This page contains the detailed and easy notes for GCSE OCR Biology Supplying the Cell for revision and understanding Supplying the Cell .
GCSE OCR BIOLOGY SUPPLYING THE CELL Complete Revision Summary
SUPPLYING THE CELL
supplying the Cell
- Diffusion
Mixing particles
Cell models
Osmosis
Practical – Effect of concentration on the mass of plant tissue
Scientific calculations – Simple compound measures of rate
Analysing results
Active transport
MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCE IN AND OUT OF THE CELLS
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of particles from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration.
- Particles move against the concentration gradient.
- It requires energy.
- Cells involved in active transport should have lots of mitochondria
PASSIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of particles from the region of high concentration to a low concentration.
- Particles move along the concentration gradient.
- It does not require energy
- Having numerous mitochondria is not a requirement
DIFFUSTON
OSMOSIS
Banner 8
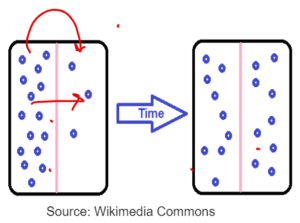
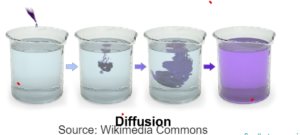
DIFFUSION
- It the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- It is passive process
- It happens along the concentration gradient
- No use of energy.
Banner 9
supplying the Cell
[download_after_email id=”9755″]
FACTORS AFFECTING DIFFUSION
SURFACE AREA
- Greater the surface area greater is the rate of diffusion as particle will get more room for movement.
- All the exchange surfaces have greater surface area like root cells has root hairs and intestine cells has villi.
CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
- Greater the difference in concentration in the two region greater is the rate of diffusion.
- All the exchange surfaces maintain steepest concentration gradient
- Like root cells are closed to xylem and Villi has rich blood supply.
DIFFUSION DISTANCE
- Smaller the diffusion distance greater is the rate of diffusion as the particles have to travel a smaller distance.
- All the exchange surfaces maintain a smaller diffusion distance by being one cell thick.
TEMPERATURE
- Greater the temperature greater is the rate of diffusion as particles will get more kinetic energy for movement
- Rate of Diffusion = Surface area x Concentration gradient/Diffusion Distance


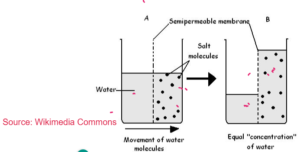
OSMOSIS – Special Case of Diffusion
Osmosis is the net movement of water particles from the region of high concentration of water particles to low concentration of water particles across a semi permeable membrane.
Movement of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a semi permeable membrane.
Special Case:
- It is the diffusion of only water molecules
- It required a semi permeable or partially membrane
- Membrane that allows only specific molecules to pass through like water.
OSMOSIS IN PLANTS
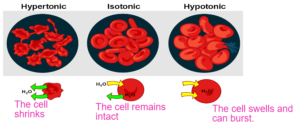
- Hypertonic – The outer solution has a less concentration of water than inside the cell.
- Isotonic – The outer solution has same concentration of water than inside the cell.
- Hypotonic – The outer solution has a greater concentration of water than inside the cell.
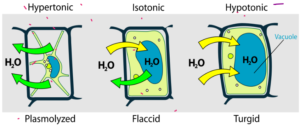
Plasmolyzed – The water moves out of the cells due to osmosis due to higher concentration of water inside the cell than outside. The cell membrane recetes from the cell wall
Flaccid – There will no net water movement so no pressure on the cell. It will be flaccid
Turgid – The water moves into the cell due to osmosis due to higher concentration of water outside the cell. The water will create pressure called turgor pressure on the cell wall making cell rigid and turgid.
Osmosis in Animals
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of substances from the region of low concentration to a region of higher concentration with the use of energy.
- Dependent on respiration as it requires energy. So the cells involved in active transport has lots of mitochondria.
- In Plants water and minerals are absorbed by active transport to absorb maximum of water and minerals.
- In animals, the digested food gets absorbed into the blood by active transport to ensure maximum absorption
- Salt glands are present in some marine organisms which removes the salt by active transport.
- Disclaimer:I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.References:BBC BitesizeWikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
Cell Structure And Transport
- Cell Structure 1 MS
- Cell Structure 1 QP
- Cell Structure 2 MS
- Cell Structure 2 QP
- Cell Structure 3 MS
- Cell Structure 3 QP
- Transport in Cells 1 MS
- Transport in Cells 1 QP
- Transport in Cells 2 MS
- Transport in Cells 2 QP
- Transport in Cells 3 MS
- Transport in Cells 3 QP
