- c) Calcium Oxide = CaO
- d) Sodium Sulphide = N2S
- e) Sodium Chloride = NaCl
- f) Magnesium chloride = MgCl2
- g) Aluminium Chloride = ACl3

FORMULAE OF COMPLEX IONS
| a) Magnesium Hydroxide | Al2(SO4)3 |
| b) Aluminium Sulphate | Al2(SO4)3 |
| c) Calcium Phosphate | Ca3(PO4)2 |
| d) Magnesium nitrate | Mg(NO3)2 |
| e) Calcium Carbonate | CaCO3 |
| f) Sodium Phosphate | Na3PO4 |
Positive
|
Negative
|
Ammonium = NH4+ Banner 4
| Carbonate = CO32- |
| Sulphate = SO42- | |
| Nitrate = NO3– | |
| Phosphate = PO43- | |
| Hydroxide = OH– |
COVALENT BONDING
- It is between two non metals
- It involves the sharing of electrons between two non metals.
- More than one electron pair can also be shared resulting in the formation of single double and triple bonds.
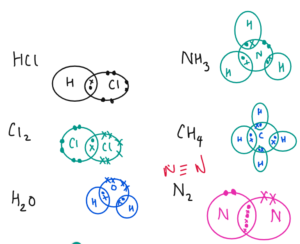
Properties of Covalent Compounds

Simple Molecule
- Eg – O2, CH4
- They have weak intermolecular forces in them so have a lower melting and a boiling points
- The intermolecular forces increases with increase in size as the surface area between the molecules increases.
- Therefore, polymers which have covalent bonding between them have high melting and boiling point due to increase in chain length.
Giant Covalent
- Diamond
- Graphite
- Silicon Dioxide
GIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES
Substances which have huge network of atoms joined together by covalent bonds form giant covalent structures.


| DIAMOND | GRAPHITE |
| It is hard. | It is soft and greasy. |
| It is an insulator | It is a conductor |
| It has a high density. | It has a lower density than diamond. |
| Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms giving it a strong rigid structure | Carbon atoms are bonded in the form of layer in the form of hexagons. No covalent bonding between the layers so they can slide past. Each carbon atom is bonded with three other carbon leaving the fourth electron has delocalized |
| No delocalised electrons present | It has delocalised electrons |
| Used in cutting or jewellery | It is used in pencil leads. |
PROPERTIES OF GRAPHITE
Q1 Why graphite is soft and slippery?
Banner 5
In graphite, Carbon atoms are bonded in the form of layers in the form of hexagons. No covalent bonding between the layers so they can slide past each other. The layers have only weak intermolecular forces between them. By applying a little pressure then layers can easily slide past each other making Graphite soft and slippery.

Q2 Why graphite conduct electricity ?
In graphite, Carbon atoms are bonded in the form of layer in the form of hexagons. No covalent bonding between the layers so they can slide past. Each carbon atom is bonded with three other carbon leaving the fourth electron has delocalized. These delocalized electrons are mobiles electrons which can move and conduct electricity.
FULLERENE AND GRAPHENE
Fullerene: Hollow shaped molecule having hexagonal rings like a bucky ball.
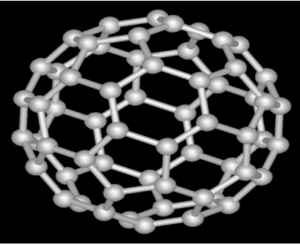
- Also known as bucky ball or buckminsterfullerene.
- Carbon can be in the form of pentagon or hexagon rings
- Used as catalyst, drug delivery and treating cancer.
- Graphene: Layer of interlocking hexagonal rings like single sheet of graphite.
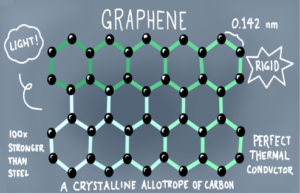
- It is a better conductor than graphite, light and have low density.
- Used in making computer chips and flexible electronic displays.
Baneer 6
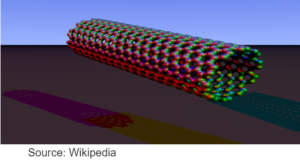
CARBON NANOTUBES
- Cylinderical fullerene with the length greater than the diameter.
- High tensile strength – Used in making reinforced composite materials
- High electronic conductivity – used in electronic industry
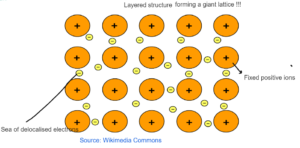
METALLIC BONDING
- It is between two metals.
- There are fixed positive ions present in the sea of delocalised electrons.
- There is strong electrostatic force of attraction between fixed positive ions and delocalized electrons resulting in metallic bonding.
Banner 8
Properties of Metals
Metals are malleable
- Malleable means that the metals can be hammered into any shape.
- Metals have layered structure and layers can slide past each other by hammering giving metals different shapes.
Metals are ductile
- Ductile means that the metals can be drawn into thin wires.
- Metals have layered structure and layers can slide past each other by hammering giving metals a wire shape.
Metallic Bonding
- Atoms in a metal are arranged in a regular manner and vibrate about fixed positions.
- The outermost electrons move freely, forming a ‘sea of electrons’ enveloping the positive metal ions.
Metals are good conductors of electricity
- Metals have delocalised electrons.
- They are mobile and conduct electricity.
- These mobile electrons or delocalised electrons conduct heat and electricity.
Metals have high melting and boiling points
- There is strong electrostatic force of attraction between fixed positive ions and delocalized electrons.
- Large amount of energy is required to overcome strong electrostatic force of attraction.
Banner 9
ALLOYS
- Alloys are the mixture of metals with another metal or a non metal which make the metal stronger.
- In metals the particles are arrranged in layers. There is a regular arrangement of fixed positive ions which can slide past each by applying pressure.
- In alloys there is a mixture of metals with another metal or a non metals. Another metal being different in shape and size distort the regular arrangement of the metal lattice.
- As a result the layers of the metal can no longer slide past each other making it strong
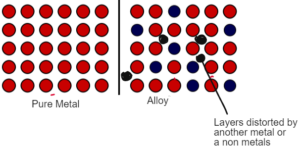
Example: Steel is the alloy of iron which is more strong and resistant to corrossion.
NANOPARTICLES
Nanoparticles are the particles that deals with the paricles of size 1 to 100 nm.
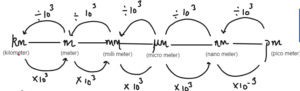
KIL- Killing
MET – Metal
MIL -Milo
MIC – Mickey
NAN – Nano
PIC – Pictures
Convert 10 nm to
- Metre = 10/109m = 10-8m
- Micrometer = 10/106m = 10-5m
SURFACE AREA TO VOLUME RATIO
As the size decreases the surface area to volume ratio Increases.
Therefore Nano particles being very small in size have large surface area to volume ratio making them very useful in Science and Medicine.
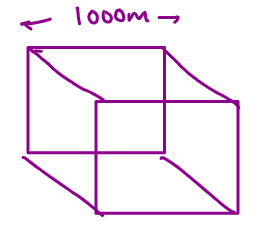
Surface area = 6 x side x side m2
= 6 x 1000 x 1000
= 6 106 m2
Volume = side x side x side
= 109m3
SA: Volume = 6 x 106/109 = 6 x 103 m
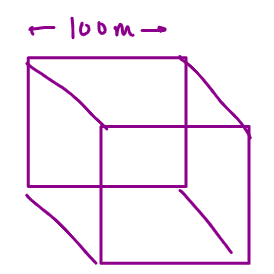
Surface area = 6 x side x side m2
= 6 x 1000 x 1000
= 6 104 m2
Volume = side x side x side
= 106m3
SA: Volume = 6 x 102 m
Banner 10
APPLICATIONS OF NANOPARTICLES
MEDICINES
- To kill cancer and tuomour cells
- For drug delievery
CATALYST
- They have large surface area to volume ratio.
- Used in small quantities so highly effective
COSMETICS
- Used in Sunscreen to block sunlight
HOUSEHOLD
- Self cleaning window panes
- Nano particles breaks dirty in the presence of sunshine which is washed away by water while raining.
RISKS OF NANOPARTICLES
- Due to small size can cause difficulty in breathing
- They can accumulate in the envrionment and cause air pollution
- Due to their large surface area a small spark can result in violent explosion making them risky to use.
- They are toxic and cause breathing and respiratory problems.
- Due to their small size they can also cause water pollution and risk the aquation life.
STATES OF MATTER
| SOLIDS | LIQUIDS | GASES |
| Particles are close to each other. | Particles are slightly closer to each other. | Particles are far apart. |
| Have fixed shape | Do not have fixed shape | Do not have fixed shape |
| Strong forces between the particles | Weak forces between the particles | Very weak forces between the particles. |
| Have definite volume | Have fixed volume | Do not have fixed volume |
| cannot be compressed | Can be compressed | Highly compressible |
| Cannot flow | Can flow | Can flow |
Banner 11
KEY TERMS !!!!
Ions – charged atoms with unequal number of protons and electrons
Ionic Bonding — bond formed between a metal and a non metal which involves complete transfer of electrons from metal to a non metal
Dot and Cross — diagram that show transfer of electron in an ionic bond or sharing of electrons in a covalent bond.
Covalent Bonding— bonding between two non metals which involves sharing of electrons.
Metallic Bonding— bonding in metals which involves strong electrostatic forces of attraction between fixed positive ions and delocalised electrons.
Intermolecular Forces — The forces between the molecules which determines the melting or a boiling point.
Giant Covalent Molecules — Covalently bonded molecules which forms large giant structure
Polymers – Molecules which are made up of many repeating units
Delocalised electrons — Mobile electrons that are free to move as they are not associated with a bond or an atom.
Fullerene— Allotrope of carbon which forms a cage like structure like bucky ball.
Graphene— Allotrope of carbon which is equivalent to single layer of graphite
Alloys— Mixture of metals with another metal or a non metal.
Nanoparticles- particles which are of the size of 1 nm to 100 nm_
Nanoscience—lt is the branch of science that deals with nanoparticles
State Of Matter-Different forms that a matter can take They are solids, liquids and gas
Solids — States of matter with fixed shape and volume.
Liquids— States of matter without fixed shape but fixed volume.
Gases— States of matter with fixed shape and volume.
TEST YOURSELF
Q1 Name the type of bonding in the following compounds :
- a) Sodium Chloride – Ionic
- b) Magnesium – Metallic
- c) Nitrogen – Covalent
- d) Carbon Dioxide – Covalent
- e) Water – Covalent
- f) Ammonia – Covalent
Q2 Draw dot and cross diagram to represent bonding in the following
- a) Sodium chloride
- b) Water
- c) Magnesium
Q3 Differentiate Between Diamond and Graphite
| DIAMOND | GRAPHITE |
| It is hard. | It is soft and greasy. |
| It is an insulator | It is a conductor |
| It has a high density. | It has a lower density than diamond. |
| Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms giving it a strong rigid structure | Carbon atoms are bonded in the form of layer in the form of hexagons. No covalent bonding between the layers so they can slide past. Each carbon atom is bonded with three other carbon leaving the fourth electron has delocalized |
| No delocalised electrons present | It has delocalised electrons |
| Used in cutting or jewellery | It is used in pencil leads. |
Q4 Why Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in solids ?
In solids, the ions are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction in the giant ionic lattice. In molten state the ions are free to move therefore conduct electricity
Q5 Why Alloys are stronger than metals
Alloys are the mixture of metals which distors the regular arrangement of metal as a result of which layers are not able to slide past each other making alloys stronger than metals.
Q6 Why alumunium has a stronger melting point than sodium
Aluminium has a greater charge. Due to greater charge of aluminium there is a stronger electrostatic forces of attraction between fixed positive ions and delocalised elecctrons. As a result aluminium has a greater melting point than sodium.
Q7 What are nanoparticles? Write the properties and applications of nanoparticles
Nanoparticles are the particles between the size of 1 to 100 nm_ Due to smaller size they have large surface area to volume ratio making them highly useful in medicine, catalysts, cosmetics and electronic industry.
Banner 12
Disclaimer:
I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
C3- Structure And Bonding
- Bonding & Structuce 1 MS
- Bonding & Structuce 1 QP
- Bonding & Structuce 2 MS
- Bonding & Structuce 2 QP
- Bonding & Structuce 3 MS
- Bonding & Structuce 3 QP
- Bulk & Surface Properties of Matter 1 MS
- Bulk & Surface Properties of Matter 1 QP
- Bulk & Surface Properties of Matter 2 MS
- Bulk & Surface Properties of Matter 2 QP
- Bulk & Surface Properties of Matter 3 MS
- Bulk & Surface Properties of Matter 3 QP
- Ionic, Covalent & Metallic Bonds 1 MS
- Ionic, Covalent & Metallic Bonds 1 QP
- Ionic, Covalent & Metallic Bonds 2 MS
- Ionic, Covalent & Metallic Bonds 2 QP
- Ionic, Covalent & Metallic Bonds 3 MS
- Ionic, Covalent & Metallic Bonds 3 QP
- Structure & Bonding Carbon 1 MS
- Structure & Bonding Carbon 1 QP
- Structure & Bonding Carbon 2 MS
- Structure & Bonding Carbon 2 QP
- Structure & Bonding Carbon 3 MS
- Structure & Bonding Carbon 3 QP
