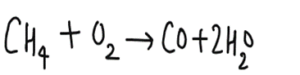This page contains the AQA GCSE Chemistry C10 Reactions of the alkenes Questions and kerboodle answers for revision and understanding Reactions of the alkenes.This page also contains the link to the notes and video for the revision of this topic.
Banner 1
C 10.1 Organic Reactions AQA GCSE Chemistry C10 Reactions of the alkenes Kerboodle Answers Page No 159
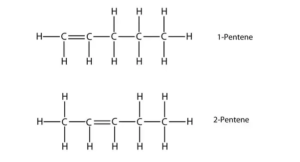
1.a.
Pentenes are alkenes with chemical formula C5H10.
b.
Answer
1.
Nonene is an alkene with the molecular formula C₉H₁₈.
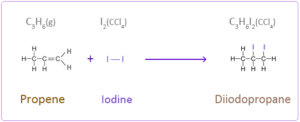
2.
a. propene reacts with iodine to form diiodopropane
1.ethene reacts with steam to form ethanol
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
c.butene reacts with chlorine to form dichlorobutane
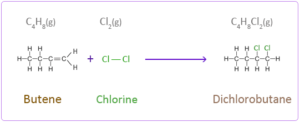
- a. Butene reacts with hydrogen in the presence of nickel catalyst to form butane
Answer.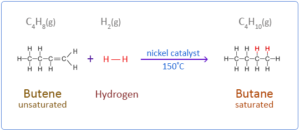
- i. propene reacts with steam in the presence of concentrated phosphoric acid catalyst to form propanol
Answer.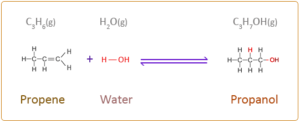
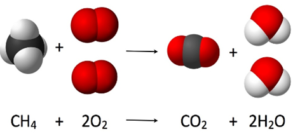
- Complete combustion of pentene forms carbon dioxide and water
Answer.
Combustion is a form of a chemical reaction in which the reactants are oxygen and (usually) a hydrocarbon. The reactants of a combustion reaction are usually water and carbon dioxide.
Thus, the combustion of pentene in oxygen to produce water and carbon dioxide becomes:
C5H10 + 7.5O2 —> 5H2O + 5CO2
Banner 2
C 10.2 Structure of alcohol carboxylic acid and esters AQA GCSE Chemistry Chapter C10 Reactions of the alkenes Kerboodle Answers Page No 161
- a. CH3COOCH2CH2CH3 belongs to homologous series of Esters.
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH belongs to homologous series of Alcohols.
- CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH belongs to homologous series of Carboxylic acids.
CH3CH2CH2OH is Propanol.
- CH3COOC2H5 is Ethyl ethanoate.
- HCOOH is Methanoic acid.
- a.
The molecular formula for ethanol is CH3CH2OH and displayed formula C2H5OH.
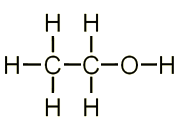
- The molecular formula and displayed formulae of ethyl ethanoate is CH3COOC2H5.
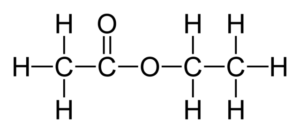
2.The molecular formula and displayed formulae of butanoic acid is C4H8O2. 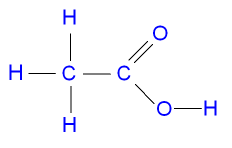
Banner 3
C 10.3 Reactions and uses of alcohols AQA GCSE Chemistry Chapter C10 Reactions of the alkenes Kerboodle Answers Page No 163
1. The main alcohol used in alcoholic drink is ethanol,Structural formula of ethanol is Ethanol – C2H5OH
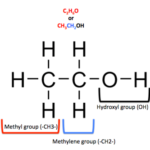
- Alcohols are used as a wide variety of uses.
They are used as sweeteners and in making perfumes, are valuable intermediates in the synthesis of other compounds, and are among the most abundantly produced organic chemicals in industry.
Perhaps the two best-known alcohols are ethanol and methanol (or methyl alcohol). Ethanol is used in toiletries, pharmaceuticals, and fuels, and it is used to sterilize hospital instruments.
It is, moreover, the alcohol in alcoholic beverages. The anesthetic ether is also made from ethanol.
Methanol is used as a solvent, as a raw material for the manufacture of formaldehyde and special resins, in special fuels, in antifreeze, and for cleaning metals.
- a. Sodium and butanol reacts to form sodium butoxide and oxygen
sodium + butanol → sodium butoxide + hydrogen.
2Na(s) + 2C4H9OH(l) → 2C4H9ONa(l) + H2(g)
- butanol, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, boiled with acidified potassium dichromate(V), a chemical oxidising agent. [2 forms butanoic acid CH3CH2CH2COOH
Answer.
- Butanol burns in air to form carbon dioxide and water
C4H9OH + 6O2 –> 4CO2 + 5H2O
- Methanol burns in air to form carbon dioxide and water
Answer.
2CH3OH + 3O2 –> 2CO2 + 4H2O
- To investigate the energy released by the three liquids we can take the help of a spirit burner. We can take three spirit burners and put an equal amount of methanol, ethanol and propanol in each one of them. We can then take a water tank and measure the temperature of water at the start of the experiment. We then burn the first spirit burner and let it burn completely. After burning, we can measure the final temperature of water. We will repeat this with rest of the two burners. The change is temperature can be multiplied with mass of water and specific heat capacity of water to find the energy released by the fuel. Greater the number of carbon molecules more will be the transfer of energy.
Banner 4
C 10.4 Carboxylic acid and esters AQA GCSE Chemistry C10 Reactions of the alkenes Kerboodle Answers Page No 165
- a. Answer.
This reaction between ethanoic acid and ethanol is called Esterification. Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst to produce the ester, ethyl ethanoate. The reaction is slow and reversible. To reduce the chances of the reverse reaction happening, the ester is distilled off as soon as it is formed.
- Volatile compound means the compound that can easily vaporise
- Esters are volatile, fragrant compounds used in flavourings and perfumes.
- a. i. When propanoic acid reacts with potassium carbonate CO2 gas is formed
- When propanoic acid react with potassium carbonate, Potassium propanoate salt is formed.
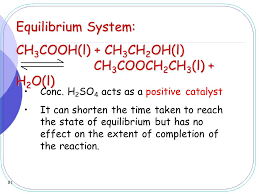
- Since hydrochloric acid is the strongest acid followed by propanoic acid and then propanol, so carbon dioxide will evolve more quickly in hydrochloric acid followed by propanoic acid and the reaction will be slow with propanol and water.
3.
Answer.
Methanoic acid is a weak acid as it is partially dissociate in water to give H+ ions.
HCOOH + H2O = HCOO- + H3O+
Banner 5
Summary Questions AQA GCSE Chemistry C10 Reactions of the alkenes Kerboodle Answers Page No 166
1.A is carboxylic acid
1.C is an alcohol
1.B belong to Esters.
- Answer.
B can be represented as the structural formaule CH3CH2COOCH2CH2CH2CH3
1.A = CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH
C = CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
- a. i.
if a small piece of sodium metal was dropped into a beaker containing some ethanol then sodium gives off bubbles of gas, gets smaller as solution is formed.
- Hydrogen Is given off when sodium reacts with ethanol.
iii. When sodium reacts with ethanol Sodium ethoxide is formed
1.Na+
v.Lithium is less reactive than sodium as lithium is above sodium. So the Reaction with Lithium will be slower and will produce hydrogen slowly.
- Sodium reacts with propanol to form sodium propoxide and hydrogen
propanol + sodium = sodium propoxide + hydrogen
- Answer.
- Pentene + Hydrogen → Pentane
- Ethene + steam → Ethanol
- Propanol + acidified potassium dichromate(VI) → Propanoic acid
- CH3CH2CH=CH2 + Cl2 ===> CH3CH2CH(Cl)CH2Cl
- C4H9OH + 6O2 → 4CO2 + 5H2O
4. a. Methanoic Acid formulae
Answer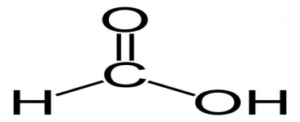
- i.When potassium carbonate reacts with methanoic acid, carbon dioxide is formed. The carbon dioxide can be tested by passing it through lime water and carbon dioxide will turn limewater milky.
- Methanoic Acid reacts with potassium carbonate to form potassium methanoate, water and carbon dioxide.
methanoic acid + potassium carbonate → potassium methanoate + water + carbon dioxide
- i.
Ethanol being the weakest acid will have the highest pH.
- Methanoic acid have the second highest pH value
- Ethanol is neutral so having pH = 7
- Rest of the solutins are acids so pH < 7
- Methanoic acid only weak acid, strong acids → lower pH
- a. Ethyl ethanoate
- Ethyl ethanoate is formed by the reaction between
Ethanol and Ethanoic acid
1(C)
Answer.
Sulphuric acid is the catalyst in the reaction between ethanoic acid and ethanol to form
Ethanoic acid + Ethanol ↔ Ethyl ethanoate + Water
d Volatile means the compound will Evaporate easily
- The compound belongs to the class of esters. Esters are used in perfumes / food colourings
6. To distinguish between the three solutions we will add Sodium carbonate to a solution of each liquid.
- only propanoic acid fizzes (carbon dioxide).
- then add sodium to two remaining liquids.
- only propanol fizzes (hydrogen).
- remaining liquid = ethyl ethanoate (smell to check).
7.
a.Answer.
0.5 moles of solute in 1 dm3 of solution.
1.
Methanoic acid has higher pH as it is a weak acid.
- Answer.
Nitric acid is a strong acid. HNO3 molecules all ionise (completely) in water.
HNO3(aq) → H+(aq) + NO3– (aq)
However, methanoic acid is weak acid so most of its molecules stay as whole molecules / only a few molecules ionise and split up in their solutions in a reversible reaction.
HCOOH(aq) ↔ HCOO– (aq) + H+(aq)
so fewer H+(aq) ions in a given volume of methanoic acid solution compared with same volume of nitric acid solution.
1.
23 g/dm3
Baneer 6
Practice Questions AQA GCSE Chemistry C10 Reactions of the alkenes Kerboodle Answers Page No 167
01.1 D is a saturated hydrocarbon.
01.2. A is an alkene.
01.3. C has the same molecular formula as organic compound E.
01.4. B will react with sodium carbonate to produce carbon dioxide gas.
01.5. C will react with B in the presence of an acid catalyst to form and an ester
2.Answer. Ethanol can be made by reacting ethene (from cracking crude oil fractions) with steam.
- A catalyst of phosphoric acid is used to ensure a fast reaction. Notice that ethanol is the only product.
- The process is continuous – as long as ethene and steam are fed into one end of the reaction vessel, ethanol will be produced.
02.2. Answer.
Oxidation reaction is the reaction when ethanol converts into ethanoic acid.
02.3 Answer.
Add a magnesium metal or any metal carbonate or metal hydrogen carbonate. Effervescence with ethanoic acid or no effervescence with ethanol or Add universal indicator. ethanoic acid will turn universal indicator red / orange / yellow or ethanol will turn universal indicator green or Add ethanol to both and a few drops of a strong acid catalyst ethanoic acid will give a sweet smell of an ester (ethyl ethanoate).
03.1 Answer.
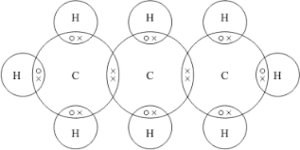
03.2.Propane is formed when propene reacts with hydrogen gas in the presence of a nickel catalyst Answer.
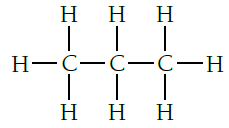
03.3. Propanol is formed when propene reacts with steam in the presence of concentrated phosphoric acid catalyst
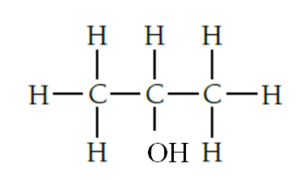
03.4. 2-bromopropane is formed with propene reacts with hydrogen bromide HBr. Answer.
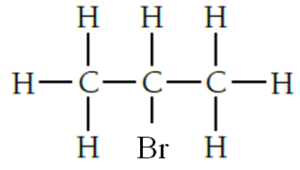
03.5.Propene undergoes addition reactions because propene is unsaturated or propene is an alkene.
Small molecules can add across a double bond or alkenes can join together or polymerize forming a saturated product.
Banner 7
DISCLAIMER
Disclaimer: I have tried by level best to provide the answers and video explanations to the best of my knowledge. All the answers and notes are written by me and if there is any similarity in the content then it is purely coincidental. But this is not an alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it. References: BBC Bitesize AQA GCSE Science Kerboodle textbook Wikipedia Wikimedia Commons Join Our Free Facebook Group : Get A* in GCSE and A LEVEL Science and Maths by Mahima Laroyia: https://www.facebook.com/groups/expertguidance.co.uk/ For Free Tips, advice and Maths and Science Help
This page contains the detailed and easy notes for AQA GCSE Chemistry Organic Chemistry for revision and understanding Organic Chemistry.
Banner 1
New (9-1) AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 2: Complete Revision Summary
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
4.7 Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons and Crude Oil
- Alkanes
- Fractional Distillation
- Properties of Hydrocarbons
- Cracking
- Alkenes
- Reaction of Alkenes
- Alcohols
- Carboxylic Acid
- Addition Polymerization
- Condensation Polymerization
- Amino Acids
- DNA
Banner 2
CRUDE OIL
- It is a black thick liquid which takes millions of years to form.
- It is the mixture of hydrocarbon.
- Hydrocarbon are the compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen only.
- The components of the crude oil are important and the crude oil is separated by the process of fractional distillation.
HYDROCARBON PROPERTIES
Banner 3
FRACTIONAL DISTILLATION OF CRUDE OIL
- Separating the mixtures on the basis of boiling points.
- It is separated in fractionating column with different substances of similar boiling points
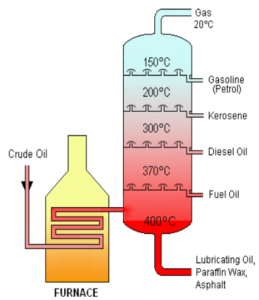
| LIQUIFIED GAS | FUEL |
| GASOLINE/PETROL | CAR FUEL |
| KEROSENE | AIRCRAFT FUEL |
| DIESEL OIL | FUEL IN DIESEL ENGINES |
| RESIDUE | MAKING ROADS |
L – Look
G – Great
K – Kid
D – Doing
R – Roll
CRACKING –Thermal decomposition of longer chain hydrocarbon into a shorter chain alkane and alkenes
Thermal Cracking Catalytic Cracking
It is done at a very high temperature It is done using a catalyst
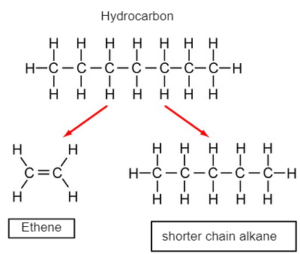
Banner 3
WHY CRACKING
- Shorter chain alkanes are more in demand as they are more efficient fuel which fractional distillation alone cannot meet.
- Alkenes are required for polymerization and synthesize other hydrocarbons which fractional distillation cannot meet.
ALKANES – Saturated Hydrocarbon
Carbon-carbon single bond made up of carbon and hydrogen
General Formulae CnH2n+2
Methane – CH4
Ethane – C2H6
Propane – C3H8
Butane – C4H10
Pentane – C5H12
Homologous Series – Members of the same family have similar functional group similar chemical properties and general formulae but different physical property and each members differs from successive by CH2.
COMBUSTION
|
COMPLETE
|
INCOMPLETE
|
| FUEL IS COMPLETELY BURNED |
FUEL IS PARTIALLY BURNED DUE TO LIMITED SUPPLY OF OXYGEN
|
| PRODUCES CARBON DIOXIDE AND WATER |
PRODUCES CARBON MONOXIDE AND WATER
|
| IT IS NOT TOXIC |
CARBON MONOXIDE IS TOXIC AS IT DECREASES. THE OXYGEN CARRYING CAPACITY OF RED BLOOD CELLS
|
PRODUCTS OF COMBUSTION
Carbon Dioxide Test
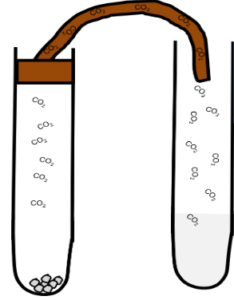
Limewater Test Carbon Dioxide will turn limewater milky
Water Test



Banner 4
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
Groups of atoms that give special properties and reactions to the organic molecule
| Functional Groups | Examples | Formation | |
| ALKENES | = | Ethene, propene, butene, pentene | Cracking of crude oil |
| ALCOHOLS | -OH | methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, pentanol | Reaction of alkene with water |
| CARBOXYLIC ACID | 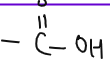 |
methanoic acid, ethanoic acid, propanoic acid, butanoic acid. | Oxidation of alcohols |
| ESTERS | 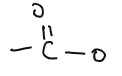 |
methyl ethanoate, ethyl ethanoate | Reaction of alcohols and carboxylic acid |
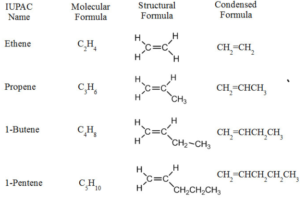
ALKENES
Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
- Compounds which have carbon-carbon double bond
- Compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen only
GENERAL FORMAULE CnH2n
Useful to make polymers, alkanes, alcohols
MANUFACTURE OF ETHANOL
| FERMENTATION | HYDRATION OF ETHENE | |
| REACTION |
Glucose Ethanol + carbon dioxide C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 |
Ethene + Steam Ethanol |
| REACTION CONDITIONS | Gentle temperature and pressure. Anaerobic conditions | Nickel catalyst and high temperature and pressure |
| ADVANTAGES | Uses renewable resources like sugarcane. Less dependent on fossil fuels and due to less energy requirements do not harm the environment. | It is a continuous process. It is rapid more efficient and have 100% atom economy. Produces more pure ethanol |
| DISADVANTAGES | It is a batch process. The ethanol has to be distilled from time to time as high concentration will kill the yeast. The reaction is slow and produces impure ethanol. Also the atom economy is not 100% | Requires ethene which is dependent on crude oil. Uses non renewable resources. |
Banner 5
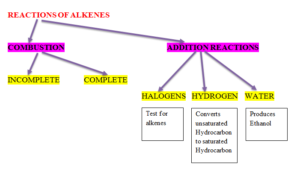
REACTIONS OF ALKENES
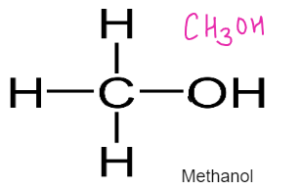
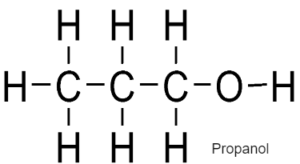
ALCOHOLS – Have functional Group –OH
General Formulae
CnH2n+1 OH
Formed by replacing hydrogen of alkane with OH group
Used as fuel, solvents, spirits
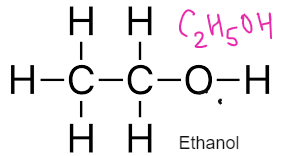
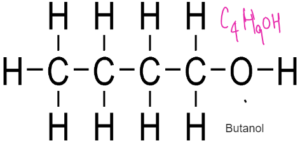
REACTIONS OF ALCOHOLS
COMBUSTION
- It can undergo complete or incomplete combustion. Complete combustion produces carbon dioxide and water.
- Ethanol + Oxygen = Carbon dioxide + water
C2H5OH + O2 CO2 + H2O
- Incomplete combustion produces carbon dioxide and water.
- Ethanol + Oxygen = Carbon monoxide + water
C2H5OH + O2 CO + H2O
OXIDATION
- Alcohols are oxidised to carboxylic acid in the presence of oxidising agent.
- Methanol Methanoic Acid
- Ethanol Ethanoic Acid
- Oxidising agent used is acidified potassium dichromate solution
METAL
Alcohols react with metals to form salt and hydrogen.
2C2H5OH + 2Ca 2C2H5OCa + H2
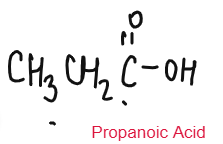
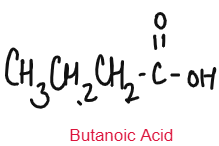
CARBOXYLIC ACID
Weak Acids
Carboxylic Acids are weak acids as they are partially dissociated in water to release H+ ions.
CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COO– + H+
Metal oxides and Metal hydroxide
Carboxylic Acid reacts with metal oxides and metal hydroxide to form salt and water.
CH3COOH + NaOH CH3COONa + H2O
Metal carbonate
Carboxylic Acid reacts with metal carbonate to form salt, water and carbon dioxide.
CH3COOH + Li2CO3 CH3COOLi + CO2 + H2O
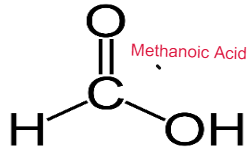
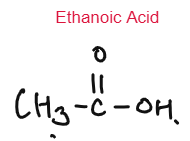
Baneer 6
ESTERS
- Fruity smelling compounds
- Used in the manufacture of perfumes, foods and cosmetics.
CARBOXYLIC ACID + ALCOHOLS ESTERS + WATER
Alkyl alkanoate
Methanoic Acid + Methanol Methyl methanoate + Water

ADDITION POLYMERIZATION
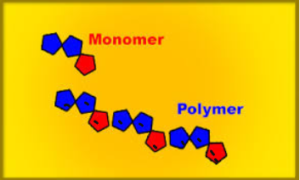
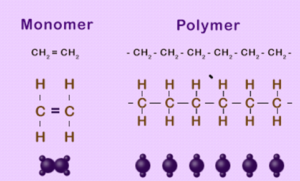
- The individuals unit that polymerizes to form a polymers is known as a monomers. Eg Ethene
- The structure formed by the polymerization of the monomer is a polymers.
Polymers are materials made by linking up smaller repeating chemical units.
Some bend and stretch – rubber and polyester.
Some hard and tough – epoxies and glass.
ADDITION POLYMERS
- a) Formed by addition reaction.
- b) Require only one monomer generally an alkene
- c) Nothing is lost in the reaction.
eg Polyethene, polypropene
CONDENSATION POLYMERS
- a) Requires two monomers
- b) Requires two functional group
- c) Formed by condensation reaction.
- d) A small molecule of water is
- e) Example: Nylon a polyester
NATURAL POLYMERS
- a) They are found naturally
- b) All the complex biomolecules are polymers
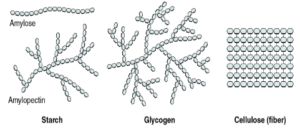
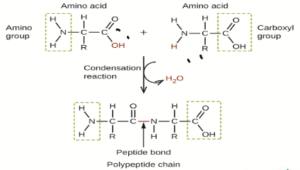
| Monomer | Polymer |
| Glucose | Starch |
| Proteins | Amino Acid |
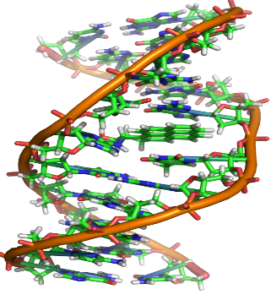
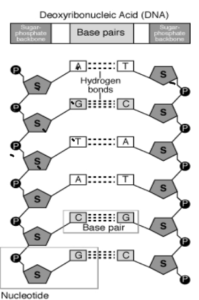
| Nucleotide | DNA |
DNA
- a) DNA is polynucleotide
- b) Nucleotide = Phosphate + Sugar + Nitrogenous Bases
- c) There are four bases present in the DNA
- Adenine
- Thymine
- Guanine
- Cytosine
KEY TERMS
Hydrocarbon – Hydrocarbon are the compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen only.
Crude Oil – It is a black thick liquid which takes millions of years to form. It is the mixture of hydrocarbon.
Fractional Distillation – Separating the mixtures on the basis of boiling points.
Alkanes – Saturated Hydrocarbon. Carbon-carbon single bond. Made up of carbon and hydrogen only
Saturated hydrocarbon – Saturated Hydrocarbons have only carbon-carbon single bonds.
Unsaturated hydrocarbon – Unsaturated Hydrocarbons have carbon-carbon double bonds and triple bonds.
General Formula – It applies to families of compounds; provides a way to predict the molecular formula of the molecule, based on the number of carbon atoms it contains.
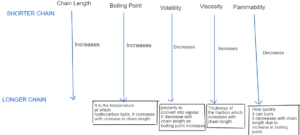
Viscosity – movement of flow. A fluid with low viscosity flows easily
Flammable – Flammable materials are combustible materials that can easily ignite at room temperature
Complete Combustion – Fuel is completely burned. Produces Carbon dioxide and water.
Incomplete Combustion – Fuel is partially burned due to limited supply of oxygen. Produces Carbon Monoxide and Water.
Cracking – Thermal decomposition of longer chain hydrocarbon into a shorter chain alkane and alkenes
Alkenes – Unsaturated Hydrocarbon. Compounds which have carbon-carbon double bond. Compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen only
Functional Group – Groups of atoms that give special properties and reactions to the organic molecule
Homologous Series – Members of the same family have similar functional group similar chemical properties and general formulae but different physical property and each members differs from successive by CH2
Alcohols – Have functional Group –OH. The General Formulae of Alcohols is CnH2n+1 OH. Used as fuel, solvents, spirits
Carboxylic Acid – Carboxylic Acids are weak acids as they are partially dissociated in water to release H+ ions.
Esters – Fruity smelling compounds. Used in the manufacture of perfumes, foods and cosmetics.
Fermentation – Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes.
Weak Acid – Weak acids are only partially ionized in their solutions.
Monomers – The individuals unit that polymerizes to form a polymers is known as a monomers. Eg Ethene
Polymers – The structure formed by the polymerization of the monomer is a polymers. Polymers are materials made by linking up smaller repeating chemical units.
Some bend and stretch – rubber and polyester.
Some hard and tough – epoxies and glass.
Addition Polymerization – It is the process of repeated addition of monomers with double or triple bonds to form polymers. There is no loss of an atom or a molecule. Ex – PVC, polyethene, Teflon.
Condensation Polymerization – It is a process that involves repeated condensation reactions between two different monomers. There is a loss of a molecule of water, ammonia etc as a by-product. Ex – Nylon, bakelite, silicon.
Monosaccharide – Simplest carbohydrates (single units). They cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller units. Ex – Glucose, fructose.
Polysaccharide – Formed of numerous monosaccharide units. Ex – starch, cellulose
Starch – It is the reserve food material of plant cells. It consists of two components- amylose and amylopectin, both glucose polymers.
Cellulose – Main structural polysaccharide of plants. It is a long, unbranched chain of about 6,000 glucose units with molecular weight between 0.5 to 2.5 million.
Proteins – The proteins are linear unbranched polymers of Amino acids. The proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and Sulphur.
DNA – It is a long, double chain of deoxyribonucleotide units. DNA is the genetic material and forms molecular basis of heredity in all organisms.
Disclaimer:
I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.
References:
BBC Bitesize
Wikipedia
Wikimedia Commons
Image Source:
Wikipedia
Wikimedia
Commons
Flickr
Pixabay
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.