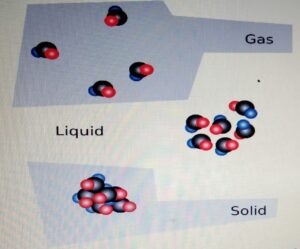
EVAPORATION AND BOILING
INTERNAL ENERGY
Energy stored by the particle of a substance KINETIC ENERGY It is the energy due to the particle’s individual motion relative to each other. POTENTIAL ENERGY It is the energy due to the particle’s individual position relative to ach other. Heating or cooling a particle changes its internal energy and changes the state of the particle.LATENT HEAT
It is the energy transferred when the substance changes its state without the change in temperature.LATENT HEAT QUESTIONS
MEASURING LATENT HEAT FROM GRAPH
Plot the graph of temperature changes with time for a given mass of ice let’s say 100 g of ice with the power supply of 50 W. Note the time for which the temperature did not change but change of state take place.SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY
It is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 Kg of a substance by 1 degrees celcius.SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY and LATENT HEAT
Calculate the total energy required to convert to 750 g of water at 50 degrees to 120 degrees. Specific Heat capacity of water = 4200 J/Kg/C and latent heat of vaporization 2,260 KJ/Kg ?PRESSURE IN GAS
BOYLE’s LAW
For a fixed amount of gas at a given temperature, the product of Pressure and Volume is constant.PARTICLE MOTION IN GAS
- The particles in the gas are moving randomly.
- The particles collide with the wall of the container and exert pressure.
- Greater the number of particles, more the collission and greater the pressure.
KEY TERMS
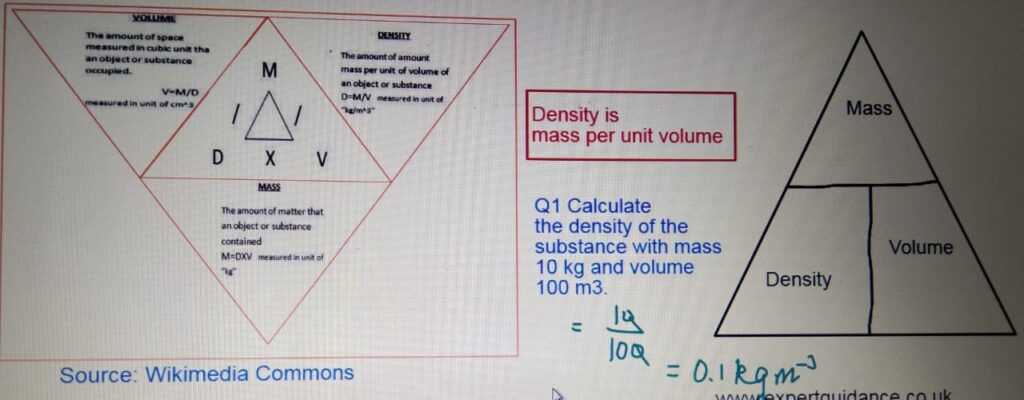
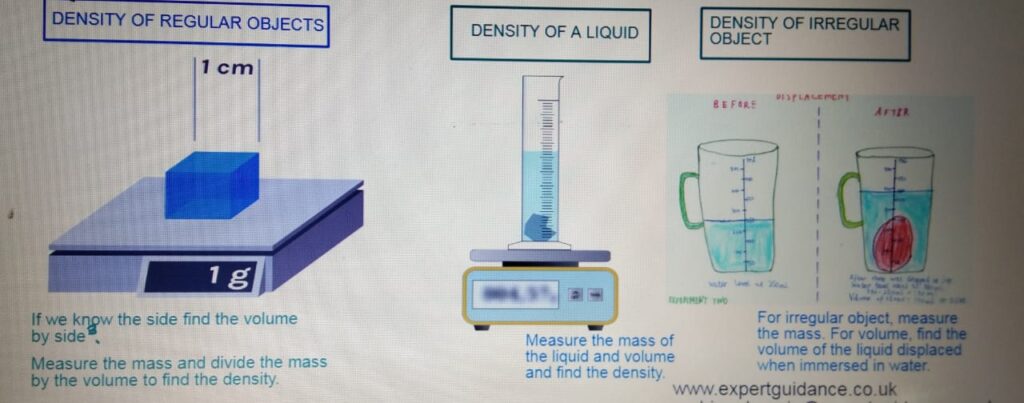
- Density:- Density is mass per unit volume.
- Melting Point:- It is the temperature at which the ice melts from solid to liquid without the change in temperature. For water, it is 0 degrees.
- Boiling Point:- It is the temperature at which the water boils from liquid to gas without the change in the temperature. It is 100 degrees for water.
- Freezing Point:- It is the temperature at which the water freeze from liquid to solid to form ice without the change in temperature. For water, it is 0 degrees.
- Evaporation:- It is the surface phenomenon in which the water is lost in the form of water vapours from the surface of the water at the temperature below the boiling point.
- Boiling:- The change of a liquid to a gas at the boiling point. Boiling occurs throughout the liquid and it results in the formation of bubbles.
- INTERNAL ENERGY:- Energy stored by the particle of a substance. It is the sum of particles potential energy and kinetic energy. Kinetic energy of a particle is the energy due to the particle’s individual motion relative to each other. Potential Energy of a particle is energy due to the particle’s individual position relative to each other.