This page contains the AQA GCSE Biology B10 The Human Nervous System kerboodle answers for revision and understanding .This page also contains the link to the notes and video for the revision of this topic.
Banner 1 B 10.1 Principles of homeostasis AQA GCSE BIOLOGY B10 The Human Nervous System: Kerboodle answer Page no. 135
1. Answer.
Homeostasis – regulation of the internal conditions of cells to maintain optimum conditions for functioning, in response to internal and external changes .It is important for maintaining optimal conditions for enzyme action and all cell functions.
2. Comparing receptors, coordination centres, and effectors.
1. Receptors:
These are the cells that detect changes in the internal or external environment.Receptors may be part of the nervous or the hormonal control systems of the body.
2. Coordination centres:
These areas receive and process the information from the receptors.They send out signals and coordinate the response of the body.
3. Effectors:
Muscles which takes action responding to stimulus are called effectors. These responses restore conditions in the body to the optimum levels.
3. a. three ways in which your external environment might vary:
1. Change in temperature
2. Stress conditions such as low oxygen content.
3. light conditions that is daytime or night.
b. each of your answers to part a affects your body as follows:
1. Change in temperature outside leads to sweating to maintain homeostasis.
2. Low oxygen content leads to increase in breathing.
3. Change in light outside leads to change in circadian rhythm.
Banner 2 B 10.2 Structure and function of human nervous system AQA GCSE BIOLOGY B10 The Human Nervous System: Kerboodle Answer Page no. 137
1. a. The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs, and all of the nerves that connect these organs with the rest of the body. Together, these organs are responsible for the control of the body and communication among its parts. The brain and spinal cord form the control center known as the central nervous system (CNS), where information is evaluated and decisions made.
b. difference between a neurone and a nerve :Neurone are the primary structures of CNS . A bundle of primary neurons is called a nerve.
c. difference between a sensory neurone and a motor neurone Sensory neurons – The cells that carry impulses from your sense organs to your CNS.
Motor neurons- They carry information from the CNS to the rest of your body. It coordinates the response and sends impulses out along special cells.
2. a. types of sense receptors:
Chemo receptors
Thermo receptors
Mechano receptors
Photo receptors
b. Chemicals -chemo receptors
Temperature – thermo receptors
Pressure – mechano receptors
Light – photo receptors
3. When you see a piece of fruit. pick it up, and eat Receptors in digestive system sends signals for appetite. When eyes see the fruit they send a message by the optic nerve to the CNS to pict it up and eat it.
3. Receptors in digestive system sends signals for appetite. When eyes see the fruit they send a message by the optic nerve to the CNS to pict it up and eat it.
Banner 3 B 10.3 Reflex actions AQA GCSE BIOLOGY B10 The Human Nervous System: Kerboodle Answer Page no. 139
1. a. Reflexes are important to a living organisms because some activities like breathing etc don’t need a signal by brain to breath.It is by the peripheral nervous system and do not involve CNS.
b. it is important that reflexes don’t go to the conscious areas of your brain. If relexes go to the brain they will take a very long time than required to avoid a injury.
2. Some actions such as breathing and swallowing are reflex actions, while others such as speaking and eating are under your conscious control. As in sleeping and breathing CNS not involved only reflexes do their work. An electrical impulse passes from the receptor along the sensory neurone to the CNS. It then passes along a relay neurone and straight back along the motor neurone. From there, the impulse arrives at the effector organ. In case of speaking there is an active role of involvement of central nervous system.
3. When you step on a pin, and just when the pin is about to pierce our PNS sends signal by reflex arc to the muscles of leg to lift off the leg as soon as possible. The mechanism involved is:
An electrical impulse from a receptor passes along a sensory neurone to the CNS – in this case, the spinal cord.
When an impulse from the sensory neurone arrives at the synapse with a relay neurone, a chemical is released.
The chemical diffuses across the synapse to the relay neurone where it sets off a new electrical impulse that travels along the relay neurone.
The chemical diffuses across the synapse and starts a new electrical impulse travelling down the motor neurone to the effector.
Banner 4 AQA GCSE BIOLOGY B10 The human nervous System Summary Questions:Kerboodle Answer Page No. 140
1. a. Maintenance of inner body environment constant in spite of changes in outer is called homeostasis.
b. the control of conditions inside your body is so important for appropriate working of the enzymes. Functioning of enzymes need proper temperature so that enzymes can work efficiently, optimal temperature and concentration of ions is required in order to do respiration.
2
A – Z
B – W
C – X
D – V
E – U
F – Y
3. a. Job of nervous system is to coordinate among body parts and giving response to stimuli.
b. nervous receptors that respond to light can be found in Eye
ii. nervous receptors that respond to sound can be found in Ear
iii. nervous receptors that respond to temperature can be found in Skin
iv. nervous receptors that respond to touch can be found in Skin
c. Diagram to show pathway:
stimulus–>receptor–>sensory neuron–> relay neurone–>response
4. a. X is sensory neurone, Y is motor neurone
b. Difference between a neurone and a nerve are:
Neurone is an individual nerve cell and the primary unit of nervous system.
While nerve is a bundle of many neurons connected with each other.
c. SYNAPSE
d. Synapses are intersections forming physical gaps between neurons. Electrical impulses travelling laterally neurons must cross synapse. When impulse reaches synapse, chemicals are released into gap between neurons. Chemicals then picked up by receptor sites on surface of next neurone across synapse, setting up new electrical impulse in next neurone.
Banner 4 AQA GCSE BIOLOGY B10 The human Nervous System Practice Question:Page No. 141
01.1. The data is shown as a scatter graph rather than a line graph because here is the same test being repeated.
01.2. The results shown in the scatter graph might be easier to understand if they were drawn as a bar chart. Calculation of mean of the data. Calculation number of repeats.
01.3. It can be made from these results Ears have shortest reaction time.
03.1. An electrical impulse from a receptor passes along a sensory neurone to the CNS – in this case, the spinal cord.
When an impulse from the sensory neurone arrives at the synapse with a relay neurone, a chemical is released.
The chemical diffuses across the synapse to the relay neurone where it sets off a new electrical impulse that travels along the relay neurone.
The chemical diffuses across the synapse and starts a new electrical impulse travelling down the motor neurone to the effector.
When the impulse reaches the effector organ, it is stimulated to response.
3.2. Reflex actions are important to the body to avoid the injury is very less time.
Banner 5
DISCLAIMER
Disclaimer: I have tried by level best to provide the answers and video explanations to the best of my knowledge. All the answers and notes are written by me and if there is any similarity in the content then it is purely coincidental. But this is not an alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it. References: BBC Bitesize AQA GCSE Science Kerboodle textbook Wikipedia Wikimedia Commons Join Our Free Facebook Group : Get A* in GCSE and A LEVEL Science and Maths by Mahima Laroyia: https://www.facebook.com/groups/expertguidance.co.uk/ For Free Tips, advice and Maths and Science Help
This page contains the detailed and easy notes for AQA GCSE Biology Cell Biology for revision and understanding Cell Biology.
Banner 1
New (9-1) AQA GCSE Biology Paper 2: Complete Revision Summary
HOMEOSTASIS AND RESPONSE
Banner 2
4.5 Homeostasis and Response
- Homeostasis
- Human Nervous System
- The Brain
- The Eye
- Thermoregulation
- Endocrine System
- Control of Blood Glucose
- Osmoregulation
- Human Reproduction
- Contraception
- Negative Feedback
- Plant Hormones
Banner 3
HOMEOSTASIS – The process of maintaining the constant internal environment

Nervous System and the Hormonal System
Homeostasis is important for the enzymes as the enzymes control all the reactions of the body and they need optimum condition to work.

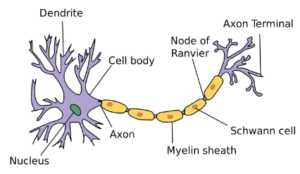
NEURONES
Motor Neurone
- Motor Neurones connect the CNS to the Effectors
- Takes impulses away from CNS
- Motor neurones sends the message from the central nervous system to the effectors.
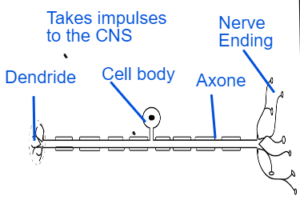
Sensory Neurone
- Sensory Neurones connect sense organs with the Central Nervous System.
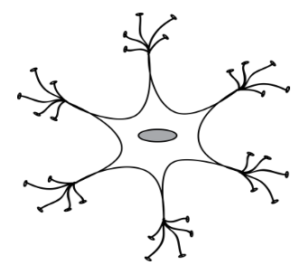
Relay Neurone
- Relay Neurones are present in the CNS and occur between the sensory and motor neurons for distant transmission of Impulses.
- Found in CNS
- Connect Sensory and Motor Neurones
Banner 3
REFLEX ACTIONS
- It is the automatic response of the body to a stimulus.
- In reflex action the message from the sensory neurones is passed to the spinal chord instead of brain.
- Spinal Chord sends the message to the effectors and produce a response
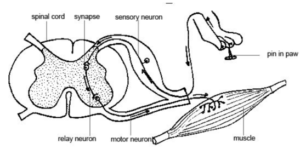
Example: Knee Jerk Reflexes,
- Touching hot object, Sudden closure of light with bright light
- It is rapid
- It is quick Automatic, Instantaneous without conscious thoughts
Stimulus
|
Receptor
| Sensory neurones |
Spinal Chord
Motor neurones
Effector
Response
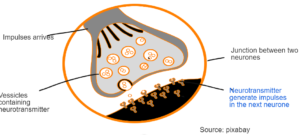
SYNAPSE
Message is transmitted by chemicals
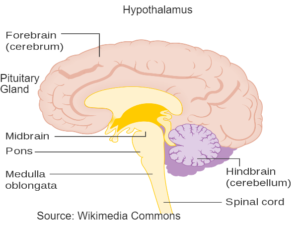
BRAIN – It is the Central information processing organ of our body, and acts as the command and Control System.
CEREBRUM (Cerebral Hemisphere) – It is nearly 80% part of the brain
- Consciousness
- Memory
- Intelligence
- Language
CEREBELLUM – It lies behind the cerebrum and above the medulla oblongata. It is the second largest part of brain and is highly convoluted area which accommodates many neurons.
- Muscle Coordination
- Balance
MEDULLA OBLONGATA or oblong marrow is oblong cylindrical part of the brain. It forms the hindermost part of the brain.
- Unconscious Activities like Heart Rate, Breathing.
- Gut Movement
Banner 4
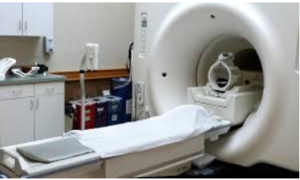
BRAIN SCAN
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) helps to take the Images of different parts of the brain and relating it with loss of functions of the individual
Problems
- Brain is complex
- Skull protects the brain
- Thousands and neurones and neurotransmitter are involved
- The functions of different parts is still not understood.
- Drugs do not reach the brain
Eye – It is lodged in orbit of skull, hollow, spherical organ, about 2.5 cm in diameter and about 6-8gram in weight
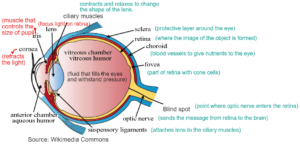
ACCOMMODATION- Ability of eye to adjust the focal length of the lens to make clear image of the objects lying at varying distances. It is a reflex mechanism and is done with the help of ciliary muscles and suspensory ligament.
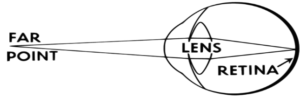
For distant vision, ciliary muscle relax making the suspensory ligaments tensed which inturn make the lens thin so that the image is focussed on the retina.
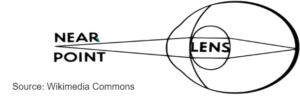
For near vision, ciliary muscle contract making the suspensory ligaments to slack which inturn make the lens thick so that the image is focussed on the retina.
Banner 5
DEFECTS OF VISION
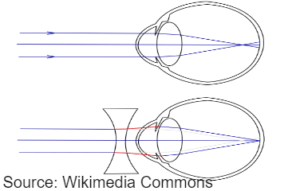
MYOPIA
- Short sightedness
- The image falls in front of the retina of the eye.
- Eye ball gets elongated
- corrected by concave lens
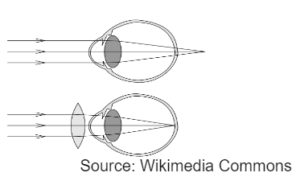
HYPERMETROPIA
- Long sightedness
- The image falls behind the retina of the eye.
- Eye balls gets shortened
- corrected by convex lens
NEW EYE TECHNOLOGIES
Contact Lenses
- Lenses are placed on the surface of the eye.
- Includes soft, silk and disposable lenses
- Can be used by any person at any age
Laser Surgery
- Laser is used to change the thickness or the curve of the cornea so that defects of vision can be corrected.
- Can be done on adults after the growing age.
Replacement Lens
- It involves either replacing the faulty lens or inserting the correct one with the faulty one.
- Include damage risk to the eye.
HORMONAL CONTROL
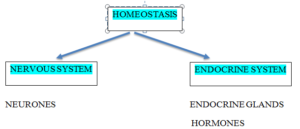
HORMONAL and NERVOUS SYSTEM
Hormones
- They are chemical messenger secreted by the endocrine glands
- they are secreted in the blood and travel to the target organ
- Target organ has receptors and hormones
- bind to the receptor and triggers a response
- It produces a slower but long term response
Nervous System
- Is the system of neurones which send electrical impulses to produce a response
- The message is transmitted via electrical impulses
- The response produced is localised and impulses do not travel large distances
- It produces quick but short term response
Baneer 6
PITUITARY : THE MASTER GLAND – Smallest endocrine gland of the body. It is pea shaped, ovoid, reddish brown gland situated at base of the brain in cavity, sella turcica of sphenoid bone. It controls almost all endocrine glands. Hence it is also called master gland
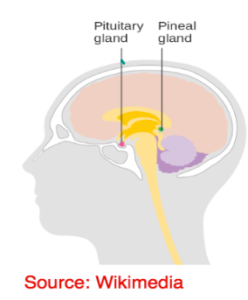
- Master Gland
- It controls other glands of the body
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone
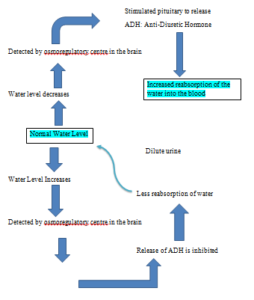
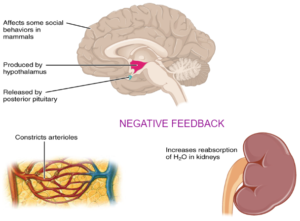
- Antidiuretic Hormone
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormones
EXAMPLES
| GLAND | HORMONE | TARGET ORGAN | EFFECT |
| Pituitary |
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) |
Ovaries Thyroid Gland Kidneys |
make the female sex hormones estrogen stimulate the gland to release thyroxine which control metabolism controls the water level by causing reabsorption of water |
| Thyroid Gland | Thyroxine | Liver and Kidneys | Controls the metabolism |
| Adrenal Gland | Adrenaline | Liver and Heart | prepares for fight and flight |
| Testes | Testosterone | Male reproductive organs | Developes secondary sexual characterstics |
| Pancreas- |
Insulin Glucagon |
Liver Liver |
Decreases blood glucose levels Increases blood glucose levels |
| Ovaries |
Oestrogen Progesterones |
Female reproductive organs | Controls the development of egg, menstural cycle and develop secondary sexual characteristics. |
Banner 7
CONTROL OF BLOOD GLUCOSE
- Pancreas Insulin and Glucagon (lowers the blood glucose level)
- Increases the blood glucose level)
- Insulin Effect
- It increases the permeability of cells to glucose
- It converts excess glucose to -glycogen
- It converts excess glucose to fats
- It stops the breakdown of fats
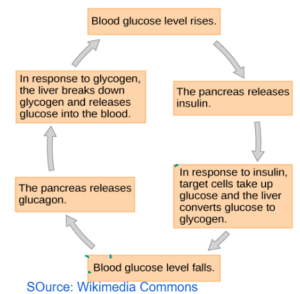
Glucagon ‘is the hormone
Glycogen is the stored carbohydrate
DIABETES
| TYPE 1 | TYPE 2 |
| Insulin dependent | Insuline independent |
| Body does not produce insulin | Body is resistance to insulin |
| Caused by damage to pancreas | Caused by poor lifestyle and diet |
| Treated with insulin injections | Treated with lifestyle changes |
| Most common in young age | Common in obese people |
| It can be genetic. | It is mostly environmental. |
| Drugs might not be required | Drugs are given to make body to respond to insulin |
Banner 8
DIABETES TREATMENT
TYPE 1
- Insulin injections directly into the blood stream.
- Less taken orally as being a protein hormone it can get digested by stomach.
- The insulin converts excess glucose into glycogen and control the blood glucose level.
- Less intake of carbohydrates.
- Pancreatic Transplant
- Pancreatic Cell Transplant
- Using stem cells to regenerate pancreatic cells.
TYPE 2
- Balanced diet
- Regular Exercise
- Weight Management
- Drug to increase sensitivity of pancreas to insulin
- Insulin injections to increase the concentration of insulin to make them more responsive to insulin.
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
- When the level of anything rises above optimum like glucose concentration, water concentration or temperature negative feedback decreases it
- When the level of anything decreases below optimum the negative feedback raises it.
FIGHT OR FLIGHT HORMONE
- Stress Hormone
- Increase heart rate
- Increase breathing rate
- Dilate the pupil

Emergency Hormones
- Increase Blood Flow
- Increase the flow of oxygen to the brain
- Divert blood flow away from the gut
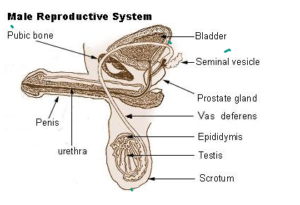
HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
TESTOSTERONE
Male hormone responsible for secondary sexual characters
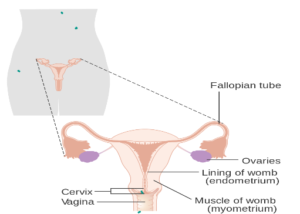
OESTROGEN
Female hormone responsible for secondary sexual characters
MENSTURATION CYCLE
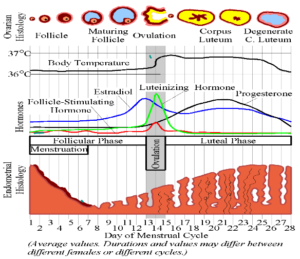
| Days | Phase | Development |
| Day 1- Day 4 | Mensturation | Shedding of the uterus linning along with the egg. Progesterone falls |
| Day 5- Day 14 | Follicular Phase | Egg is matured in the ovary. Increase in FSH |
| Day 14 | Ovulation | Egg is released. Caused by Lutenizing Hormone |
| Day 14-Day 28 | Luteal Phase | Increase in progesterone and oestrogen which maintains the uterus linning and wait for eggs to fertilize. If not fertilize in next 14 days linning breaks. |
HORMONES OF MENSTURATION
| Hormone | Gland | Effective Days | Effect |
| Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) | Pituitary | Day I-Day 14 | Maturation of egg in the follicle. Stimulate the production of Oestrogen |
| Lutenizing Hormone (LH) | Pituitary | Day 14 | Cause Ovulation |
| Oestrogen | Ovaries | Day 14-Day 28 | Develops uterus lining. Stimulates LH and inhibit FSH |
| Progesterone | Empty egg follicle in the ovaries | Day 14- Day 28 | Maintains linning of uterus and prepare for pregnancy. Inhibits both LH and FSH So no mensturatlon happen during pregnancy. |
CONTRACEPTION METHODS
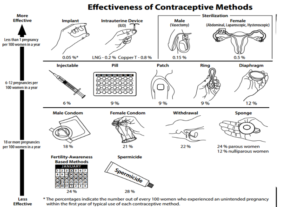
Preventing Sperms to reach the egg. Preventing the implantation of the zygote in the uterus.
Barrier Methods: Prevent the sperm to meet the eggs
Hormonal Methods: Prevents the eggs to mature or prevent the implantation of eggs in the uterus.
Chemical Methods: Kills the sperm
Intrauterine Device: Prevent embryo from implanting
Surgical Method: It is permanent contraception
HOW CONTRACEPTION WORKS?
Contraceptive Pills
- They contain the mix of female hormones oestrogen and progesterone. -MIX PILL
- Prevent the release of FSH preventing the maturation of eggs
- Make thick mucus in the cervix to prevent the entry of sperms.
- Prevent the uterus linning development, preventing implantation.
- Some pills are progesterone only pills.
- A contraceptive implant is also inserted which slowly release progesterone in the uterus.
- A contraceptive patch also absorbs the mix of hormones into the blood
- Side Effects: blood pressure, has to be taken daily changes in menstural pattern
Contraceptive Pills
- They contain the mix of female hormones oestrogen and progesterone. -MIX PILL
- Prevent the release of FSH preventing the maturation of eggs
- Make thick mucus in the cervix to prevent the entry of sperms.
- Prevent the uterus linning development, preventing implantation.
- Some pills are progesterone only pills.
- A contraceptive implant is also inserted which slowly release progesterone in the uterus.
- A contraceptive patch also absorbs the mix of hormones into the blood
- Side Effects: blood pressure, has to be taken daily changes in menstural pattern
Intra Uterine Device
- Copper T is inserted into the uterus
- It releases copper ions which are toxic to sperms
- The device also prevent the implanting of the embryo into the uterus
- Some releases progesterones which works the same like contraceptive pills
- Prevent the release of FSH preventing the maturation of eggs
- Make thick mucus in the cervix to prevent the entry of sperms.
- Prevent the uterus linning development, preventing implantatiom
- Side Effects: Infection; Internal Bleeding
Surgical Methods
VASECTOMY: Male Sterlization
- Sperms ducts are cut and sealed so that the sperms cannot enter the urethra preventing fertilization.
TUBECTOMY: Femal Sterlization
- The oviducts are cut and tied to prevent the release of egg which prevent
- Sterlizatlom
- Side Effects – It is permanent.
INFERTILITY PROBLEMS
OVULATION PROBLEM
- The eggs do not mature or problem ovulating.
- The women is given fertility drugs which are the mix of FSH and LH that stimulated maturation and ovulation
FAULTY TUBES
IMPLANTATION
- In Vitro Fertilization where fertilization is performed in the laboratory and the embryo is implanted back in the uterus for the development
PREGNANCY DEVELOPMENT
- Surrogate Mother where the fertilized egg is implanted into another mother who gives birth
IN VITRO FERTILIZATION
- Expensive
- Results in multiple embryos
- Premature births
- Birth with disability
- Not always successful
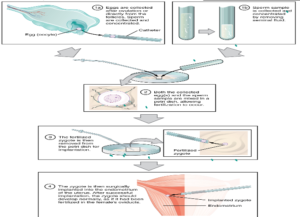
Fertility drugs to stimulate ovulation
Ovary and sperm are collected to perform fertilization.
Fertilized egg is developed in the laboratory giving suitable conditions to develop into an embryo.
Embryo is inserted into the uterus
Develops into a baby.
Plant Hormones
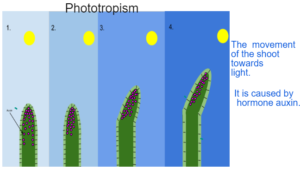
Auxin is produced in the shoot tip. When light falls on auxin it is displaced to the shader side promoting growth of the shader region resulting in growth of shoot towards light.
Gravitropism – The movement of roots towards gravity.
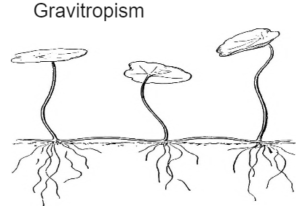
- It is also caused by auxin. In roots auxin inhibits the growth of the roots at the lower side resulting in bending of the root downwards.
- Auxin is displaced to lower side in response to gravity.
PLANT HORMONES
AUXINS
- It stimulates cell divsion and growth of the plant
- It is used to stimulate rooting in tissue culture.
- Used as Weedicide causing excess growth of the weed and killing them.
GIBBERLINS
- Seed germination
- Promote flowering
- End seed dormancy
- Elongation of stem.
ETHENE
- It is a gaseous hormone
- It is involved in fruit ripening
- Allows transportation of raw fruit to long distances and then they can be ripped by ethene.
Cytokinin
Caused Cell Division
Abscicic acid
Stress hormone prepared the plant for stress conditions
Banner 9
WASTE PRODUCTS
The products produced during metabolic reactions like respiration, digestion etc.
Carbon Dioxide
- Produced during respiration.
- Is excreted out through the lungs by the process of expiration
- Carbon dioxide is harmful as it can alter the pH of the blood affecting enzyme activity.
Water
- Produced during respiration and digestion process.
- Is excreted through skin in the forms of sweating or some by breathing and by kidney in the form of urine.
- Water can also disturb the osmotic balance and salt level of the body.
Urea
- Produced by the liver by metabolising excress proteins as it is toxic and cannot be stored.
- It is excreted by Kidney in the form of Urine.

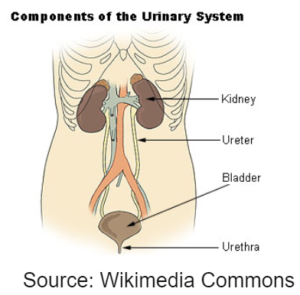
HUMAN EXCRETORY SYSTEM
ULTRAFILTRATION
- Kidneys filters the blood at a very high pressure.
- All the water, glucose, and useful components gets into the kidney filtrate. The blood cells and blood proteins due to their bigger Size are not filtered.
SELECTIVE REABSORPTION
- Since the kidney contains useful substance in the filtrate it reabsorbs back them into the blood.
- The water also gets reabsorbed depending on the needs of the body.
OSMOREGULATION
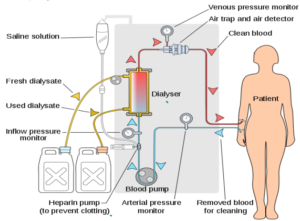
DIALYSIS
- Artificial Kidney blood flows into the dialysis machine which contains dialysis fluid.
- Dialysis fluid contains the same concentration of essential minerals ions,as that of blood but no urea.
- As blood flows into the dialysis fluid, urea is diffused out along the concentration gradient and excess salt is also removed maintaing the normal salt and mineral ions level.
- The clean blood is then pumped back.
- Lifestyle changes, regular visits, change in diet and regular expenditure are some of the disadvantages.
Banner 10
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
- Replacing diseased kidney with the healthy one.
- The donor should be a close relative to prevent rejection.
- The person has to be on Immuno – suprresant drugs so that the body immune system does not reject it.
- Does not last long and person is prone to other infectious diseases due to immuno suppresant drugs.
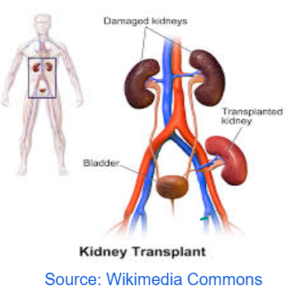
DIALYSIS KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
DIALYSIS
Advantages
- No surgery
- No infection
- No immuno supressant drugs
- Easyily available
Disadvantages
- Lifestyle changes
- Regular visits and long procedure
- Restricted Diet
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
Advantages
- No regular visit
- No lifestyle changes
- No diet restriction
Disadvantages
- Does not last forever
- Chances of rejection
- Immuno supressant drugs to be taken
- Person is more prone to infections.
- Finding a suitable donor is a problem
Banner 11
KEY TERMS
- Homeostasis – Homeostasis is the process of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment adequate to sustain life.
- Receptors – Receptor is any cell or organ of an animal capable of detecting a stimulus is a change in the external or internal environment and which subsequently brings about a response in the behavior of the animal.
- Effectors – Effector is any muscle, gland or an organ capable of responding to a stimulus, particularly a nervous impulse.
- Stimulus – A biological stimulus is any external change in the environment that can be detected by an organism.
- Neurones – These are structural and functional Units of Neural System. Each Neuron consists of the cell body (cyton) and nerve fibre (axon)
- Central Nervous System – Consists of Brain and Spinal cord
- Sensory Neurones – These connect sense organs with the Central Nervous System.
- Motor Neurones – These connect the CNS to the Effectors
- Relay Neurones – These are present in the CNS and occur between the sensory and motor neurons for distant transmission of Impulses.
- Reflex Arc – The path followed by the stimulus (impulse) from beginning to end is the reflected arc.
- Brain – It is the Central information processing organ of our body, and acts as the command and Control System.
- Cerebral Cortex – Grey matter forms 2-4mm thick outer cortex of cerebrum called cerebral cortex
- Cerebellum – literally means little cerebrum. Cerebellum has grey matter on outer side and made of three layers of cells and fibres. 2nd largest part of the brain.
- Medulla – directly controls some ANS responses, such as heart rate, respiration, dilation of blood vessels, digestion, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting. It is a part of the brain stem, located just below the prominence and just above the spinal cord.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – It helps to take the Images of different parts of the brain and relating it with loss of functions of the individual
- Eye – Hollow spherical organ, about 2.5cm in diameter and about 6-8gm in weight. It is lodged in orbit of skull.
- Blind Spot – The spot on the retina which has no receptor.
- Accomodation- Ability of eye to adjust the focal length of the lens to make clear image of the objects lying at varying distances. It is a reflex mechanism and is done with the help of ciliary muscles and suspensory ligament.
- Ciliary Muscles – help in accommodation and ciliary process that secrets aqueous humour.
- Iris – Visible coloured portion of the eye, contains two types of muscles- circular and radial.
- Pupil – In front of the lens the aperture surrounded by the iris is called the pupil.
- Myopia – Also known as near sightness or short sightness. Near object is Clear. Far object is not clear. Eyeball become longer.
- Hypermetropia – long sightness. Far object is clear, near object is not Clear. Eyeball becomes short.
- Endocrine System – the endocrine system consists of glands widely separated from each other with no direct anatomical links. Also called ductless glands
- Hormones – Hormones are the chemical substances produced in the body that controls and regulates the activity of some cells or organs.
- Adrenaline – It is a hormone released by the adrenal glands and its main action, along with norepinephrine, is to prepare the body to “fight or flee”.
- Insulin – Secreted by Pancreas, is a small protein whose molecule consists of two polypeptide chains
- Pituitary Gland – Smallest endocrine gland of the body. It is Pea shaped, ovoid, reddish brown gland situated at base of the brain. It controls almost all endocrine glands. Hence it is also called master gland.
- FSH – Follicle Stimulating Hormone. In males stimulates spermatogenesis. In females growth of ovarian follicles upto ovulation.
- Oestrogen – stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs, development of growing ovarian follicles, mammary gland development.
- Progesterone – it acts on the mammary glands and stimulates the formation of alveoli, milk secretion and supports pregnancy.
- Glucagon – Glucagon is produced to maintain blood glucose levels during fasting and to increase very low glucose levels.
- Glycogen – Glycogen is the major carbohydrate storage form in animals, and corresponds to starch in plants.
- Diabetes – Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high.
- Mensturation – Menstruation or your period is the shedding of the uterine lining once a month.
- Ovulation – the release of an egg from an ovary — occurs about midway through the menstrual cycle.
- Phototropism – It is the ability of a plant, or other photosynthesizing organism, to grow directionally in response to a light source.
- Gravitotropism – Gravitropism is a plant’s natural growth response to the effects of gravity.
- Auxins – Auxin is involved in cell growth and cell expansion
- Gibberlins – Gibberellins promote stem elongation between nodes on the stem.
- Dialysis – The process of removing waste products and excess fluid from the body.
- Selective Reabsorption – Selective reabsorption is the process by which some molecules (eg – Ions, glucose and amino acids), after having been filtered by capillaries together with nitrogen waste products (eg Urea) and water in the glomerulus, are reabsorbed by filtration as they pass through the nephron.
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definitions before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well
