This page contains the detailed and easy notes for GCSE OCR 21st Century Physics Matter -model and explanations for revision and understanding Matter -model and explanations .
GCSE OCR 21st Century Physics Matter -model and explanations Complete Revision Summary
Matter -model and explanations
Matter -model and explanations
- Density
- Change of State
- Internal Energy
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Latent Heat
- Particle Motion in Gases
- Pressure in Gases
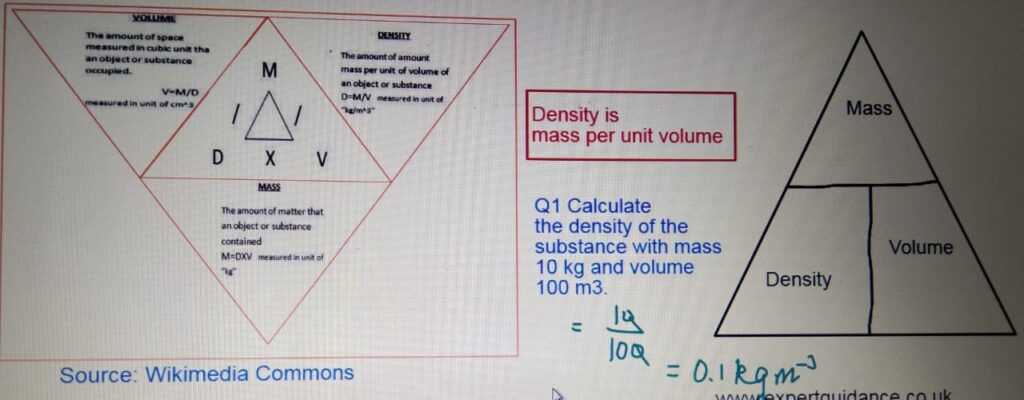
DENSITY
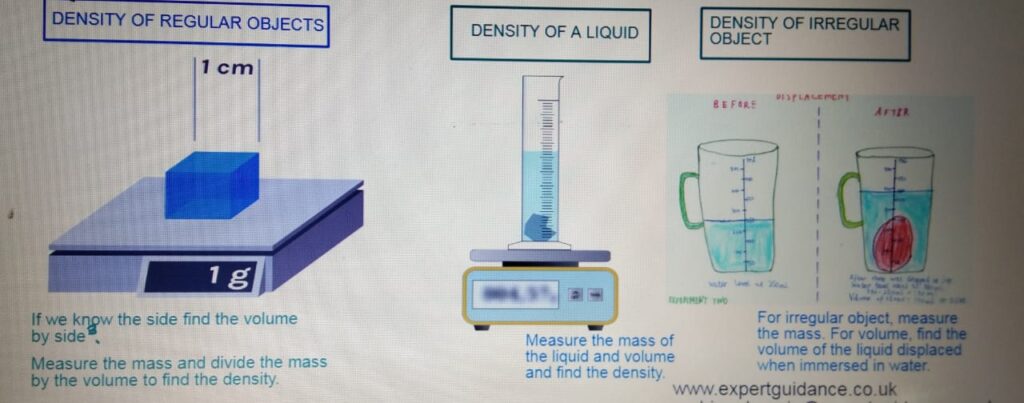
MEASURING DENSITY
DENSITY CALCULATION QUESTIONS
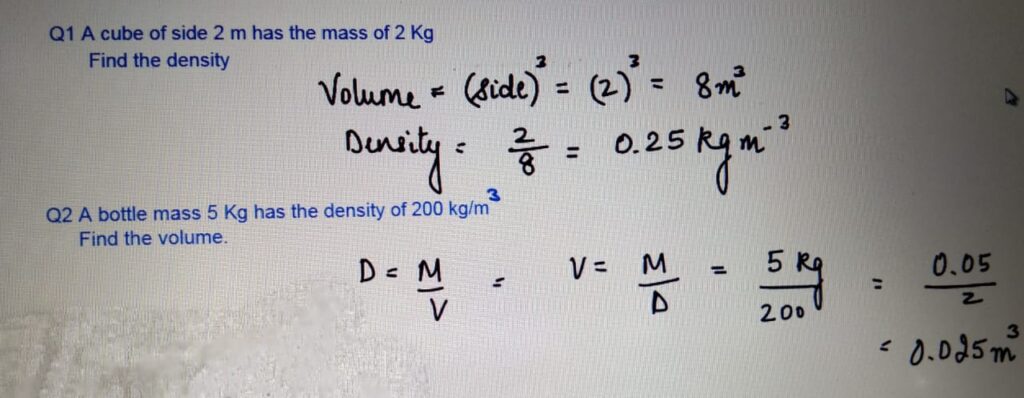
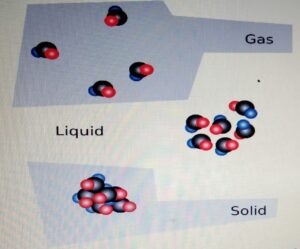
STATES OF MATTER
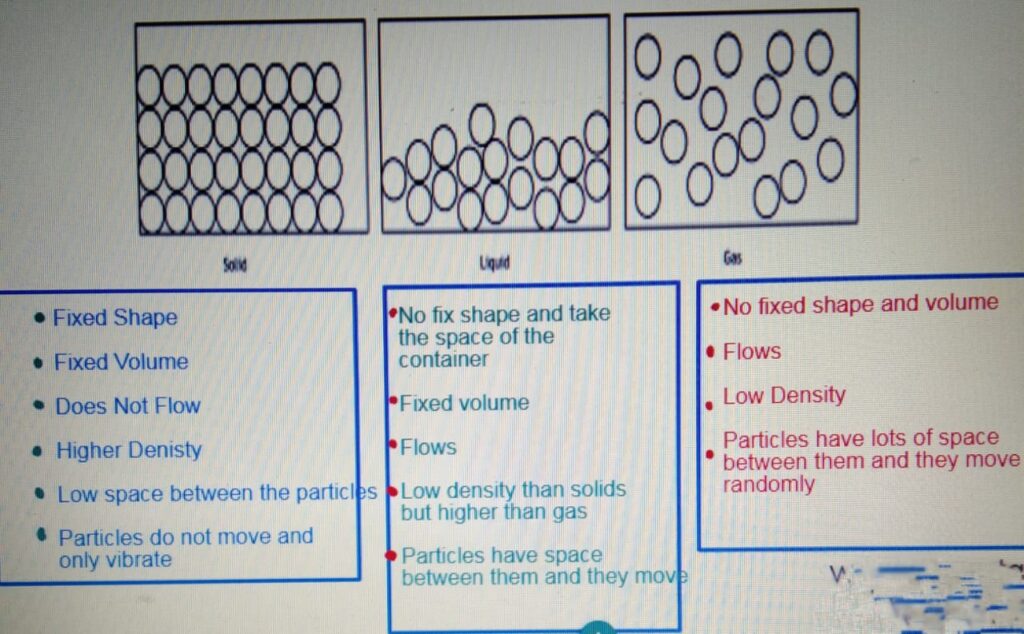
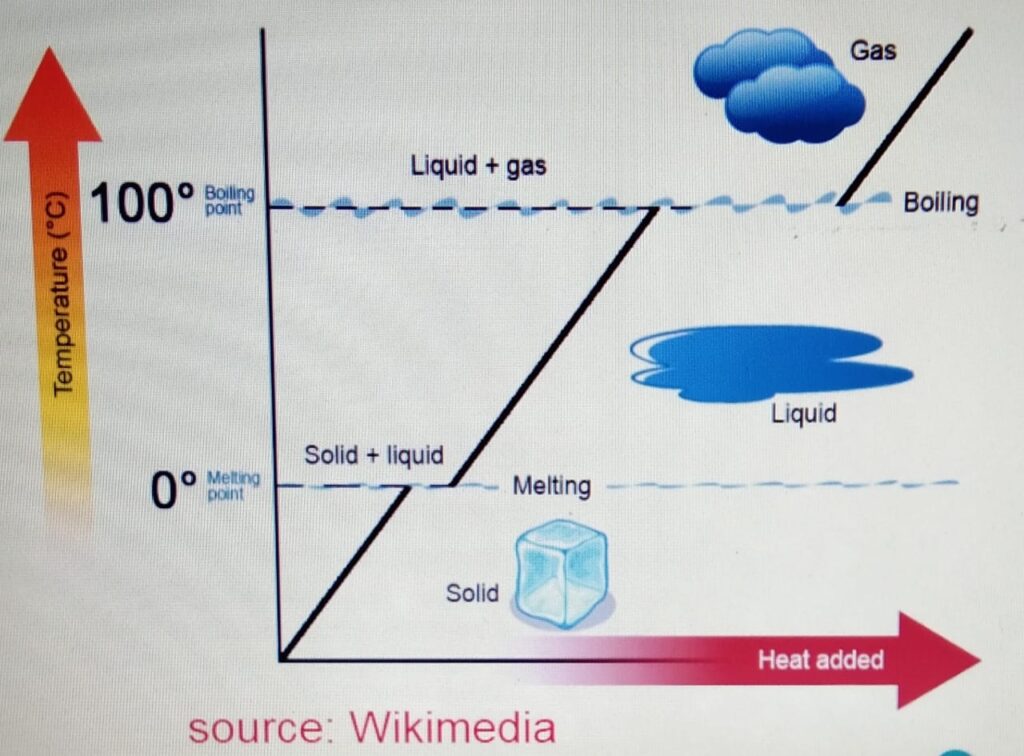
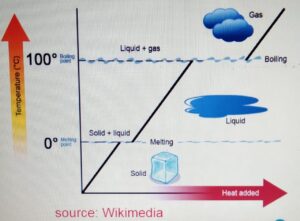
CHANGE OF STATE
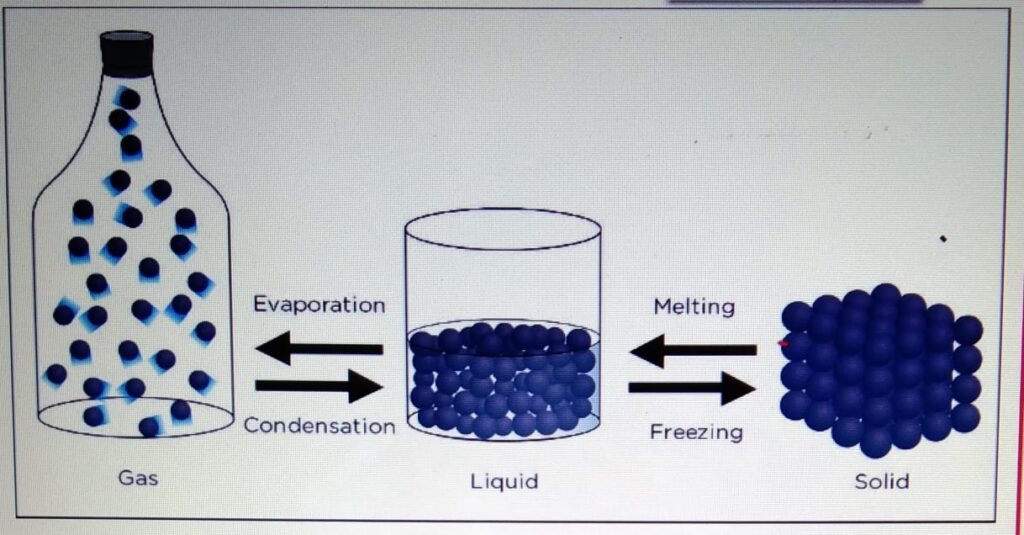
- One state of matter can
be changed to another
by heating or cooling. - During the change of state, the mass
is conserved. - When the particle is heater
it gains kinetic energy and particles
tend to move far apart.
When the particle is cooled, it looses
energy and the particles move closer.
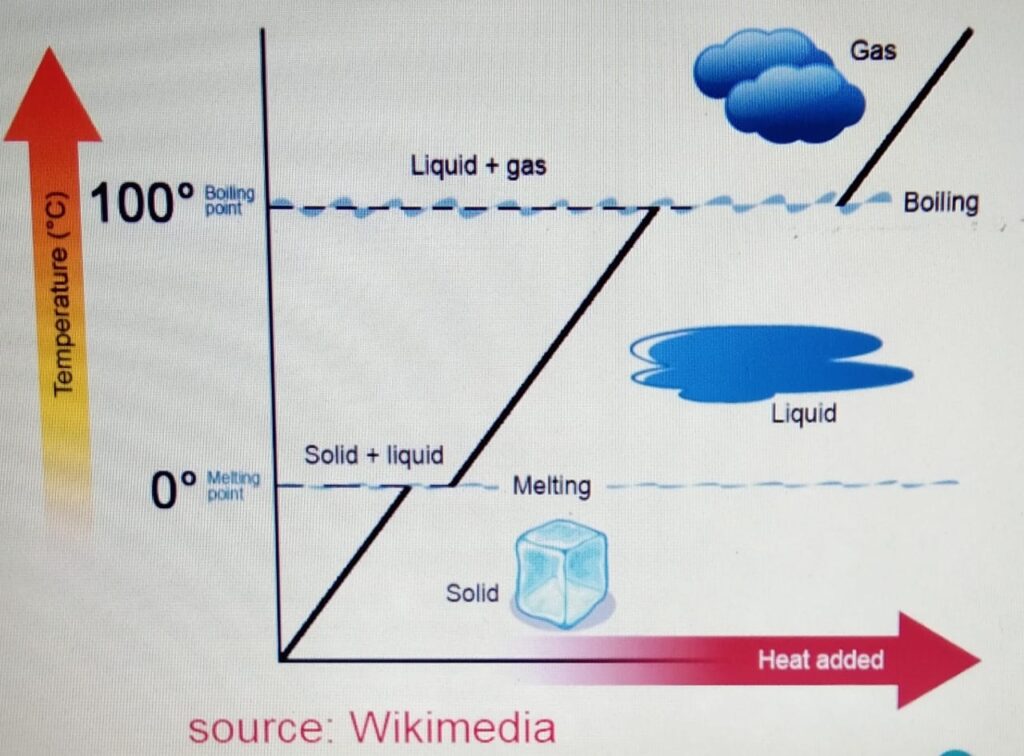
Melting Point
It is the temperature at which the ice
melts from solid to liquid without the change
in temperature. For water it is 0 degrees.
Boiling Point
It is the temperature at which the water
boils from liquid to gas without the change
in the temperature. It is 100 degrees for
water.
Freezing Point
It is the temperature at which the water
freeze from liquid to solid to form ice without
the change in temperature.For water it is 0 degrees.
When we heat the ice :-
a) The ice is heated. The temperature increases
to zero degrees. At zero degrees, the melting
point is reached.
b) At the melting point, the ice melts to form water.
At this stage there is no change in the temperature
and if we plot the graph then it will be the flat
section of the graph.
c) After the ice is melted and forms liquid, the liquid
is heated again until it reaches its boiling
point at 100 degrees.
d) At the boiling point, the water boils to form the gas or
water vapor without any change in temperature.
[download_after_email id=”5799″]
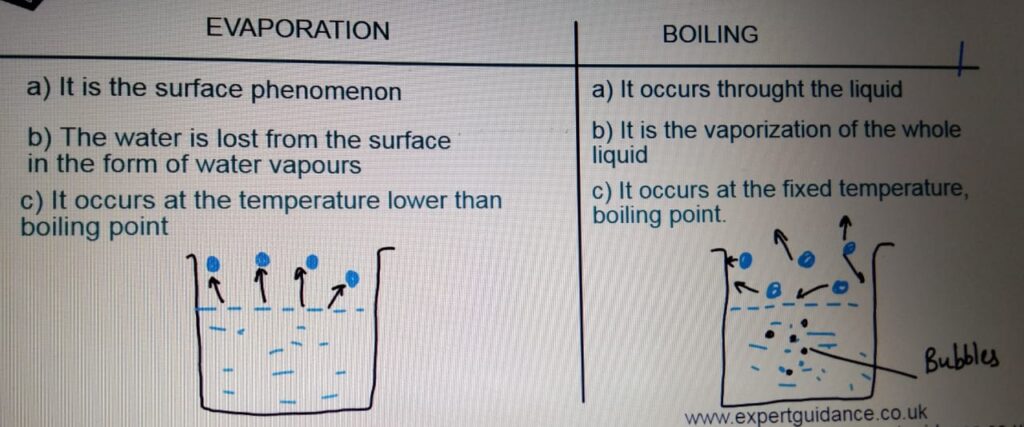
EVAPORATION AND BOILING
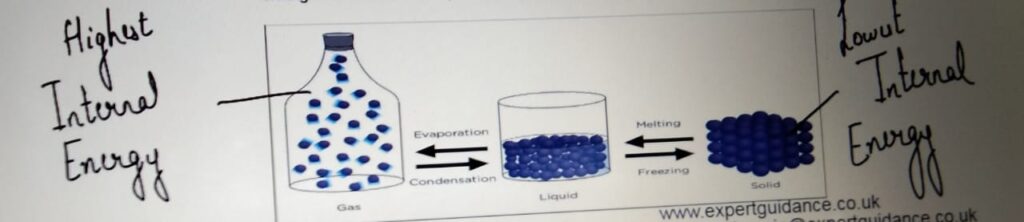
INTERNAL ENERGY
Energy stored by the particle of a substance
KINETIC ENERGY
It is the energy due to the particle’s
individual motion relative to each other.
POTENTIAL ENERGY
It is the energy due to the particle’s
individual position relative to ach other.
Heating or cooling a particle changes its internal energy and
changes the state of the particle.
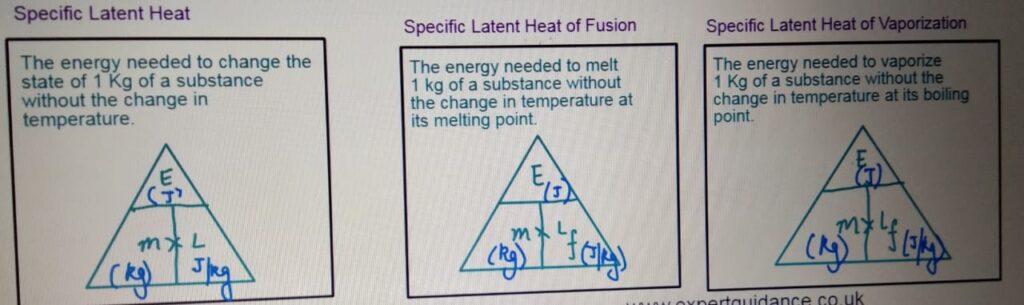
LATENT HEAT
It is the energy transferred when the substance changes its state without
the change in temperature.
LATENT HEAT QUESTIONS
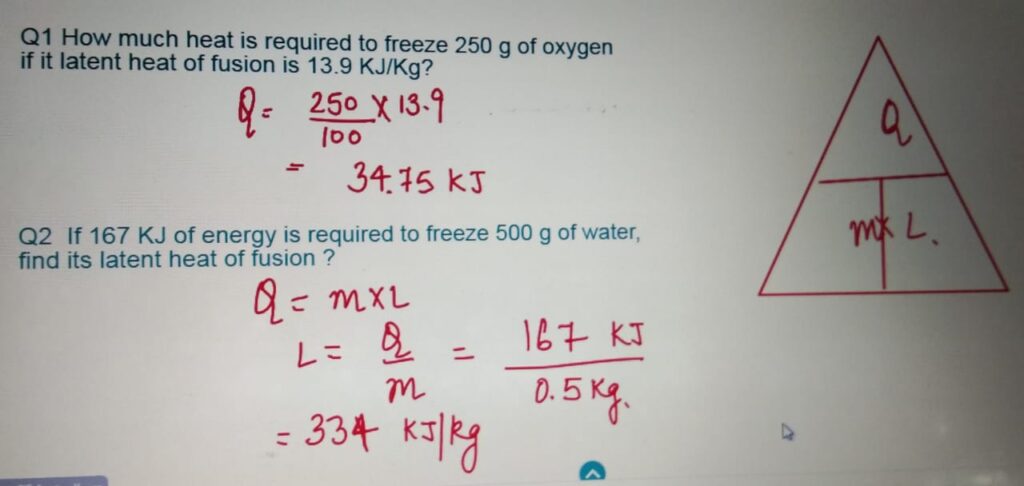
MEASURING LATENT HEAT FROM GRAPH
Plot the graph of temperature changes with time
for a given mass of ice let’s say 100 g of ice with
the power supply of 50 W. Note the time
for which the temperature did not change but change
of state take place.
LATENT HEAT OF FUSION
Power= 50 W
Time= 60 minutes= 3600 seconds
E= Power X time
= 3600 X50
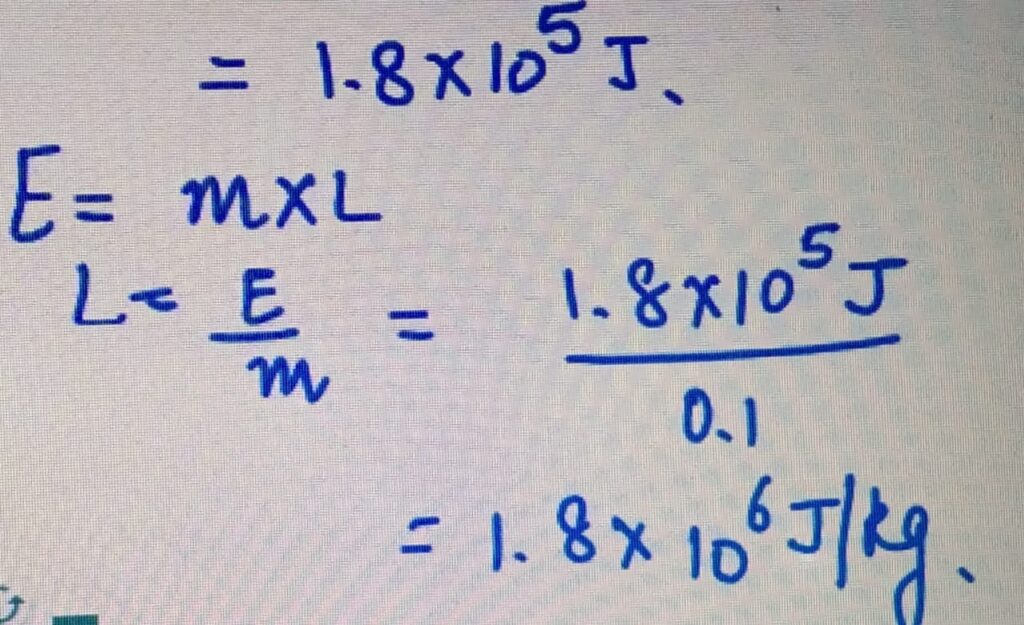
LATENT HEAT OF VAPORIZATION
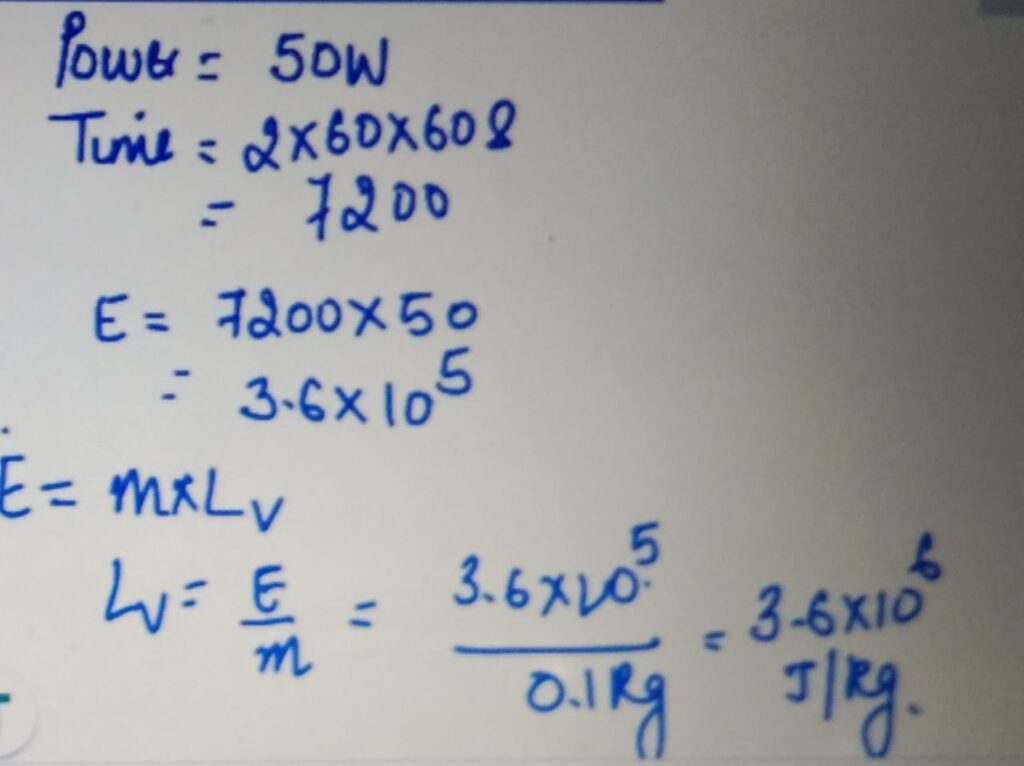
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY
It is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature
of 1 Kg of a substance by 1 degrees celcius.
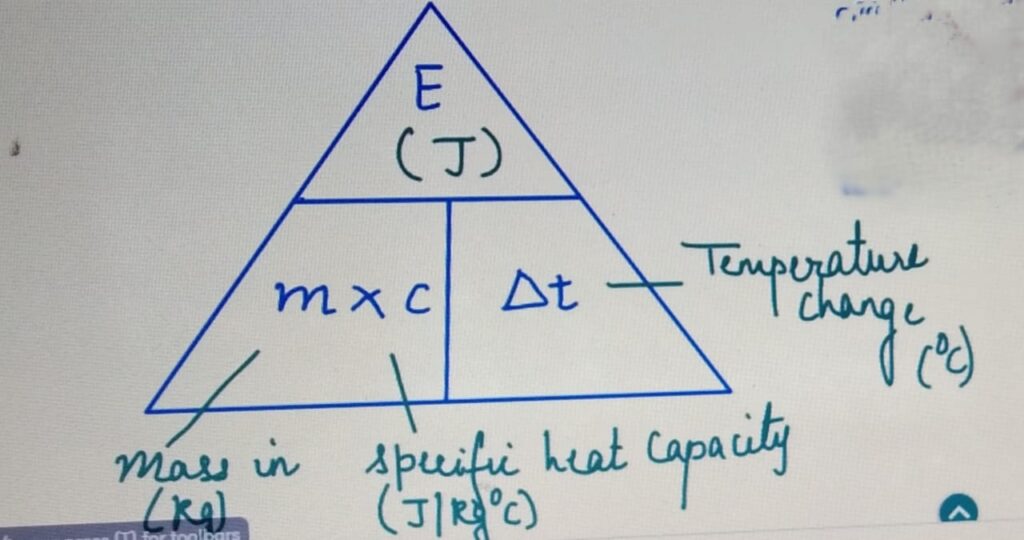
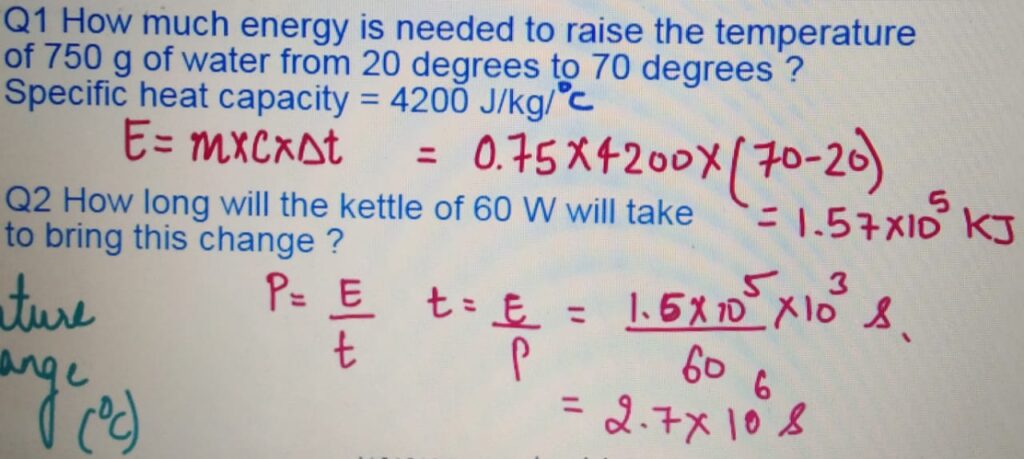
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY and
LATENT HEAT
Calculate the total energy required to convert to 750 g of water
at 50 degrees to 120 degrees. Specific Heat capacity
of water = 4200 J/Kg/C and latent heat of vaporization 2,260 KJ/Kg ?
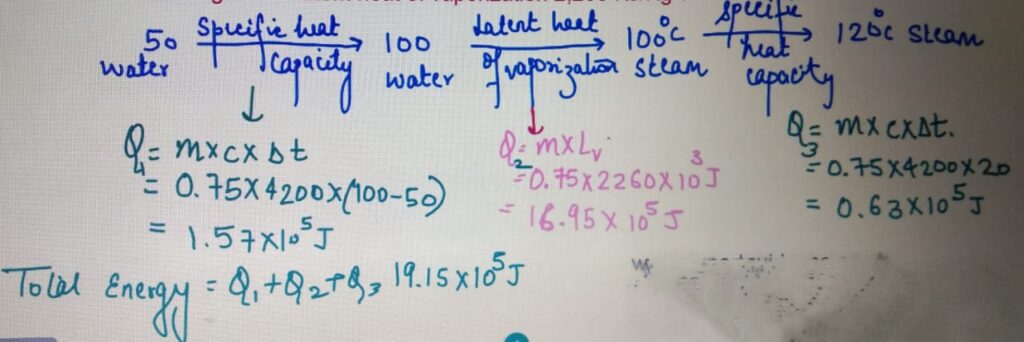
PRESSURE IN GAS

Increasing the temperature
increases the kinetic energy of the molecules
So, the particles collide more and increases
the pressure.
BOYLE’s LAW
For a fixed amount of gas at a given temperature,
the product of Pressure and Volume is constant.

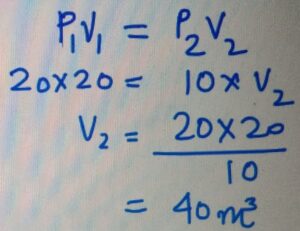 If a gas at 20 KPa occupies the
If a gas at 20 KPa occupies the
volume of 20 m3, then how much
volume it will occupies if it is compressred
to 10 KPa.
PARTICLE MOTION IN GAS
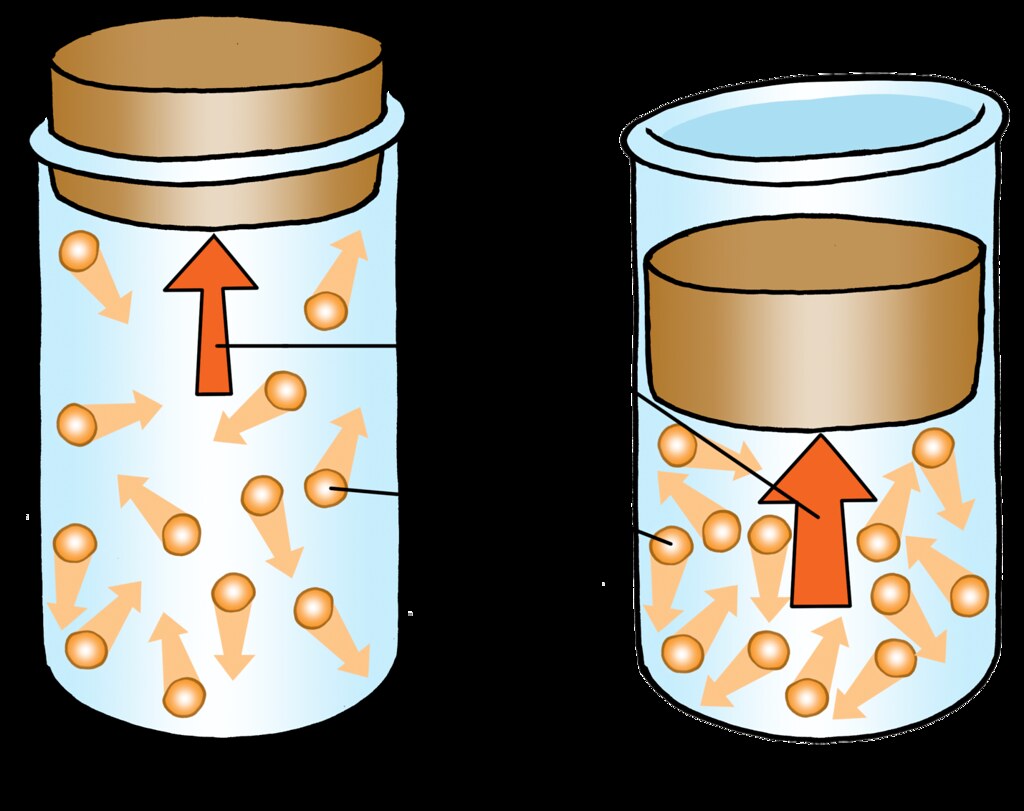
- The particles in the gas are moving randomly.
- The particles collide with the wall of the
container and exert pressure. - Greater the number of particles, more the
collission and greater the pressure.
KEY TERMS
- Density:- Density is mass per unit volume.
- Melting Point:- It is the temperature at which the ice melts from
solid to liquid without the change
in temperature. For water, it is 0 degrees. - Boiling Point:- It is the temperature at which the water boils
from liquid to gas without the change in the
temperature. It is 100 degrees for
water. - Freezing Point:- It is the temperature at which the water freeze
from liquid to solid to form ice without
the change in temperature. For water, it is 0
degrees. - Evaporation:- It is the surface phenomenon in which the water
is lost in the form of water vapours from
the surface of the water at the temperature
below the boiling point. - Boiling:- The change of a liquid to a gas at the
boiling point. Boiling occurs throughout the liquid
and it results in the formation of bubbles. - INTERNAL ENERGY:- Energy stored by the particle of a substance. It
is the sum of particles potential energy and
kinetic energy. Kinetic energy
of a particle is the energy due to the particle’s
individual motion relative to each other.
Potential Energy of
a particle is energy due to the particle’s
individual position relative to each other.
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
Molecule And Matter
- Changes of State and the Particle Model 1 MS
- Changes of State and the Particle Model 1 QP
- Changes of State and the Particle Model 2 MS
- Changes of State and the Particle Model 2 QP
- Internal Energy 1 MS
- Internal Energy 1 QP
- Internal Energy 2 MS
- Internal Energy 2 QP
- Internal Energy 3 MS
- Internal Energy 3 QP
- Temperature Changes & Specific Heat Capacity 1 MS
- Temperature Changes & Specific Heat Capacity 1 QP
- Temperature Changes & Specific Heat Capacity 2 MS
- Temperature Changes & Specific Heat Capacity 2 QP
- Temperature Changes & Specific Heat Capacity 3 MS
- Temperature Changes & Specific Heat Capacity 3 QP
