This page contains the detailed and easy notes for GCSE OCR Biology Cell Structures for revision and understanding Cell Structures .
Banner 1
GCSE OCR BIOLOGY CELL STRUCTURES Complete Revision Summary
CELL STRUCTURES
CELL STRUCTURES
Cell measurement
Electron microscopes
Animal cells
Plant cells
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Investigating cells with a light microscope
Measuring cell size
Comparing sizes
Eukaryotic Cells – Plants and Animals
Prokaryotic Cells – Bacteria
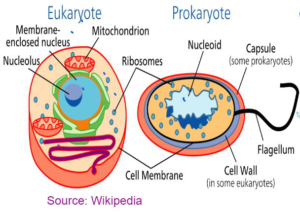
| EUKARYOTIC | PROKARYOTIC |
| Nucleus is present. | Nucleus is absent. |
| All membrane bound organelles are present | Membrane bound organelles are absent. |
| DNA is enclosed in the nucleus | DNA lies naked in the cytoplasm. |
| They are multicellular | They are mostly unicellular |
| DNA is linear | DNA Is circular |
| Ribosomes are big | Ribosomes are small |
| They are big cells | They are small cells. |
| Example: Plants and Animals | Example: Bacterial Cell |
Banner 2
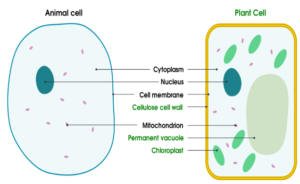
Animal Cells
NUCLEUS
- It is the brain of the cell
- It controls the activities of the cells
- It contains DNA which holds our genetic information.
RIBOSOMES
- It is the site for protein synthesis.
- They are involved in making of proteins and enzymes required by the cell
CYTOPLASM
- Jelly like fluid which fills the cell.
- It is the site where all the chemical reactions of the cells take place as it contains all the major enzymes
CELL MEMBRANE
- It the membrane that surrounds the cells
- It controls what goes in and out of the cell.
MITOCHONDRIA
- It is the powerhouse of the cell
- It produced energy for the cell as it is the site for aerobic respiration
Banner 3
Plant Cell
PERMANENT VACUOLE
- It is filled with cell sap.
- It gives rigidity to the cells and makes the cell turgid
CELL WALL
- Made up of cellulose.
- It is the layer outside of the cell membrane
- It supports the plant and maintain its shape.
CHLOROPLAST
- It is the site for photosynthesis
- It contains a green pigment, chlorophyll which absorbs light and prepared food.
Plant versus Animal Cell
| ORGANELLE | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Nucleus | Present | Present |
| Cell Membrane | Present | Present |
| Mitochondria | Present | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present | Present |
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Permanent Vacuole | Present | Absent |
| Chloroplast | Present | Absent |
Banner 4
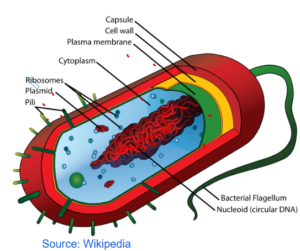
Bacterial Cell
Cell Wall
- No cellulosic
- made up of peptidoglycan
Circular DNA
- No nucleus
- Single DNA loop found naked in the cytoplasm
Plasmid
- Extra chromosomal materials
- They are in the form of small rings
- They give special properties to bacteria like antibiotic resistance
Pilli
- Hair like structures
- Found on the surface
- That helps bacteria to reproduce
Capsule
- Slime layer
- that protects the bacteria
Flagellum
- Tail like structure
- Helps the bacteria to move.
Banner 5
[download_after_email id=”9747″]
BACTERIAL VERSUS PLANT VERSUS ANIMAL CELLS
SPECIALISED ANIMAL CELLS
Special cells which have some extra features that allows them to perform specific functions
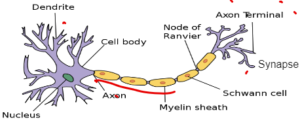
NERVE CELL
Function is to send electrical impusles round the body
- Dendrites – They are hair like structures that receives the impulses
- Axon – Long stalk the transmits the nerve impulses
- Synapse – They transmit impulses from one neurone to another
MUSCLE CELL
- Functions is to contract to bring about the movement of different parts of the body
- They are made up of special fibres which helps them to contract and relax
- Contain special proteins that allows them to contract and relax
- They have loads of mitochondria which provides them energy to contract
- They can store special storage carbohydrate called glycogen which acts as fuel for the muscles

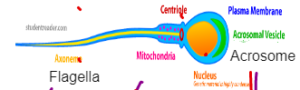
SPERM CELL
Functions is to swim to the egg and fertilize it
- Flagella – Helps it to swim to large distances
- Mitochondria – Provides Energy to swim
- Nucleus – Contains genetic information
- Acrosome – Contains Hydrolytic enzyme to break the egg wall and penetrate inside the egg to fuse with the egg nucleus
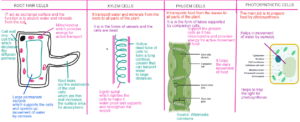
Specialized Plant Cells
MICROSCOPES
Are the devices that use to see the cells which we cannot see by our naked eye.
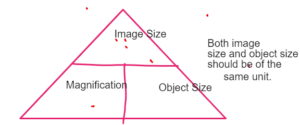
MAGNIFICATION
The property of the microscope to enlarge the object.
RESOLUTION
The property of the microscope to distinguish between two closed placed objects.

Baneer 6
Light and Electron Microscopes
| LI&HT MICROSCOPES | ELECTRON MICROSCOPES |
| Uses beam of light to focus on the object. | Use beam of electron.to focus on the object. |
| It is easy to handle | It is not easy to handle |
| It is small and compact | It is big and non portable |
| It does not require much expertise to handle | It requires proper training to handle |
| It can view the live samples | Samples have to be dead |
| No special sample preparations are required | Special sample preparations ace required |
| Lower resolving power – 0.2μm | Greater resolving power 0.5nm |
| Small magnifying power – x1000 -1500 | Greater magnifying power – x100000 |
| Can form colour images | Form 2D or 3D black and white images |
- Banner 12
Disclaimer:I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.References:BBC BitesizeWikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
