Notes
Question by Topic
Notes
This page contains the detailed and easy notes for GCSE OCR Biology Mitosis and Cell Specialisation for revision and understanding Mitosis and Cell Specialisation .
GCSE OCR BIOLOGY MITOSIS AND CELL SPECIALISATION Complete Revision Summary
MITOSIS AND CELL SPECIALISATION
CELL CYCLE
Interphase –
- It is the longest phase of the cell cycle
- The cell grows in size and prepares all the proteins and enzymes needed for division.
- Replication of DNA where DNA duplicates its content.
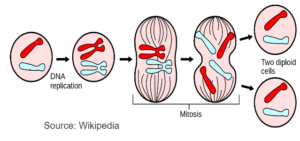
Mitosis
- It is the division of the nucleus in which parent cell splits into two daughter nuclei containing same number of chromsomes as the parent cell.
Cytokinesis
- It is the division of the cytoplasm which .takes place after the division of the nucleus.
Mitosis
- It is the type of cell division in which a parent nucleus divides to form two daughter nuclei with exactly the same number of chromomes as that of the parent nucleus.
- The daughter cells produced are genetically identical to the parent and are clones.
- This division is important for growth, regneration and repair.
- Mitosis is also important in asexual reproduction.
MITOSIS AND CELL SPECIALISATION
[download_after_email id=”9763″]
CELL DIFFERENTIATION
- It is the process by which cell becomes specialised to perform a specific function.
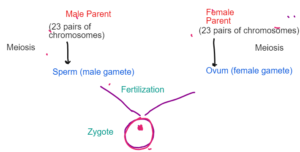
- Male Parent (23 pairs of chromosomes) Meiosis
Sperm (male gamete)
- Female Parent (23 pairs of chromosomes) Meiosis
Ovum (Female gamete)
Animal Differentiation
- In animals majority of the cells are differentiated at an early stage and different cells have specific functions like nerve cell, muscle cells.
- Adult stem cells replaced the old and worn out cells in human but adult stem cells have limited specialization power
- Majority of the differentiation is permanent
Plant Differentiation
- Plants are the storehouse of stem cells
- Root meristems and shoot meristems are the parts of actively growing part of the cells which contains stem cells.
- The plants can be cloned easily as it has many undifferentiate cells and differentiation is not permanent.
STEM CELLS
- Undifferentiate mass of cells that can differentiate into any cell type are known as stem cells.
- Sources of Stem Cells : Embryo, left over remains of the embryo and the umbilical chord are the sources of embryonic stem cells.
- Bone marrow is the source of adult stem cells.
- Can solve the rejection problem if the transplanted organ is made from the person’s own stem cells.
- Can be possible cure of neuro-degenerative diseases
- Can be the potential cure of diabetes.
- Therapeutic cloning.
- Organ damage problem
ISSUES AGAINST STEM CELLS
- It can lead to cancer as the stem cells are rapidly dividing.
- The stem cells can be contaminated and can cause unwanted diseases to the patient.
- Research is still slow and expensive
- Research happens on aborted embryos which is considered as a potential source of life and many religions have ethical concerns against it.
- The knowledge of the genes switched on and off using differentiation is still incomplete.
Banner 11
KEY TERMS!!!
- Cells – Basic structural and functional unit of the living organism.
- Mitochondria —The cell organelle which is the site of aerobic respiratiom
- Nucleus — The cell organelle which controls the activities of the cell
- Cytoplasm –The jelly like fluid which fills the cell and contains enzymes for chemical reactions.
- Ribosomes — The cell organelle which is the site for protein synthesis
- Prokaryotic – Cell The primitive cell without nucleus or membrane bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cell —The advanced cell type with nucleus and membrane bound organelle
- Cell Wall— The outer layer of the plant cell which provide shape and support
- Cell Membrane – The layer that controls what goes in and out of the cell.
- Vacuole – Organelle present in plant cell which has cell sap and make the cell turgid.
- Microscopes – Devices that is used to see the object which are not visible by a naked
- Resolution – Ability to distinguish between closely placed objects.
- Magnification — Ability to enlarge an object
- Xylem – Transport tissue in plants that transports water and minerals.
- Phloem – Transport tissue in plants that transports food
- Diffusion – Movement of substance from a higher concentration to a lower concentration.
- Osmosis — Movement of water from high concentration of water to low concentration of water across semi permeable membrane
- Plasmolysis— Shrinking of plant cell when placed in hypertonic solution.
- Turgid — Fully swollen cell which has gained water by osmosis.
- Flaccid— soft cell due to no net movement of water.
- Mitosis — Cell division that produces identical daughter cells.
- Differentiation – Cell specialization
- Stem Cells – Undifferentiated mass of cells that can specialize to any cell type
- Therapeutic cloning — Using adult stem cells to produce embryonic stem cells and differentiating them to produce a required cell type Banner 12
Disclaimer:I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.References:BBC BitesizeWikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Question by Topic
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
Cell Structure And Transport
- Cell Structure 1 MS
- Cell Structure 1 QP
- Cell Structure 2 MS
- Cell Structure 2 QP
- Cell Structure 3 MS
- Cell Structure 3 QP
- Transport in Cells 1 MS
- Transport in Cells 1 QP
- Transport in Cells 2 MS
- Transport in Cells 2 QP
- Transport in Cells 3 MS
- Transport in Cells 3 QP
