This page contains the detailed and easy notes for GCSE EDUQAS Physics Electricity for revision and understanding Electricity.
Banner 1
GCSE EDUQAS Physics Electricity Complete Revision Summary
ELECTRICITY
Banner 2
ELECTRICITY
- Circuit Symbols
- Circuit Diagram
- Charge, Current, Resistance and
- Potential Difference
- Voltage-Current Graph of
- Resistor, Filament Bulb and diode
- Series Circuit
- Parallel Circuit
- Main electricity
- Power
- Energy Efficiency
- National Grid
- Static Electricity
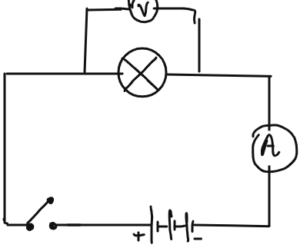
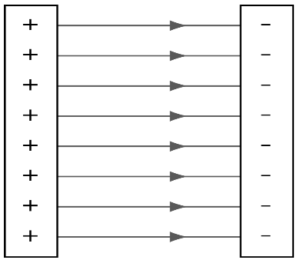
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
- Draw a circuit diagram with a battery, bulb and a switch.
- How will you measure the current and potential Difference of the Circuit ?
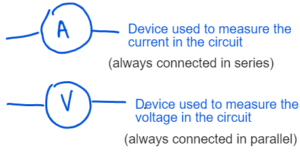
CURRENT, POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE AND RESISTANCE
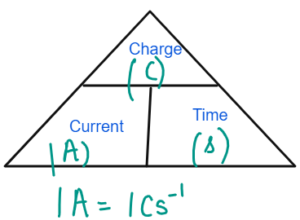
- Current is the rate of flow of charge measured in Ampere.
- One Ampere is the current flowing when one coulomb of charge flows through one second.
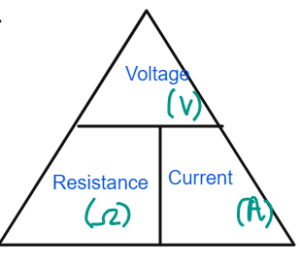
- Resistance is the obstruction to the flow of current measured in ohms
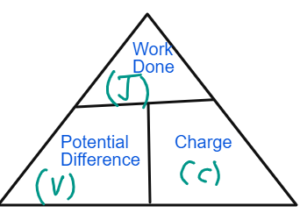
- Potential difference measured in Volts is the work done per unit charge.
- 1V = 1JC-1
- One volts is the potential difference when 1 J of energy is transferred per coulomb of charge.
Banner 3
CIRCUIT SYMBOLS
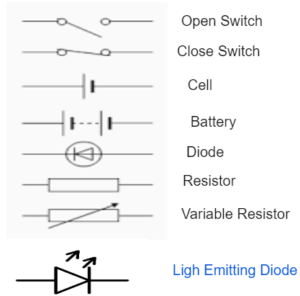
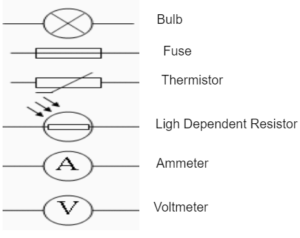
EXAMPLES
Q1 Calculate the current flowing when 4 C of charge flows for 2 minutes ?
I = Q/T = 4/2 X 60 S = 0.033A
Q2 Calculate the energy transferred when 2 V of potential difference creates a charge of 2 C
E = V x Q = 2 x 2 =4J
Q3 Calculate the resistance of the circuit when 4V of potential difference produces a current of 2 A.
R = V/I =4/2 = 2 Ω
Q4 Calculate the charge when 5A of current flows for 5 minutes
Q = I x T = 5 x 5 x 60 =1500C
Q5 Calculate the potential difference when 10 J of work done is done to move the charge of 5 C.
V = E/Q =10/5 = 2V
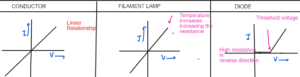
VOLTAGE-CURRENT GRAPH
Banner 4
Conductor
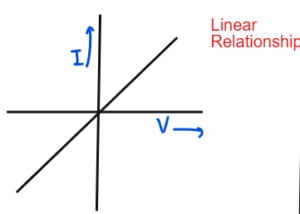
As the voltage increases, the current Increases. The resistance is constant.
Filament Lamp
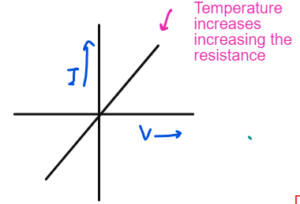
As the voltage increases, the current increases at the start but after that bulb gets heated and increase in temperature increases resistance so the current do not increases and the graph curves.
Diode
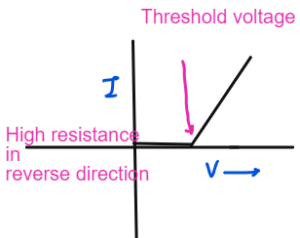
Diode conduct electricity in one direction. In reverse direction, the resistance is too high so no current flows. When it reaches a threshold voltage, the current starts to increases then linearlt.
SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS
Series Circuit
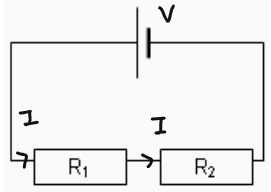
- Total Resistance is greater than individual: R 1+ R2 = R(Total)
- Current Across each component is the same: V(total)/R(Total)= I
- Voltages get divided between each component
Parallel Circuit
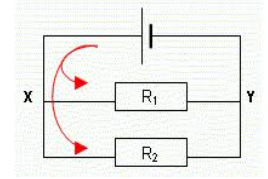
- Total resistance is less than individual = R(total) = R1R2/R1 +R2
- Voltage is same across is each component = V
- Current gets divided between the components
- I1 = V/R1 I2 = V/R2
Banner 5
[download_after_email id=”8976″]
EXAMPLE OF SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS
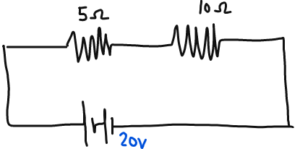
- Total Resistance RI + R2 = 15 Ω
- Voltage: 20V
- Current = 20/15 =1.33A
- Voltage across 5 ohms = 1.33 x 5 = 6.7V
- Voltage across 10 ohms = 1.33 X 10 = 13.3V
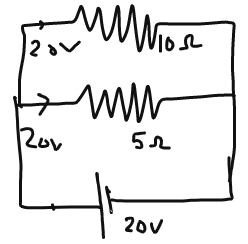
- Total Resistance R1R2/ R1 + R2 = 50/15 = 3.33
- Voltage: 20V
- Current = 20/3.33 =6A
- Current across 5 ohms = 20/5 = 4A
- Current across 10 ohms = 20/10 = 2A
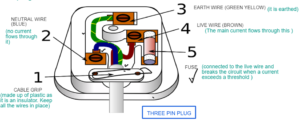
MAIN ELECTRCITIY
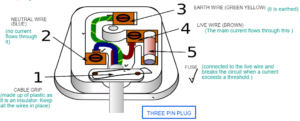
Outer casing is made up of plastic as It is an insulator and Pins are made up of brass as it is a conductor and resistant to corrosion
UK MAIN SUPPLY
Voltage = 230V
Frequency = 50H3
ELECTRIC POWER
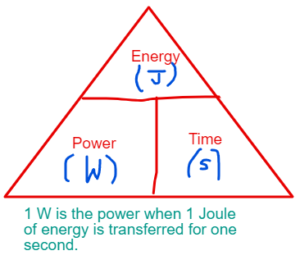
Electrical Power = V x I
(Voltage ) x (Current)
P = I2 x R [V= I x R]
P = V2/R
Q1 Calculate the current product by 200 W bulb if it generate a voltage of 10 v.
P = I x V
200/10 = I = 20
Q2 which is the fuse for this appliance. 12, 20, 23A or 25A
P = V x I
I = P/V = 200/10 = 20A
So the fuse of slightly greater than 20 A will be useful. So it has to be 23 A.
Baneer 6
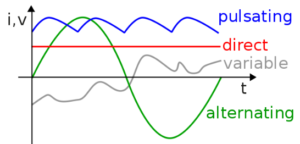
DIRECT AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
| DIRECT | ALTERNATING |
| Current that flows in one direction. | Current that changes direction. |
| Current in cell and batteries. | Current in the mains supply. |
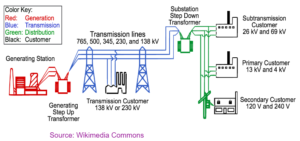
NATIONAL GRID
- A network of cable and transformers that transmits electricity from a power station to homes and buildings.
- Step up transformer is used to increase the voltage for transmission. As higher voltage will have less current and so less loss of energy due to heating effect of current.
Banner 7
STATIC ELECTRICITY
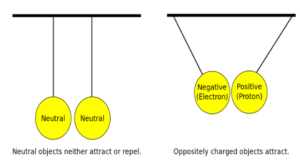
- Electricity due to the charge produced by rubbing.
- Atom is neutral. Due to rubbing there is a movement of electrons from one surface to another.
- The surface that loose electrons become positively charged and the surface that gains electron become negatively charged.
Banner 8
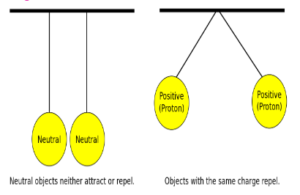
LIKE CHARGES REPEL and UNLIKE CHARGES ATTRACT EACH OTHER
ELECTRIC FIELDS
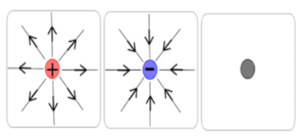
Electric Field of line always travel from positive to negative.
It is the area around a charge object where force of electricity can be felt.
Banner 9
TEST YOUTSELF
Q1 Sketch and explain the Voltage and Current graph of
- a) Resistor
- b) Filament Lamp
- c) Diode
Q2 What are the components of a three pin plug
Q3 What is the voltage and frequency of UK Mains Supply ?
UK MAIN SUPPLY
Voltage = 230V
Frequency = 50H3
Q4 How do your calculate efficiency of an appliance
Efficiency = Output Power/ Input Power x 100
Banner 10
Disclaimer:
I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
Electric Circuits
- Static Electricity 1 MS
- Static Electricity 1 QP
- Static Electricity 2 MS
- Static Electricity 2 QP
- Current, Potentiagy Tl Difference & Resistance 1 MS
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 1 QP
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 2 MS
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 2 QP
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 3 MS
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 3 QP
