This page contains the detailed and easy notes for GCSE Biology OCR Maintaining internal environment for revision and understanding Maintaining internal environment .
GCSE OCR GATEWAY Biology Complete Revision Summary
Maintaining internal environments
Maintaining internal environments
- Homeostasis
Control of body temperature
Control of blood glucose concentration by pancreas and insulin
Role of glucagon in control of blood sugar levels – Higher
Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes
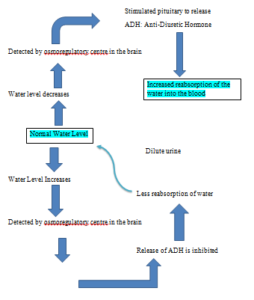
Maintaining water balance in the body
The effect of ADH on tubule permeability and water balance – Higher
Responses of the body to extreme conditions – Higher
Scientific calculations – Translate tables and bar charts
WASTE PRODUCTS
The products produced during metabolic reactions like respiration, digestion etc.
Carbon Dioxide
- Produced during respiration.
- Is excreted out through the lungs by the process of expiration
- Carbon dioxide is harmful as it can alter the pH of the blood affecting enzyme activity.
Water
- Produced during respiration and digestion process.
- Is excreted through skin in the forms of sweating or some by breathing and by kidney in the form of urine.
- Water can also disturb the osmotic balance and salt level of the body.
Urea
- Produced by the liver by metabolising excress proteins as it is toxic and cannot be stored.
- It is excreted by Kidney in the form of Urine.

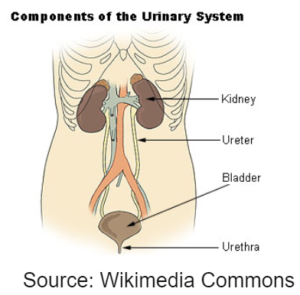
HUMAN EXCRETORY SYSTEM
ULTRAFILTRATION
- Kidneys filters the blood at a very high pressure.
- All the water, glucose, and useful components gets into the kidney filtrate. The blood cells and blood proteins due to their bigger Size are not filtered.
SELECTIVE REABSORPTION
- Since the kidney contains useful substance in the filtrate it reabsorbs back them into the blood.
- The water also gets reabsorbed depending on the needs of the body.
OSMOREGULATION
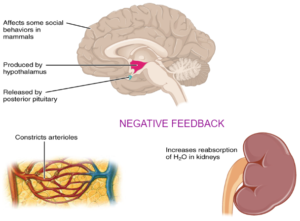
Maintaining internal environment
[download_after_email id=”9139″]
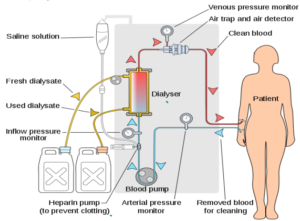
DIALYSIS
- Artificial Kidney blood flows into the dialysis machine which contains dialysis fluid.
- Dialysis fluid contains the same concentration of essential minerals ions,as that of blood but no urea.
- As blood flows into the dialysis fluid, urea is diffused out along the concentration gradient and excess salt is also removed maintaing the normal salt and mineral ions level.
- The clean blood is then pumped back.
- Lifestyle changes, regular visits, change in diet and regular expenditure are some of the disadvantages.
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
- Replacing diseased kidney with the healthy one.
- The donor should be a close relative to prevent rejection.
- The person has to be on Immuno – suprresant drugs so that the body immune system does not reject it.
- Does not last long and person is prone to other infectious diseases due to immuno suppresant drugs.
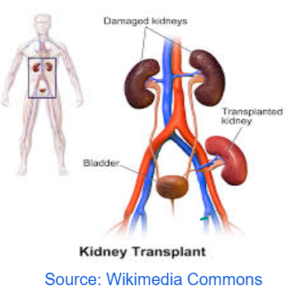
DIALYSIS KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
DIALYSIS
Advantages
- No surgery
- No infection
- No immuno supressant drugs
- Easyily available
Disadvantages
- Lifestyle changes
- Regular visits and long procedure
- Restricted Diet
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
Advantages
- No regular visit
- No lifestyle changes
- No diet restriction
Disadvantages
- Does not last forever
- Chances of rejection
- Immuno supressant drugs to be taken
- Person is more prone to infections.
- Finding a suitable donor is a problem
KEY TERMS
- Homeostasis – Homeostasis is the process of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment adequate to sustain life.
- Receptors – Receptor is any cell or organ of an animal capable of detecting a stimulus is a change in the external or internal environment and which subsequently brings about a response in the behavior of the animal.
- Effectors – Effector is any muscle, gland or an organ capable of responding to a stimulus, particularly a nervous impulse.
- Stimulus – A biological stimulus is any external change in the environment that can be detected by an organism.
- Neurones – These are structural and functional Units of Neural System. Each Neuron consists of the cell body (cyton) and nerve fibre (axon)
- Central Nervous System – Consists of Brain and Spinal cord
- Sensory Neurones – These connect sense organs with the Central Nervous System.
- Motor Neurones – These connect the CNS to the Effectors
- Relay Neurones – These are present in the CNS and occur between the sensory and motor neurons for distant transmission of Impulses.
- Reflex Arc – The path followed by the stimulus (impulse) from beginning to end is the reflected arc.
- Brain – It is the Central information processing organ of our body, and acts as the command and Control System.
- Cerebral Cortex – Grey matter forms 2-4mm thick outer cortex of cerebrum called cerebral cortex
- Cerebellum – literally means little cerebrum. Cerebellum has grey matter on outer side and made of three layers of cells and fibres. 2nd largest part of the brain.
- Medulla – directly controls some ANS responses, such as heart rate, respiration, dilation of blood vessels, digestion, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting. It is a part of the brain stem, located just below the prominence and just above the spinal cord.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – It helps to take the Images of different parts of the brain and relating it with loss of functions of the individual
- Eye – Hollow spherical organ, about 2.5cm in diameter and about 6-8gm in weight. It is lodged in orbit of skull.
- Blind Spot – The spot on the retina which has no receptor.
- Accomodation- Ability of eye to adjust the focal length of the lens to make clear image of the objects lying at varying distances. It is a reflex mechanism and is done with the help of ciliary muscles and suspensory ligament.
- Ciliary Muscles – help in accommodation and ciliary process that secrets aqueous humour.
- Iris – Visible coloured portion of the eye, contains two types of muscles- circular and radial.
- Pupil – In front of the lens the aperture surrounded by the iris is called the pupil.
- Myopia – Also known as near sightness or short sightness. Near object is Clear. Far object is not clear. Eyeball become longer.
- Hypermetropia – long sightness. Far object is clear, near object is not Clear. Eyeball becomes short.
- Endocrine System – the endocrine system consists of glands widely separated from each other with no direct anatomical links. Also called ductless glands
- Hormones – Hormones are the chemical substances produced in the body that controls and regulates the activity of some cells or organs.
- Adrenaline – It is a hormone released by the adrenal glands and its main action, along with norepinephrine, is to prepare the body to “fight or flee”.
- Insulin – Secreted by Pancreas, is a small protein whose molecule consists of two polypeptide chains
- Pituitary Gland – Smallest endocrine gland of the body. It is Pea shaped, ovoid, reddish brown gland situated at base of the brain. It controls almost all endocrine glands. Hence it is also called master gland.
- FSH – Follicle Stimulating Hormone. In males stimulates spermatogenesis. In females growth of ovarian follicles upto ovulation.
- Oestrogen – stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs, development of growing ovarian follicles, mammary gland development.
- Progesterone – it acts on the mammary glands and stimulates the formation of alveoli, milk secretion and supports pregnancy.
- Glucagon – Glucagon is produced to maintain blood glucose levels during fasting and to increase very low glucose levels.
- Glycogen – Glycogen is the major carbohydrate storage form in animals, and corresponds to starch in plants.
- Diabetes – Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high.
- Mensturation – Menstruation or your period is the shedding of the uterine lining once a month.
- Ovulation – the release of an egg from an ovary — occurs about midway through the menstrual cycle.
- Phototropism – It is the ability of a plant, or other photosynthesizing organism, to grow directionally in response to a light source.
- Gravitotropism – Gravitropism is a plant’s natural growth response to the effects of gravity.
- Auxins – Auxin is involved in cell growth and cell expansion
- Gibberlins – Gibberellins promote stem elongation between nodes on the stem.
- Dialysis – The process of removing waste products and excess fluid from the body.
- Selective Reabsorption – Selective reabsorption is the process by which some molecules (eg – Ions, glucose and amino acids), after having been filtered by capillaries together with nitrogen waste products (eg Urea) and water in the glomerulus, are reabsorbed by filtration as they pass through the nephron.
Disclaimer:
I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definitions before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well
Human Nervous System
- Human Nervous System 1 MS
- Human Nervous System 1 QP
- Human Nervous System 2 MS
- Human Nervous System 2 QP
- Human Nervous System 3 MS
- Human Nervous System 3 QP
